
How do you write $y=\left| 6+2x \right|+1$ as a piecewise function?
Answer
535.2k+ views
Hint: A piecewise is a function which is defined differently in different intervals within its domain. So we have to write the different definitions of the given function in the different intervals of x, which can be determined by using the definition of the modulus function. The modulus function returns the absolute value of the argument. So we have to consider two cases, one for $6+2x\ge 0$ and the other for $6+2x<0$.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The function given in the above question is
$\Rightarrow y=\left| 6+2x \right|+1......\left( i \right)$
We know that the modulus function returns the absolute value of the argument. Therefore, we can consider the two cases as below.
Case I: When $6+2x\ge 0$
$\Rightarrow 6+2x\ge 0$
Subtracting $6$ from both sides
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 6+2x-6\ge 0-6 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x\ge -6 \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both sides by $2$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{2}\ge \dfrac{-6}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x\ge -3 \\
\end{align}$
Since in this case, the argument of the modulus function is non-negative, its absolute value will be equal to the argument. Therefore for $x\ge -3$ we can write
$\Rightarrow \left| 6+2x \right|=6+2x$
Substituting this in the equation (i) we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=6+2x+1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=2x+7 \\
\end{align}$
Case II: When $6+2x\ge 0$
$\Rightarrow 6+2x<0$
Subtracting $6$ from both sides
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 6+2x-6<0-6 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x<-6 \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both sides by $2$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{2}<\dfrac{-6}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x<-3 \\
\end{align}$
Since in this case, the argument of the modulus function is non-negative, its absolute value will be equal to the argument. Therefore for $x<-3$ we can write
\[\Rightarrow \left| 6+2x \right|=-\left( 6+2x \right)\]
Substituting this in the equation (i) we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=-\left( 6+2x \right)+1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-6-2x+1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-2x-5 \\
\end{align}\]
From the above two cases, we can write the given function in the piecewise form as
\[\Rightarrow y=\left\{ \begin{align}
& 2x+7;x\ge -3 \\
& -2x-5;x<-3 \\
\end{align} \right\}\]
We can see these two pieces of the given function in the below graph.
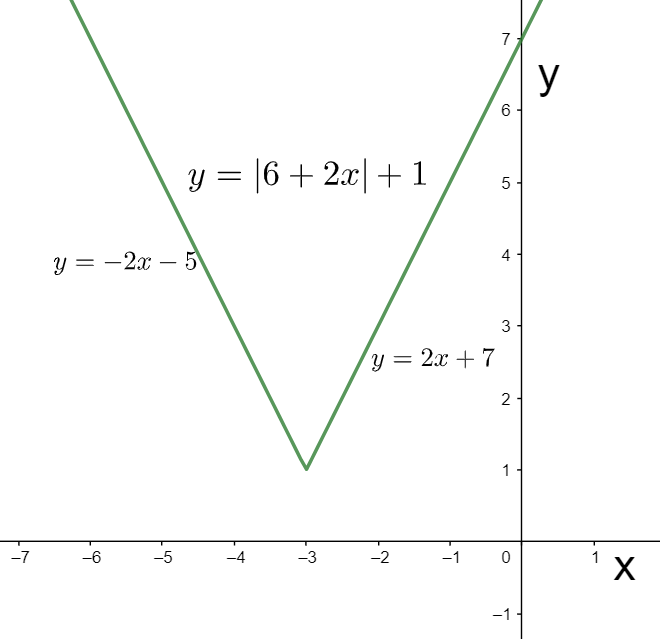
Hence, we have written the given function in the piecewise form.
Note: Whenever a function is defined in terms of modulus, greatest integer, fractional part etc. it is written in the piecewise form, since these have different definitions for the different intervals. We can put the equality sign on both of the inequalities for two intervals also.
Complete step-by-step solution:
The function given in the above question is
$\Rightarrow y=\left| 6+2x \right|+1......\left( i \right)$
We know that the modulus function returns the absolute value of the argument. Therefore, we can consider the two cases as below.
Case I: When $6+2x\ge 0$
$\Rightarrow 6+2x\ge 0$
Subtracting $6$ from both sides
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 6+2x-6\ge 0-6 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x\ge -6 \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both sides by $2$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{2}\ge \dfrac{-6}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x\ge -3 \\
\end{align}$
Since in this case, the argument of the modulus function is non-negative, its absolute value will be equal to the argument. Therefore for $x\ge -3$ we can write
$\Rightarrow \left| 6+2x \right|=6+2x$
Substituting this in the equation (i) we get
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=6+2x+1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=2x+7 \\
\end{align}$
Case II: When $6+2x\ge 0$
$\Rightarrow 6+2x<0$
Subtracting $6$ from both sides
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow 6+2x-6<0-6 \\
& \Rightarrow 2x<-6 \\
\end{align}$
Dividing both sides by $2$
$\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow \dfrac{2x}{2}<\dfrac{-6}{2} \\
& \Rightarrow x<-3 \\
\end{align}$
Since in this case, the argument of the modulus function is non-negative, its absolute value will be equal to the argument. Therefore for $x<-3$ we can write
\[\Rightarrow \left| 6+2x \right|=-\left( 6+2x \right)\]
Substituting this in the equation (i) we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow y=-\left( 6+2x \right)+1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-6-2x+1 \\
& \Rightarrow y=-2x-5 \\
\end{align}\]
From the above two cases, we can write the given function in the piecewise form as
\[\Rightarrow y=\left\{ \begin{align}
& 2x+7;x\ge -3 \\
& -2x-5;x<-3 \\
\end{align} \right\}\]
We can see these two pieces of the given function in the below graph.

Hence, we have written the given function in the piecewise form.
Note: Whenever a function is defined in terms of modulus, greatest integer, fractional part etc. it is written in the piecewise form, since these have different definitions for the different intervals. We can put the equality sign on both of the inequalities for two intervals also.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




