




How to Write and Solve a Division Statement in Maths
Here in this topic, we are going to learn to solve simple division problems. Dividing can be understood by distribution. In simple words, division means breaking large numbers into small numbers of equal parts. In other words, it can be understood by finding how many times a number is of another number. After studying this topic you will be able to know about basic division problems and how to solve a division problem. Let us get deeper into the pool of big numbers and break the numbers into smaller ones.
Parts of the Division Statement
The division has four parts. The first part is the number that is to be divided. This number is called Dividend. The second part is the number which will divide the dividend is called the divisor. The third part is the main answer which we will get by dividing the number. It is called a quotient. And the fourth part is called a remainder, which we get if the divisor can not divide the dividend completely.
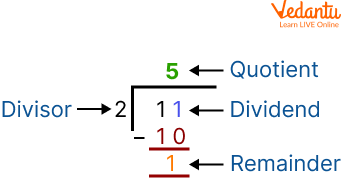
Parts of the division statement
Here in the image, 11 is the number that is to be divided so it is a dividend. 2 is the number that will divide the dividend 11, so it is the divisor. The main answer is the quotient. Here 5 is the quotient and the divisor could not divide the dividend completely, so here remainder is 1. A detailed explanation will be given later. In this section, just the name of parts of the division are given.
Formula of Division
To divide a number you have to remember a simple formula which is given below.

Formula of division
How to Solve a Division Problem?
Now we know the basic terminology of division and the formula of division. Now we will understand how to solve a division problem. For this, we will have to see how many times the divisor is of the dividend. In other languages, you just need to recall the table of divisors till you get the dividend or value less than it. Its value should not be greater than the dividend. Now you minus the dividend and the value you get. If the value after subtraction is 0, this means the divisor could divide the dividend completely. Otherwise, you have to repeat the process until the remainder is less than the divisor.
Division process
Properties of Division
There are mainly 4 properties of division, which are given below :
When zero is divided by a number the quotient is zero.
Example: $0 \div 5=0$
If we divide any number by one, the quotient is the number itself.
Example: $7 \div 1=7$
If we divide a non zero number by itself, the quotient is one.
Example: $8+8=1$
Division of a number by zero is not possible.
Solved Basic Division Problems
Q 1: Divide 8 by 4.
Ans. We have 8 as a dividend and 4 as a divisor. To solve this first we will have to make sure that the divisor should be less than the dividend. If this is the case next we will have to recall the table of 4 till we get 8. So 2 times 4 is 8. So here the answer that is quotient will be 2. And because the divisor that is 4 could divide the dividend that is 8 completely so the remainder will be 0.
Thus the quotient and remainder of the basic division problem are 2 and 0 respectively.
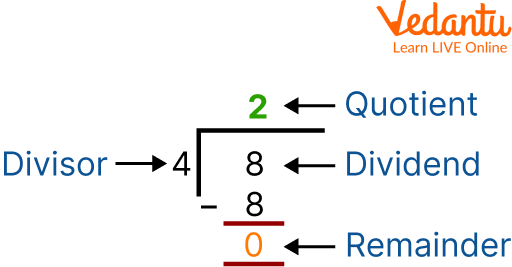
Basic division problem
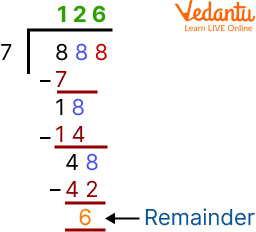
Example 2: Divide 140 by 6.
Ans. As we can see the dividend is a large number in comparison to the previous example. We will take one value at a time for the dividend to be divided. We will take 1. We can see that 1 is smaller than 6.
But we have seen earlier that the divisor should be smaller than the dividend. So we will take the next digit of the dividend with it. In this way, we get 14, which is larger than 6. So we will recall the table of 6 till we get 14 or some number less than it, but it should not be greater than 14. So it will be 2 times 6.
Now we are subtracting 14 - 12, it will be 2 and 0 will now be get together with it. So, now $6 \div 20$.
So, if 6 multiplied by 3 we get 18, so now again on solvinhg it. We get 2 as remainder in the end. And now it can’t be divided anymore.
Thus the quotient and remainder of the basic division problem are 23 and 2 respectively.
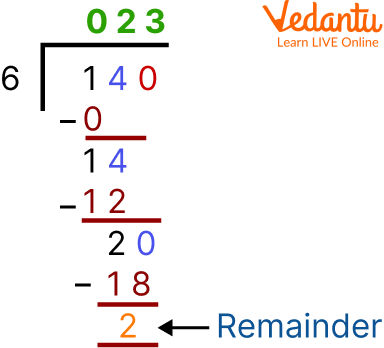
Division of 140 by 6
Simple Division Problems for Practice
Q 1. Evaluate $625 \div 5$.
Ans. 125
Q 2. Solve $999 \div 9$.
Ans. 111
Q 3. What is $96 \div 6$?
Ans. 16
Summary
Now we know that division is the distribution of equal parts. To some extent division is related to multiplication, as division is the opposite of multiplication. In this article, we have learned how to solve division problems by understanding the concept of division statements, simple division problems, and basic division problems. You need to just practice as much as you can. We have studied the basic division problems with examples for solving them in detail. If you have any doubts you just need to read the “detailed explanation” of the division again to get a better understanding. Now you are ready to break the big numbers into small numbers in equal parts.
FAQs on Division Statement Explained: Concepts, Steps & Practice
1. What is a division statement in mathematics?
A division statement is a mathematical expression that shows the relationship between the four components of division. It is also known as the division algorithm. The standard formula is: Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder. This statement is primarily used to verify if a division calculation is correct.
2. What are the four main parts of a division statement?
The four essential parts that make up a division statement are:
Dividend: The number that is being divided.
Divisor: The number by which the dividend is divided.
Quotient: The result or the main answer obtained after the division.
Remainder: The amount left over after the division process is complete.
3. Can you provide an example of a complete division statement?
Certainly. Let's consider the problem 25 ÷ 4. Here, when you divide 25 by 4, the quotient is 6 and the remainder is 1. We can write this using the division statement to verify the answer:
Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder
25 = (4 × 6) + 1
25 = 24 + 1
25 = 25
Since both sides of the equation are equal, the division is correct.
4. How is the division statement used to check a division problem?
To check a division problem, you perform the division to find the quotient and remainder. Then, you substitute the values of the divisor, quotient, and remainder into the division statement formula: `Dividend = (Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder`. If the calculation on the right side equals the original dividend, your answer is correct.
5. How are multiplication and division related within the division statement?
Multiplication and division are inverse operations, and the division statement highlights this relationship. Division breaks down a dividend into groups (the divisor), while the statement `(Divisor × Quotient) + Remainder` uses multiplication to rebuild the dividend from those parts. It essentially proves that division is the process of finding a missing factor in a multiplication problem.
6. Why must the remainder always be less than the divisor?
The remainder must always be smaller than the divisor because if it were equal to or larger than the divisor, it would mean the division is incomplete. A larger remainder indicates that the divisor could be subtracted at least one more time from the dividend, which would change the quotient. A correct division ensures the remainder is the smallest possible non-negative number left over.
7. What is the significance of a remainder of zero in a division statement?
A remainder of zero signifies that the division is exact. It means the dividend is perfectly divisible by the divisor, and the dividend is a multiple of the divisor. In this case, the division statement simplifies to Dividend = Divisor × Quotient, which is the basic structure of a multiplication fact.
8. Can you explain why division by zero is undefined using the division statement?
Yes. Division by zero is undefined because it creates a logical contradiction. Let's try to divide a number, for example 5, by 0. According to the division statement, this would be written as 5 ÷ 0 = Q, which implies 5 = 0 × Q. However, any number multiplied by 0 is 0, not 5. This makes the equation impossible to solve. Therefore, there is no meaningful answer, and division by zero is considered undefined in mathematics.

















