
How do you write the vertex form equation of the Parabola \[x = {y^2} + 6y + 1\]?
Answer
552k+ views
Hint: Here, we will use the completing the square method to simplify the equation. Then by using the suitable algebraic identity we will convert the equation into vertex form of the Parabola. A parabola is a U- shaped curve which is at an equal distance from the fixed point and the fixed straight line.
Formula Used:
We will use the following formulas:
1. Completing the square method is given by the formula \[a{y^2} + by + c = {\left( {y \pm \dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2} + c + {\left( {\dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2}\]
2. The square of the sum of the numbers is given by the algebraic identity \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\]
3. Equation of Parabola in the Vertex form is given by \[x = a{\left( {y - k} \right)^2} + h\] where \[\left( {h,k} \right)\] be the coordinates of the vertex of a Parabola and \[a\] is the multiplier.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given an equation of Parabola \[x = {y^2} + 6y + 1\].
Now, we will use the completing square method to convert the quadratic equation into the vertex form.
Now, we will group the \[y\]- term on one side of the equation and the \[x\]- term and the constant term on the other side of the equation, we get
Completing the square method is given by the formula \[a{y^2} + by + c = {\left( {y \pm \dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2} + c + {\left( {\dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2}\]
Quadratic equation \[\left( {{y^2} + 6y} \right)\] is of the form \[a{y^2} + by + c = 0\].
Comparing the given quadratic equation, we get \[a = 1\] and \[b = 6\].
Now, by using the completing the square method for the \[y\]- term, we get
\[x - 1 + {\left( {\dfrac{6}{2}} \right)^2} = {y^2} + \dfrac{6}{2}y + {\left( {\dfrac{6}{2}} \right)^2}\]
By simplifying the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x - 1 + {\left( 3 \right)^2} = {y^2} + 3y + {\left( 3 \right)^2}\]
Applying the exponent on the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x - 1 + 9 = {y^2} + 3y + 9\]
Subtracting the like terms on RHS, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x + 8 = {y^2} + 3y + 9\]
The square of the sum of the numbers is given by the algebraic identity \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\] .
Now, by using the algebraic identity, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x + 8 = {\left( {y + 3} \right)^2}\]
Subtracting 8 from both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = {\left( {y + 3} \right)^2} - 8\]
We know that the equation of Parabola in the Vertex form is given by \[x = a{\left( {y - k} \right)^2} + h\] where \[\left( {h,k} \right)\] be the coordinates of the vertex of a Parabola and \[a\] is the multiplier.
Now, we will write the vertex form for the given equation by using the general vertex form of the Parabola. Therefore, we get
\[x = {\left( {y + 3} \right)^2} - 8\]
So, the vertex of the Parabola \[\left( {h,k} \right)\] is\[\left( { - 8, - 3} \right)\] and the multiplier \[a\] is \[1\].
Now, we will draw the Parabola with the vertex \[\left( { - 8, - 3} \right)\].
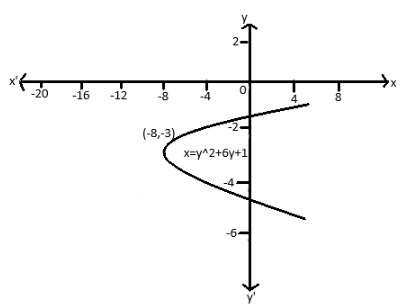
Therefore, the vertex form of the given equation of Parabola \[x = {y^2} + 6y + 1\] is \[x = {\left( {y + 3} \right)^2} - 8\].
Note:
We know that a parabola is symmetric with its axis. If the equation has \[{y^2}\] term, then the axis of symmetry is along the x-axis and if the equation has \[{x^2}\] term, then the axis of symmetry is along the y-axis. We should know that the vertex of a Parabola is the minimum or maximum point of a Parabola. We will find the type of Parabola, by using the sign of the multiplier \[a\] in the vertex form of the parabola. If \[a\] is positive in \[x = a{(y - k)^2} + h\], then the parabola is open rightwards and if \[a\] is negative in \[x = a{(y - k)^2} + h\], then the parabola is open leftwards. So, the given equation of Parabola is open rightwards.
Formula Used:
We will use the following formulas:
1. Completing the square method is given by the formula \[a{y^2} + by + c = {\left( {y \pm \dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2} + c + {\left( {\dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2}\]
2. The square of the sum of the numbers is given by the algebraic identity \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\]
3. Equation of Parabola in the Vertex form is given by \[x = a{\left( {y - k} \right)^2} + h\] where \[\left( {h,k} \right)\] be the coordinates of the vertex of a Parabola and \[a\] is the multiplier.
Complete step by step solution:
We are given an equation of Parabola \[x = {y^2} + 6y + 1\].
Now, we will use the completing square method to convert the quadratic equation into the vertex form.
Now, we will group the \[y\]- term on one side of the equation and the \[x\]- term and the constant term on the other side of the equation, we get
Completing the square method is given by the formula \[a{y^2} + by + c = {\left( {y \pm \dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2} + c + {\left( {\dfrac{b}{2}} \right)^2}\]
Quadratic equation \[\left( {{y^2} + 6y} \right)\] is of the form \[a{y^2} + by + c = 0\].
Comparing the given quadratic equation, we get \[a = 1\] and \[b = 6\].
Now, by using the completing the square method for the \[y\]- term, we get
\[x - 1 + {\left( {\dfrac{6}{2}} \right)^2} = {y^2} + \dfrac{6}{2}y + {\left( {\dfrac{6}{2}} \right)^2}\]
By simplifying the equation, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x - 1 + {\left( 3 \right)^2} = {y^2} + 3y + {\left( 3 \right)^2}\]
Applying the exponent on the terms, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x - 1 + 9 = {y^2} + 3y + 9\]
Subtracting the like terms on RHS, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x + 8 = {y^2} + 3y + 9\]
The square of the sum of the numbers is given by the algebraic identity \[{\left( {a + b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} + 2ab\] .
Now, by using the algebraic identity, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x + 8 = {\left( {y + 3} \right)^2}\]
Subtracting 8 from both sides, we get
\[ \Rightarrow x = {\left( {y + 3} \right)^2} - 8\]
We know that the equation of Parabola in the Vertex form is given by \[x = a{\left( {y - k} \right)^2} + h\] where \[\left( {h,k} \right)\] be the coordinates of the vertex of a Parabola and \[a\] is the multiplier.
Now, we will write the vertex form for the given equation by using the general vertex form of the Parabola. Therefore, we get
\[x = {\left( {y + 3} \right)^2} - 8\]
So, the vertex of the Parabola \[\left( {h,k} \right)\] is\[\left( { - 8, - 3} \right)\] and the multiplier \[a\] is \[1\].
Now, we will draw the Parabola with the vertex \[\left( { - 8, - 3} \right)\].

Therefore, the vertex form of the given equation of Parabola \[x = {y^2} + 6y + 1\] is \[x = {\left( {y + 3} \right)^2} - 8\].
Note:
We know that a parabola is symmetric with its axis. If the equation has \[{y^2}\] term, then the axis of symmetry is along the x-axis and if the equation has \[{x^2}\] term, then the axis of symmetry is along the y-axis. We should know that the vertex of a Parabola is the minimum or maximum point of a Parabola. We will find the type of Parabola, by using the sign of the multiplier \[a\] in the vertex form of the parabola. If \[a\] is positive in \[x = a{(y - k)^2} + h\], then the parabola is open rightwards and if \[a\] is negative in \[x = a{(y - k)^2} + h\], then the parabola is open leftwards. So, the given equation of Parabola is open rightwards.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




