
Write the structures of the main products of the following reactions.

Answer
575.4k+ views
Hint:Primary, secondary, and tertiary amines are traced and discerned using Hinsberg test. The given reactant is benzene sulfonyl chloride which is known as Hinsberg reagent. Along with the Hinsberg reagent, aqueous ${\text{KOH}}$ is also added. So based on the solubility of the product formed, three of them can be differentiated.
Complete step by step solution:
Amines are organic compounds having one or more nitrogen groups. Amines are divided into primary, secondary, tertiary, and aromatic amines. Primary, secondary, tertiary amines are detected and distinguished by the Hinsberg test. This was introduced by Oscar Heinrich Daniel Hinsberg.
Hinsberg reagent is the benzene sulfonyl chloride, ${\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{Cl}}$. Benzene sulfonic acid or its salt is chlorinated with phosphorus oxychloride which produces benzene sulfonyl chloride.
${\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }\xrightarrow[{{\text{POC}}{{\text{l}}_3}}]{{{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_5}}}{\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{Cl}}$
When primary amine is reacted with Hinsberg reagent, it forms a sulfonamide which on reaction with base gives sulfonamide salt. It is water-soluble.
\[{\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{N}}\left( {\text{H}} \right){\text{R}} + {\text{NaOH}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }\left[ {{\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{R}}^ - }} \right] + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\]
Tertiary amines can react with Hinsberg reagent under certain conditions only. Reaction speed, concentration, solubility and temperature have to be considered.
${\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{Cl}} + {{\text{R}}_3}{\text{N}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {{\text{R}}_3}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}^ + }\left[ {{\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - } \right] + {\text{HCl}}$
This also gives water-soluble sulfonate salts.
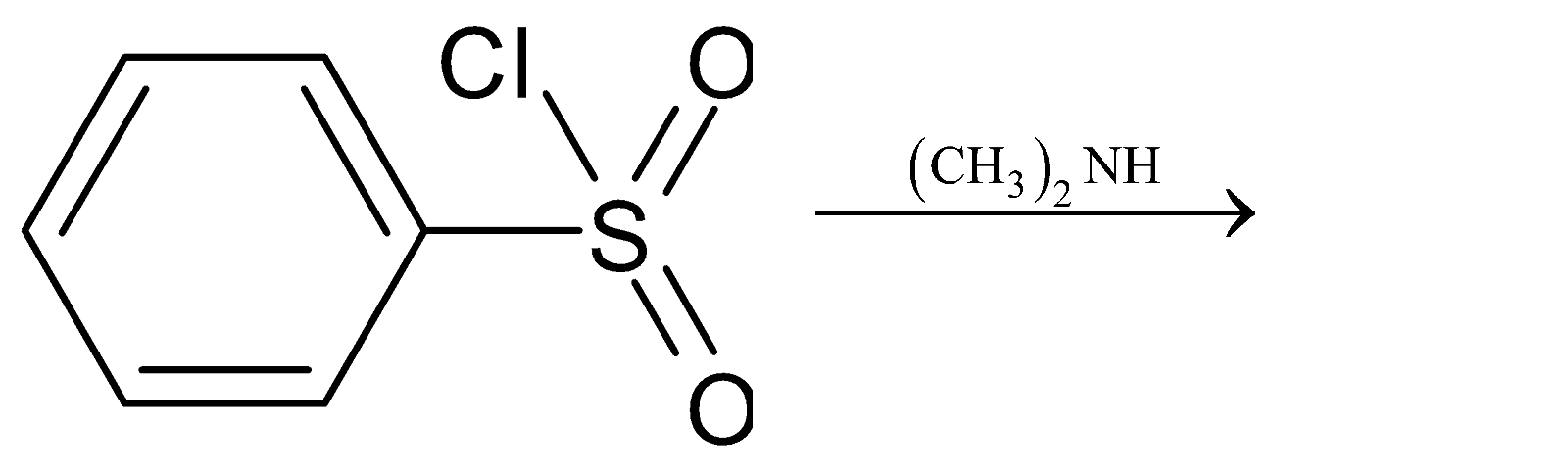
This benzene sulfonyl chloride is reacted with the amine \[{{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_9}{\text{N}}\]in the presence of aqueous KOH. It should be shaken well.
There is a direct formation of an alkali insoluble sulfonamide when secondary amine is treated with Hinsberg reagent. The reaction of benzene sulfonyl chloride is reacted with secondary amine, ${\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_2}{\text{NH}}$ to give the following products:
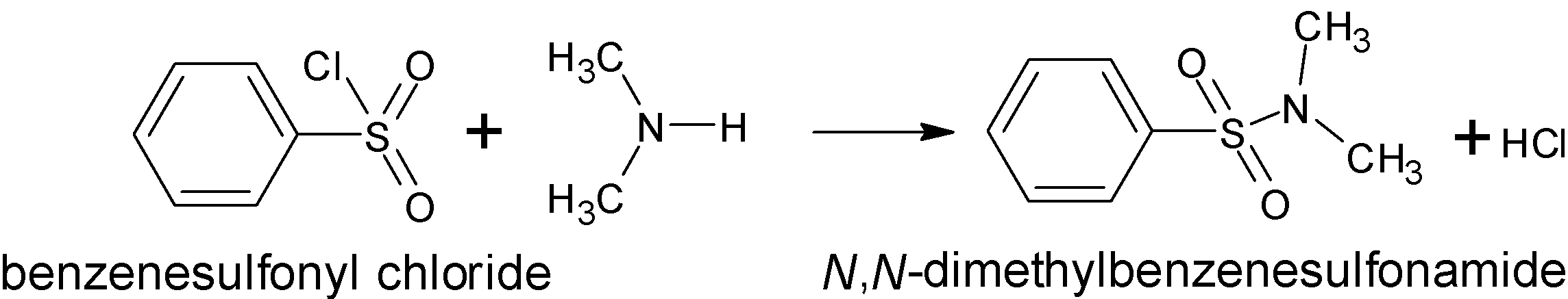
Thus the product formed is N,N-dimethyl benzene sulfonamide.
Note:
Sulfonyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis when reacted with tertiary amines which produces water soluble sulfonate salts. Differentiation of primary, secondary, tertiary amines are based on solubility of the product in alkali.
Complete step by step solution:
Amines are organic compounds having one or more nitrogen groups. Amines are divided into primary, secondary, tertiary, and aromatic amines. Primary, secondary, tertiary amines are detected and distinguished by the Hinsberg test. This was introduced by Oscar Heinrich Daniel Hinsberg.
Hinsberg reagent is the benzene sulfonyl chloride, ${\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{Cl}}$. Benzene sulfonic acid or its salt is chlorinated with phosphorus oxychloride which produces benzene sulfonyl chloride.
${\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }\xrightarrow[{{\text{POC}}{{\text{l}}_3}}]{{{\text{PC}}{{\text{l}}_5}}}{\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{Cl}}$
When primary amine is reacted with Hinsberg reagent, it forms a sulfonamide which on reaction with base gives sulfonamide salt. It is water-soluble.
\[{\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{N}}\left( {\text{H}} \right){\text{R}} + {\text{NaOH}} \to {\text{N}}{{\text{a}}^ + }\left[ {{\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{N}}{{\text{R}}^ - }} \right] + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}}\]
Tertiary amines can react with Hinsberg reagent under certain conditions only. Reaction speed, concentration, solubility and temperature have to be considered.
${\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_2}{\text{Cl}} + {{\text{R}}_3}{\text{N}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O}} \to {{\text{R}}_3}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}^ + }\left[ {{\text{PhS}}{{\text{O}}_3}^ - } \right] + {\text{HCl}}$
This also gives water-soluble sulfonate salts.
This benzene sulfonyl chloride is reacted with the amine \[{{\text{C}}_3}{{\text{H}}_9}{\text{N}}\]in the presence of aqueous KOH. It should be shaken well.
There is a direct formation of an alkali insoluble sulfonamide when secondary amine is treated with Hinsberg reagent. The reaction of benzene sulfonyl chloride is reacted with secondary amine, ${\left( {{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}} \right)_2}{\text{NH}}$ to give the following products:

Thus the product formed is N,N-dimethyl benzene sulfonamide.
Note:
Sulfonyl chloride undergoes hydrolysis when reacted with tertiary amines which produces water soluble sulfonate salts. Differentiation of primary, secondary, tertiary amines are based on solubility of the product in alkali.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




