




An Overview of Class 11 Chemistry Determination Of Ph Values Of Hydrochloric Acid Strengths Using Ph Papers And Universal Indicator Experiment
pH is the amount of hydronium ions present in a given solution. The pH of a solution can be found by the formula: pH =-log[H3O+]. An acidic solution contains a pH starting from 0, and it extends up to 6. A solution is considered acidic if it contains more H+ ions. A solution is called basic if it contains more OH- ions and the pH value comes to 8 or above 8. Neutral solutions have a pH of 7. The pH is an essential parameter in the functioning of various metabolic processes in humans, animals, plants and various microorganisms; hence, its study and maintenance of pH are very important.
Table of Contents
Aim
Apparatus Required
Theory
Procedure
Using pH Paper
Using a Universal Indicator Solution
Observation
Result
Precautions
Lab Manual Questions
Viva Questions
Practical Based Questions
Aim
To determine the pH values of hydrochloric acid at different strengths using (i) pH papers and (ii) universal indicator solution.
Requirements
Test Tubes
HCl of Varying Concentrations - 0.1M HCl
0.01 M HCl
0.001 M HCl
0.0001 M HCl
0.00001 M HCl
pH Paper
Universal Indicator Solution
pH Indicator Chart
Glass Rods
Measuring Cylinder
Theory
‘p’ in pH stands for Potential, and ‘H’ indicates hydronium ion concentration. Hence, pH is the power of hydronium ions present in a given solution.
The pH paper and universal indicator work on the principle of colour change.
When a pH paper or universal indicator is dipped/poured into the solution, they indicate the pH of a solution by showing a change in colouration of the pH paper or the universal indicator solution.
Acids generally show warm colours that range from Red to Yellow colours while bases show cool colours from blue to violet colours.
On a pH scale, the colours on the extremities indicate strong acids and strong bases whereas the colours in the centre of the pH scale indicate weak acids or weak bases.
The green colour on the pH scale indicates neutral solutions.
Procedure
Using pH Paper:
Take 5 test tubes and label them with varying concentrations of HCl solutions.
Cut the pH paper strips into equal parts.
Using forceps, dip the pH paper in each of the test tubes containing different concentrations of HCl.
Observe the colour change of the pH paper and compare different shades of colour with the pH indicator chart and tabulate the results.
Determine the approximate pH of the sample solutions using this method.
Using a Universal Indicator Solution:
Take 5 test tubes and pour 5ml of each of the given solutions using a measuring cylinder in the test tubes.
Label the test tubes carefully.
Using a dropper, add 2-3 drops of universal indicator solution in each of the given solutions.
Observe the change in colour of the solution and compare the various shades obtained, with the pH indicator chart.
Record your observations and determine the approximate pH of the sample solutions using this method.
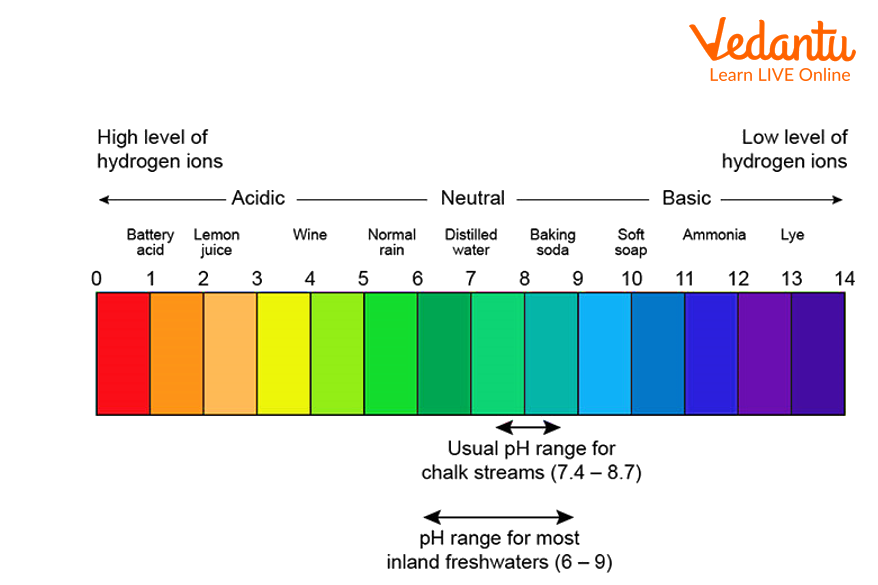
pH scale chart
Observations and Result
Result
The pH of acids is less than 7 on the pH indicator chart.
The pH of the acidic solution is increased or moved towards neutral, with a decrease in the concentration of an acidic substance.
Colour of HCl in universal indicator is colourless.
Precautions
Hydrochloric acid is a very strong acid and hence should be handled with care.
Universal indicators should be used in minimal quantities and should not be wasted.
The pH papers should be used judiciously.
Lab Manual Questions
1. How is a universal indicator made?
Ans: Universal indicator is made by mixing different indicators; hence, it can detect the pH of acids, bases and neutral solutions of varying strengths.
2. What is the pH scale?
Ans: pH scale is used to measure the acidity or basicity of a solution. The pH scale ranges from 0 to 14. 0 indicates that the solution is a strong acid, whereas 14 indicates that the solution is a strong base.
3. What is an Arrhenius acid?
Ans: Arrhenius acids are substances which contain hydrogen and upon dissociation give H+ ions or protons. They can donate hydrogen ions. It converts blue litmus paper to red; on pH paper and universal indicator show red-yellow colouration.
4. What is the colour of dilute HCl on pH paper?
Ans: The dilute HCl colour on pH paper is Red.
Viva Questions
1. What is a Universal indicator colour in acids?
Ans: Universal indicator shows warm colours such as red, yellow, orange etc. in acidic solutions.
2. What colour would Hydrochloric give on treatment with pH paper?
Ans: Acids show a colour range from Red to Yellow on a pH paper; hence, dilute HCl will show red colour on a pH paper.
3. What is the pH of human blood?
Ans: Human blood is a neutral solution and its pH ranges between 7.35 and 7.45.
4. Name various methods to detect the pH of a solution.
Ans: pH of a solution can be detected by using the following:
pH paper
Universal indicator
pH metre
5. What colour does potassium hydroxide give to the universal indicator?
Ans: When the universal indicator is put into KOH, the colour changes to dark violet colour which indicates that KOH is a strong base.
6. What is pH level of Hydrochloric acid?
Ans: The pH of the hydrochloric acid is 2 according to the given data, which indicates that it is acidic in nature.
7. What is methyl orange?
Ans: Methyl orange is an indicator which is used to detect acidic and basic solutions. Methyl orange gives red colouration when put into an acidic solution and yellow colour when put into the basic solution.
8. What is the pH of KCl salt?
Ans: Salts such as KCl are made from a neutralisation reaction between an acid and base and hence are neither too acidic nor too basic but are neutral and hence have a pH of 7.
9. What are Arrhenius’s bases?
Ans: Arrhenius bases are those compounds which help in increasing the OH- ions concentration in a solution.
10. Define acids and bases based on Lewis’s definition.
Ans: According to Lewis, acids are electron pair acceptors and bases are electron pair donors.
Practical Based Questions (MCQs)
What is the colour of hydrochloric acid?
Colourless
Pink colour
Red colour
Blue colour
Ans: Colourless
What is the pH level of hydrochloric acid?
0-3
6-7
8-11
0-14
Ans: 0-3
Acids and bases can be detected using:
pH paper
Litmus paper
Universal indicator
All of the above
Ans: All of the above
As you move towards the right on the pH scale, the acidity of a solution
Increases
Decreases
Remains constant
None of the above
Ans: Decreases
Basicity of the solution increases towards the _____of the pH scale.
Right
Left
Center
Downwards
Ans: Right
The pH of a strong acid is _____on the _____.
2, litmus paper scale
3, universal indicator chart
0, pH scale
14, pH scale
Ans: 0, pH scale
pH 14 is_____, pH 6 is_____ and pH 8 is_____.
Strong acid, Weak base, Weak base
Strong base, Weak acid, Weak base
Weak base, Weak acid, Strong base
Strong base, Weak base, Weak acid
Ans: Strong base, Weak acid, Weak base
At pH 1.0, 7.0, 9.5 and 5.5, the colour of the solution is_____, ____, ___and_____,respectively.
Orange, Green, Blue, Red
Red, Blue, Green, Orange
Red, Green, Blue, Orange
Green, Red, Orange, Blue
Ans: Red, Green, Blue, Orange
Which of the following is the strongest acid?
HCl
H2SO4
HNO3
CH3COOH
Ans: H2SO4
_____is the acid obtained from tamarind.
Citric acid
Acetic acid
Vinegar
Tartaric acid
Ans: Tartaric acid
Conclusion
Acids are compounds which can donate H+ ions when present in a solution. They turn blue litmus paper red. They are colourless and sour to taste. Furthermore, they are very harmful as they have corrosive properties. Acids when put on pH paper show red to yellow colouration depending on whether they are strong acids or weak acids. Some common strong acids are H2SO4, HNO3 and HCl and some weak acids are CH3COOH, Carbonic acid, etc. Hydrochloric acid colour is red.
FAQs on Class 11 Chemistry Determination Of Ph Values Of Hydrochloric Acid Strengths Using Ph Papers And Universal Indicator Experiment
1. What is the primary aim of the experiment to determine the pH values of hydrochloric acid of different strengths for the CBSE Class 11 curriculum?
The primary aim of this experiment is to determine and compare the pH values of hydrochloric acid (HCl) solutions at different concentrations. This is achieved by using both pH paper and a universal indicator, allowing students to observe how pH changes with the strength (concentration) of a strong acid.
2. For a 3-mark question, outline the procedure to find the pH of different HCl solutions using pH paper as per the 2025-26 CBSE syllabus.
To determine the pH of HCl solutions of varying strengths, follow these steps:
Preparation: Take four clean, dry test tubes and label them A, B, C, and D. Add 5 ml of the provided HCl solutions of different concentrations into the respective test tubes.
Testing: Place a strip of pH paper on a clean surface. Using a fresh, clean glass rod or dropper for each solution, transfer a single drop of the solution from test tube A onto the pH paper. Observe the colour change.
Comparison & Recording: Immediately match the colour developed on the pH paper with the standard pH colour chart. Record the corresponding pH value. Repeat the process for the solutions in test tubes B, C, and D, ensuring a fresh dropper and a new pH strip are used each time to avoid contamination.
3. What observation is expected when a universal indicator is added to a dilute HCl solution, and what does it signify?
When a few drops of universal indicator are added to a dilute hydrochloric acid solution, the solution is expected to turn a shade of red, orange, or yellow. This colour indicates a highly acidic nature, corresponding to a low pH value, typically in the range of 1 to 3. The exact colour depends on the concentration; a more concentrated acid will show a deeper red colour.
4. What are the most important safety precautions to be observed while handling hydrochloric acid in this experiment?
Handling hydrochloric acid requires strict safety measures. The most important precautions include:
Always wear safety goggles to protect your eyes from accidental splashes.
Wear a lab coat or apron and chemical-resistant gloves to protect skin and clothing.
Handle the acid in a well-ventilated area or under a fume hood to avoid inhaling corrosive fumes.
In case of a spill or skin contact, immediately wash the affected area with plenty of water and inform the teacher.
Never add water to concentrated acid; always add acid slowly to water during dilution.
5. Why is using a universal indicator often considered a more effective method than litmus paper for this specific experiment?
A universal indicator is more effective than litmus paper in this experiment because it provides an approximate numerical pH value by displaying a wide spectrum of colours. Litmus paper, on the other hand, can only indicate if a solution is acidic (turns red) or basic (turns blue) but cannot differentiate between the varying strengths of the different HCl solutions. The goal is to see how pH changes with concentration, which the universal indicator shows clearly.
6. Why does the pH value of an HCl solution increase when it is diluted with water, even though HCl remains a strong acid?
This is a key concept. HCl is a strong acid, meaning it dissociates completely in water to release H⁺ ions. The pH is the negative logarithm of the hydrogen ion concentration (pH = -log[H⁺]). When you dilute the solution with water, you are decreasing the concentration of H⁺ ions per unit volume. As the [H⁺] concentration decreases, its negative logarithm (the pH value) increases, moving closer to 7 (neutral).
7. A student is given a solution labelled 0.01 M HCl. What is the theoretically expected pH value, and how would they verify it experimentally?
Theoretically, since HCl is a strong acid, it fully dissociates:
HCl → H⁺ + Cl⁻
For a 0.01 M HCl solution, the [H⁺] concentration is also 0.01 M, or 10⁻² M. The pH is calculated as:
pH = -log[H⁺] = -log(10⁻²) = 2
To verify this, the student would dip a pH paper or add a universal indicator to the solution and compare the resulting colour to the pH chart. The colour should correspond to a pH value of 2.
8. How would the observations differ if this experiment was conducted with a weak acid like acetic acid (CH₃COOH) of the same concentration instead of HCl?
If the experiment were repeated with acetic acid (a weak acid) of the same concentration, the observed pH would be significantly higher than that of HCl. For example, a 0.01 M HCl solution has a pH of 2, whereas a 0.01 M acetic acid solution would have a pH closer to 3.4. This is because acetic acid only partially dissociates in water, resulting in a much lower concentration of H⁺ ions compared to the complete dissociation of HCl.
9. What are two common sources of error in this experiment that can lead to an incorrect pH reading?
Two common sources of error in this pH determination experiment are:
Contamination: Using the same dropper or glass rod for different solutions without cleaning it thoroughly can cross-contaminate the samples, leading to inaccurate pH readings. To minimise this, a fresh, clean dropper must be used for each distinct concentration.
Incorrect Colour Matching: Subjectively misinterpreting the colour on the pH paper against the standard chart can lead to errors. This can be minimised by matching the colour in good lighting and, if possible, getting a second opinion or using a digital pH meter for a more precise reading.
























