
Z is known as:
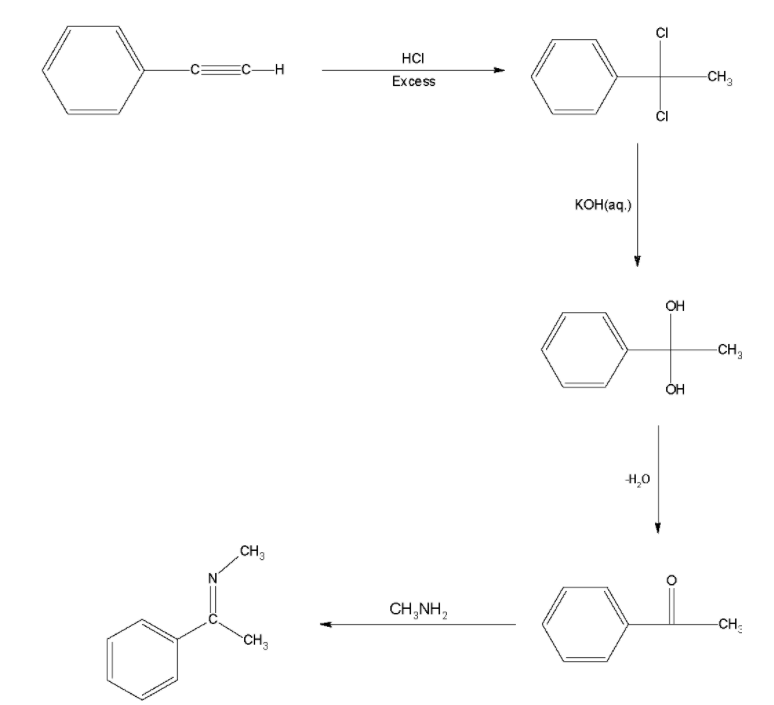
${\text{Ph}} - \equiv {\text{CH}}\xrightarrow[{excess}]{{HCl}}X\xrightarrow[{}]{{KOH\left( {aq} \right)}}Y\xrightarrow[{}]{{C{H_3} - N{H_2}}}Z$
A.Schiff’s reagent
B.Magenta dye
C.Schiff’s dye
D.Schiff’s base
Answer
544.2k+ views
Hint: To answer this question, you must recall the various reactions between organic compounds and the purposes of reactions of each of the given reagents. Hydrogen chloride on reaction with an unsaturated alkene undergoes hydrohalogenation reaction.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In hydrohalogenation reaction, the hydrogen halide breaks into a hydrogen cation and halide anion by the heterolytic cleavage. This additional reaction takes place according to Markovnikov's rule. The hydrogen cation preferably attacks the terminal carbon of the alkene so that the carbocation formed is more substituted and hence stable. The incoming halide ion attaches to the inner carbon and thus a secondary alkyl halide is formed. Another mole of hydrogen chloride is added in a similar way and a dihaloalkane is formed.
When aqueous ${\text{KOH}}$ is used, ${\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$ ion is both a strong base as well as a strong nucleophile. But in an aqueous solution, the hydroxide ions are highly hydrated. This reduces the basic character of ${\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$ ions and thus it fails to abstract a hydrogen from the $\beta $- carbon of the alkyl chloride to form a double bond. Thus, it results into a nucleophilic substitution reaction and both the chlorine molecules are replaced by hydroxyl group and a geminal diol is formed
Geminal diols undergo condensation and a ketone is formed. In this case, we obtain acetophenone.
Acetophenone on reaction with a primary amine undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction forming a Schiff’s base.
Thus, the correct answer is D.
Note: Geminal diols undergo loss of a water molecule due to the vicinity of two hydroxyl groups to each other. It is highly unstable due to high lone pair- lone pair repulsion and thus a water molecule is lost.
Complete step-by-step answer:
In hydrohalogenation reaction, the hydrogen halide breaks into a hydrogen cation and halide anion by the heterolytic cleavage. This additional reaction takes place according to Markovnikov's rule. The hydrogen cation preferably attacks the terminal carbon of the alkene so that the carbocation formed is more substituted and hence stable. The incoming halide ion attaches to the inner carbon and thus a secondary alkyl halide is formed. Another mole of hydrogen chloride is added in a similar way and a dihaloalkane is formed.
When aqueous ${\text{KOH}}$ is used, ${\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$ ion is both a strong base as well as a strong nucleophile. But in an aqueous solution, the hydroxide ions are highly hydrated. This reduces the basic character of ${\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ - }$ ions and thus it fails to abstract a hydrogen from the $\beta $- carbon of the alkyl chloride to form a double bond. Thus, it results into a nucleophilic substitution reaction and both the chlorine molecules are replaced by hydroxyl group and a geminal diol is formed
Geminal diols undergo condensation and a ketone is formed. In this case, we obtain acetophenone.
Acetophenone on reaction with a primary amine undergoes nucleophilic substitution reaction forming a Schiff’s base.

Thus, the correct answer is D.
Note: Geminal diols undergo loss of a water molecule due to the vicinity of two hydroxyl groups to each other. It is highly unstable due to high lone pair- lone pair repulsion and thus a water molecule is lost.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




