




Why Is Cobalt Important in Everyday Life?
There are about 108 elements that have been discovered all over the world from the earth's crust to date. They all have unique properties and functions essential for ecosystems and humans. Cobalt is the 27th element on the elemental periodic table belonging to groups 9 and 4th period. It is also called a d-block element which shows various valent states. Cobalt is denoted as 'Co' in the periodic table.
Cobalt is a metal that is similar to iron and nickel chemically. It has been used for generations to give pottery and acrylics a deep blue colour. Nowadays, it is mixed with other metals to introduce a variety known as alloys, which are used in industry. A component of vitamin B12 is cobalt.
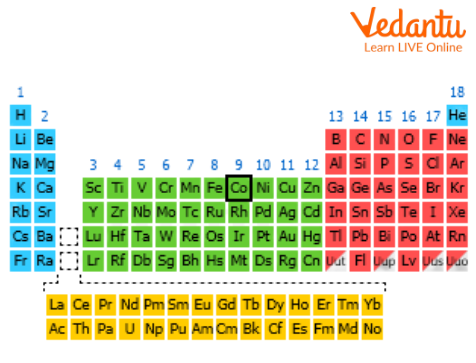
Position of Cobalt
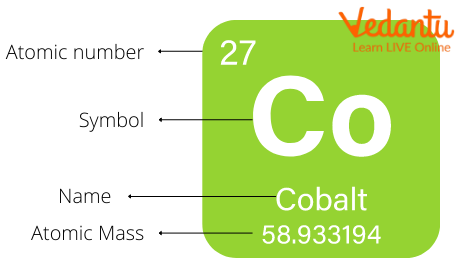
Cobalt Symbol
Cobalt is an element with the symbol Co and its atomic number is 27 and was discovered in 1735. Cobalt has an atomic mass of 58.933, approximately 60 amu (60 atomic mass units), and the element is metallic. Scientifically, while writing the atomic symbol of cobalt, its atomic mass is written on the top left of the symbol of cobalt. In contrast, the atomic mass is written at the base left side of the atomic symbol. The electronic configuration of the element is(Ar)4s23d7.
As stated earlier, the element belongs to d-block elements. These are also called transitional elements as they show variable valent states. For cobalt, the variable oxidation states are −3, −1, +1, +2, +3, +4, +5.
Symbolic Representation of Cobalt
Characteristics of Cobalt
Cobalt is found in relatively low abundance in the earth's crust and water. The element cobalt is a brittle (easily shatterable) yet hard metal, which resembles iron and nickel in physical appearance, implying that it is silver-white and lustrous. Cobalt usually exists as a mixture of two allotrophic forms over a wide range of temperatures.

Cobalt
Cobalt occurs as ore in mineral states like cobaltite, smaltite, and erythrite and can also be found associated with nickel, silver, lead, copper, and iron ores, from which cobalt is usually obtained as a by-product.
Cobalt in Environment
Cobalt is not easily degradable once it has entered the environment. It may react with other already present particles or may get adsorbed on soil particles, water, and sediments. Cobalt can only be mobilised under acidic conditions, but in the end, most cobalt particles end up in soils as sediments.
Soils that contain very low amounts of cobalt are essential for growing plants that have a deficiency of cobalt. When animals feed on these grounds, they get cobalt intake, which is essential for them. Soils containing about 0.13 to 0.30 ppm of cobalt are found to be proper for animal nutrition.
Uses of Cobalt
Cobalt is widely used for electroplating objects because of its properties like rust-prone, hardness, and resistance to oxidation and also makes the surface of objects attractive by giving them a lustrous shiny finish.

Cobalt Electroplated Objects
It is also used for making alloys. For example, Alnico is an alloy made of aluminium, nickel, and cobalt and is used to make strong permanent magnets. Stellite is another alloy that contains cobalt, chromium, and tungsten and is used to make high-speed and high-temperature cutting tools and dyes. Cobalt is also widely used to make alloys that are used in jet engines and gas turbines, magnetic steel, and some other types of stainless steel.
Cobalt salts have been used for centuries to produce beautiful, bright, and permanent blue colours for porcelain, glass, pottery, tiles, and enamels. It is the main component in Sevre's and Thenard's blue.

Pottery made out of Cobalt Blue Colour
Conclusion
Cobalt is a useful and unique element required for various purposes in the world and is still under research for more knowledge. Its unique properties make it of more use. It is tough and simple to turn into a magnet. Most alloy steels are made with cobalt.
The cobalt adds to the alloy's strength and prevents corrosion. Tools for cutting metal at high speeds and temperatures are one application for these alloys. Additionally, magnetic materials are made with cobalt. Enamel paints and acrylics still employ cobalt in combination with other ingredients to create the color blue.
FAQs on How Many Electrons Are in a Cobalt Atom?
1. How many electrons, protons, and neutrons does cobalt have?
A neutral cobalt (Co) atom has 27 electrons and 27 protons. Its atomic number is 27, which defines the number of protons. The most common isotope, cobalt-59, has 32 neutrons, calculated by subtracting the atomic number (27) from the mass number (59).
2. What is the electron configuration of a neutral cobalt atom?
The complete electron configuration for a neutral cobalt atom is 1s² 2s² 2p⁶ 3s² 3p⁶ 4s² 3d⁷. For simplicity, this is often written using the noble gas shorthand as [Ar] 4s² 3d⁷, where [Ar] represents the stable electron configuration of argon.
3. How many electrons are in cobalt's outermost shell?
Cobalt has two electrons in its outermost shell, which is the 4s orbital (the fourth energy level). These two electrons are its valence electrons, which are the ones involved when cobalt forms chemical bonds with other elements.
4. Why does cobalt often form Co²⁺ or Co³⁺ ions?
Cobalt forms positive ions to achieve a more stable electron arrangement. It's a common characteristic of transition metals.
- It easily loses the two electrons from its outermost 4s orbital to form the Co²⁺ ion.
- It can also lose an additional electron from its 3d orbital to form the Co³⁺ ion. This state is also quite stable.
5. How does the number of electrons in cobalt affect its magnetic properties?
Cobalt is strongly magnetic (a property called ferromagnetism) because of its electron structure. Its 3d orbital contains unpaired electrons. The spins of these unpaired electrons can align in the same direction, creating a strong collective magnetic field that allows cobalt to be used in powerful permanent magnets.
6. Where is cobalt on the periodic table and what does its position tell us?
Cobalt (Co) is in Group 9 and Period 4 of the periodic table. Its position places it in the central block known as the transition metals. This location suggests that cobalt is a typical metal that has properties like high density, multiple stable ions (oxidation states), and the ability to form coloured compounds.
7. What are some of the most important real-world uses of cobalt?
Cobalt is a crucial element in modern technology. Its most important uses include:
- Batteries: It is a key component in rechargeable lithium-ion batteries used in smartphones, laptops, and electric vehicles.
- Superalloys: It is mixed with other metals to create alloys that can withstand extreme temperatures, used in jet engines and industrial turbines.
- Magnets: It is used to make strong, permanent magnets for speakers, motors, and scientific equipment.
- Pigments: Cobalt compounds are used to create the famous deep blue colour in glass, ceramics, and paints.
8. Is cobalt beneficial or harmful to the human body?
Cobalt is both. In very small amounts, it is an essential element as it forms the core of vitamin B12, which is necessary for healthy nerve cells and the production of red blood cells. However, in large amounts, cobalt is toxic and can cause cobalt poisoning, leading to serious health issues with the heart, thyroid, and hearing.









