
Write the structures of the following organic halogen compounds.
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
(ii) p-Bromochlorobenzene
(iii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
(iv) 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-iodooctane
(v) 2-Bromobutane
(vi) 4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
(vii) 1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene
(vii) 1,4-Dibromobut-2-ene
Answer
593.1k+ views
Hint: Derivatives of organic compounds in which one or more hydrogens are replaced with halogen atoms, i.e. fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br) and iodine (I). Halogen atoms are always added as prefix while naming organic halogen compounds.
Complete answer:
Let us write the structure of the given organic halogen compounds one by one:
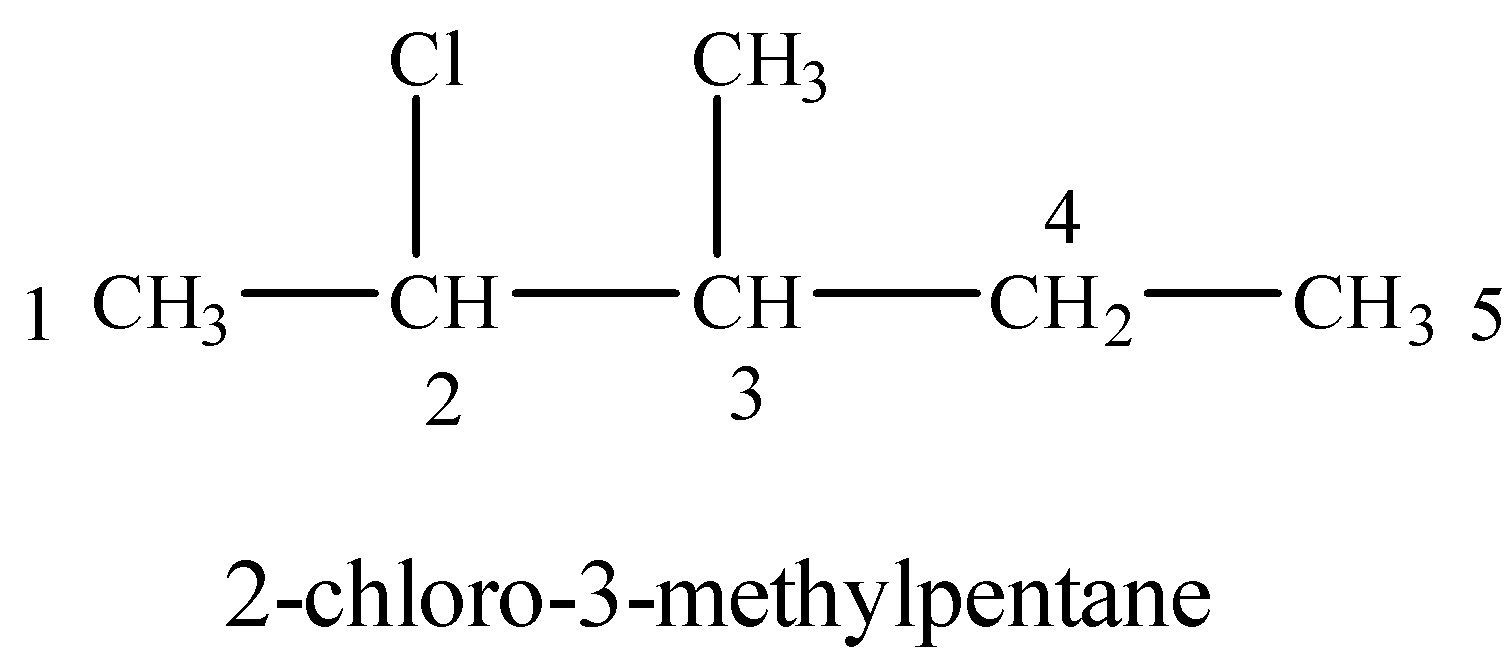
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
Numbering on the longest carbon chain starts from the end in which Cl gets a lower number than methyl-group.
(ii) p-Bromochlorobenzene
p-Bromochlorobenzene is the common or trivial name of 1-bromo-4-chlorobenzene.
Br is present at the para-position with respect to the Cl on the benzene ring.

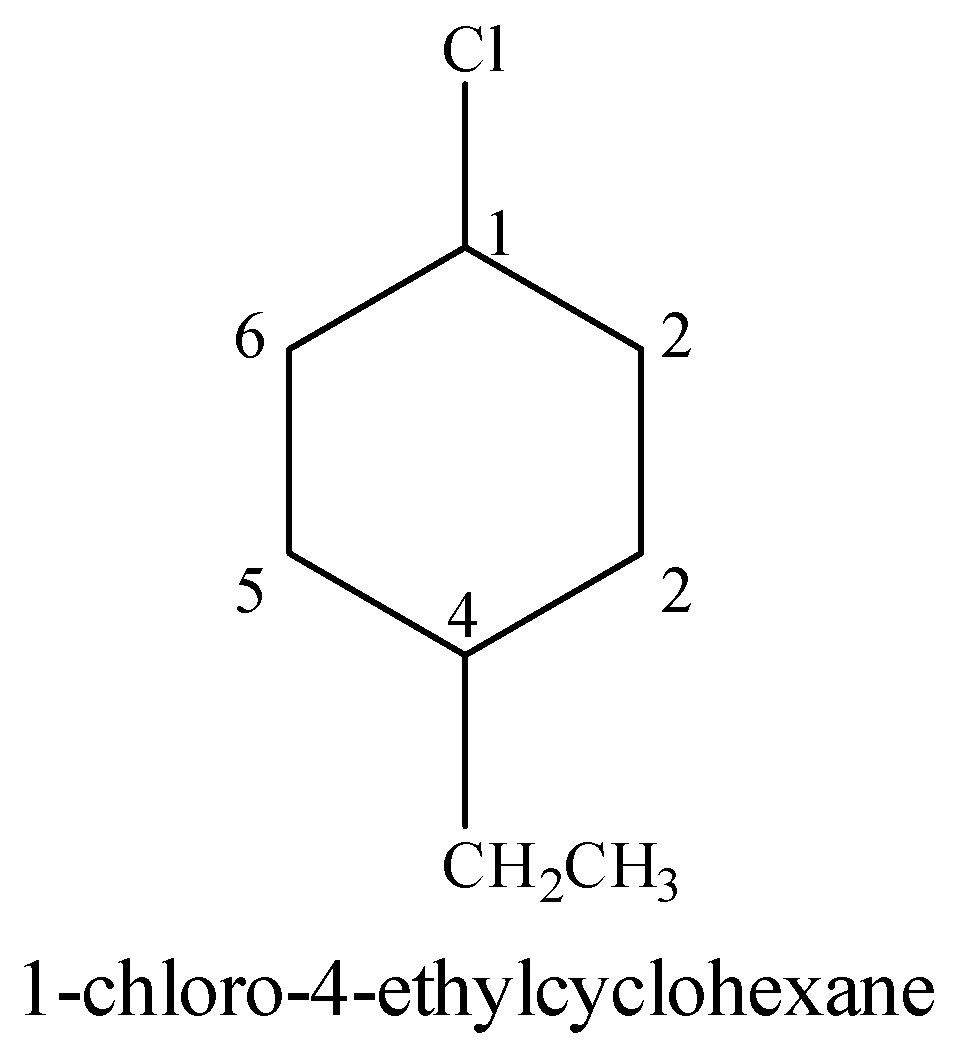
(iii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a six membered aliphatic ring. Ethyl ($C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}-$) group is present at the 4-position with respect to Cl on the cyclohexane.
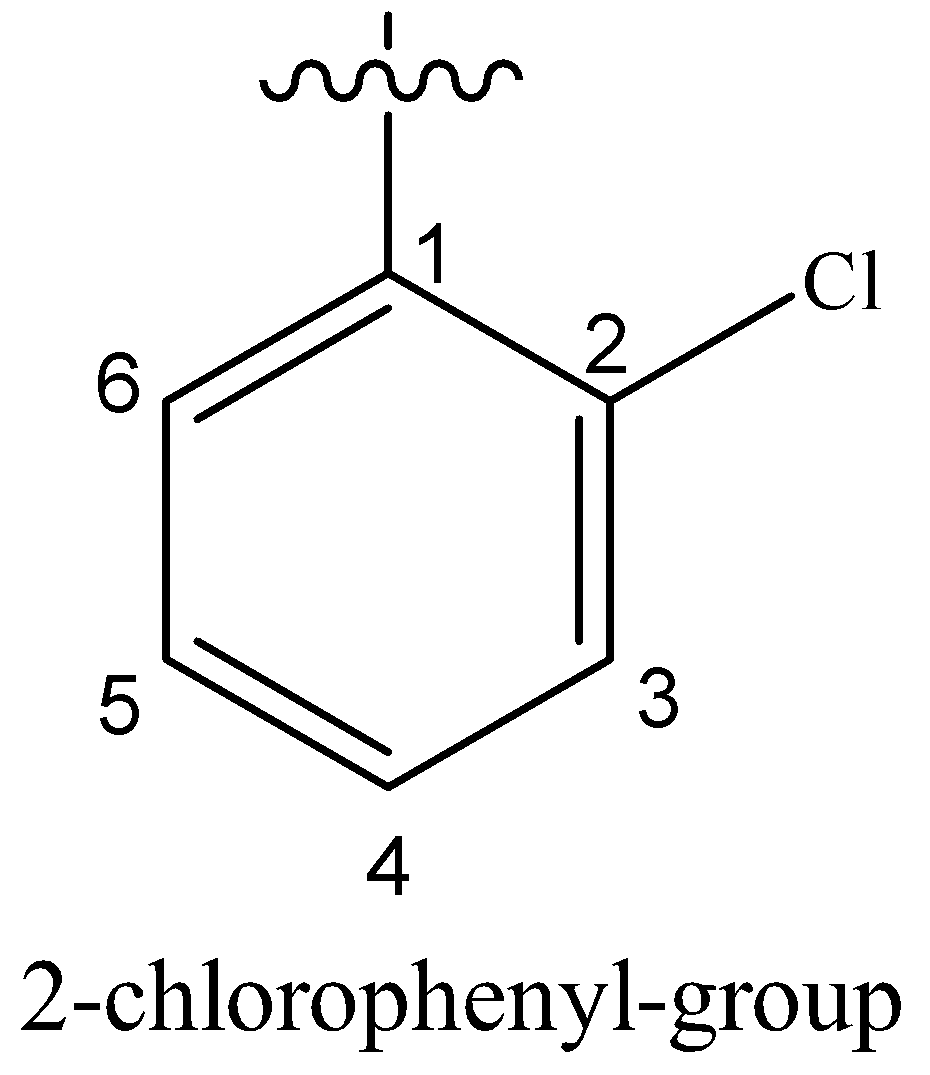
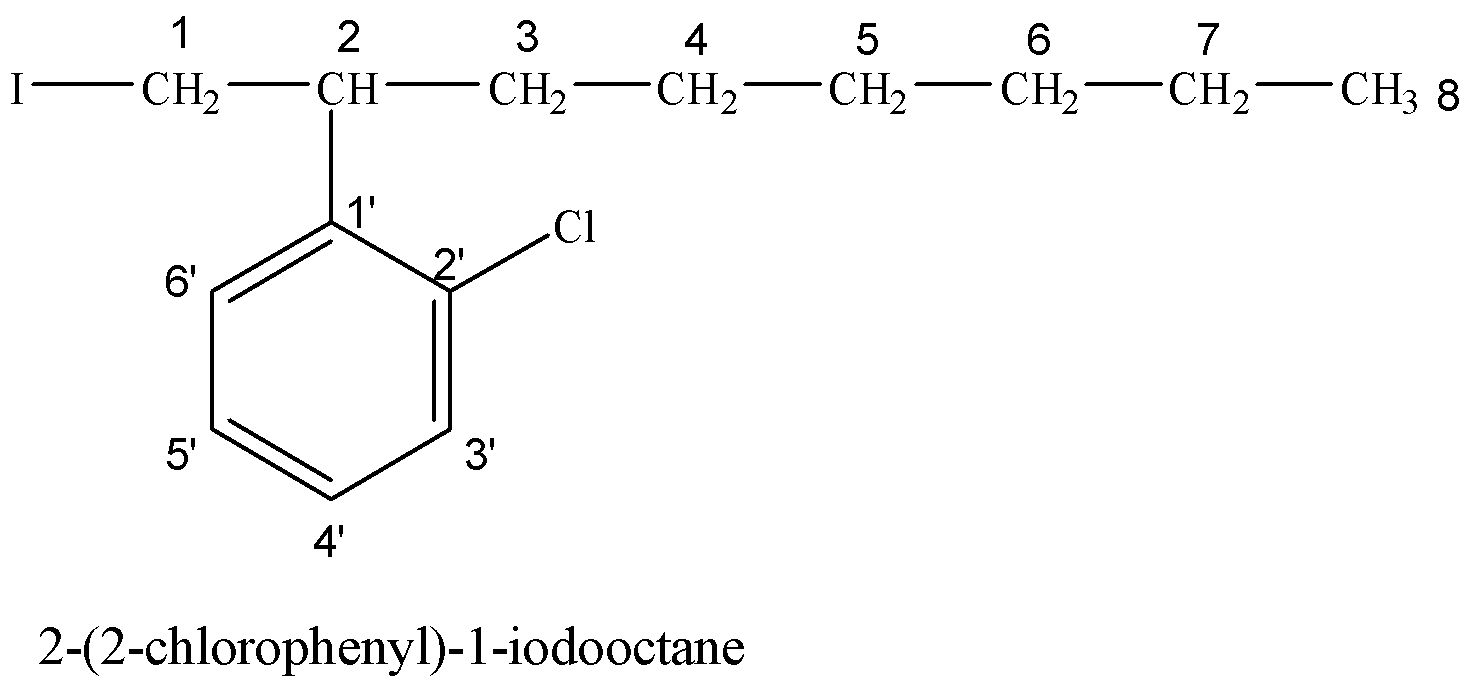
(iv) 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-iodooctane
Hydrocarbon chain having eight carbon atoms is called octane. On the 2-position with respect to I, a phenyl group containing Cl at 2’-position is attached.
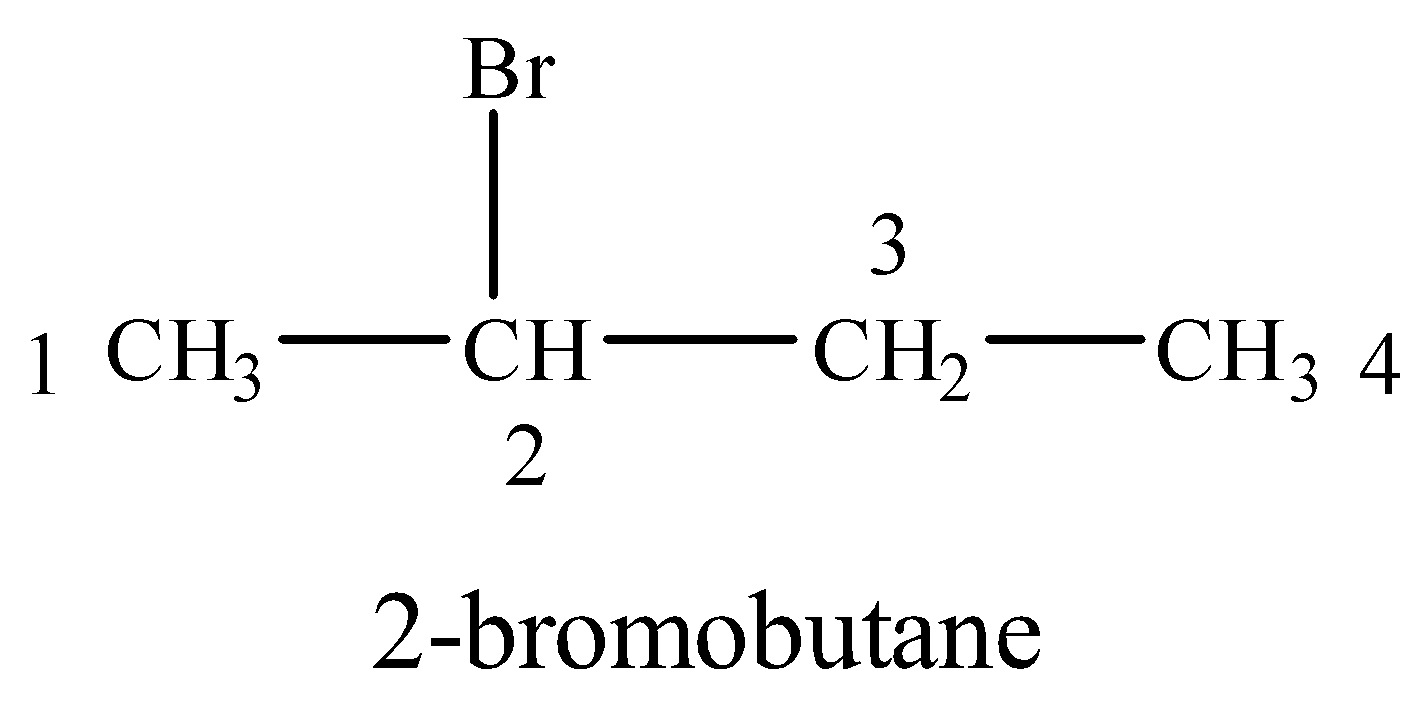
(v) 2-Bromobutane
Br is attached to a four carbon chain at 2-position.
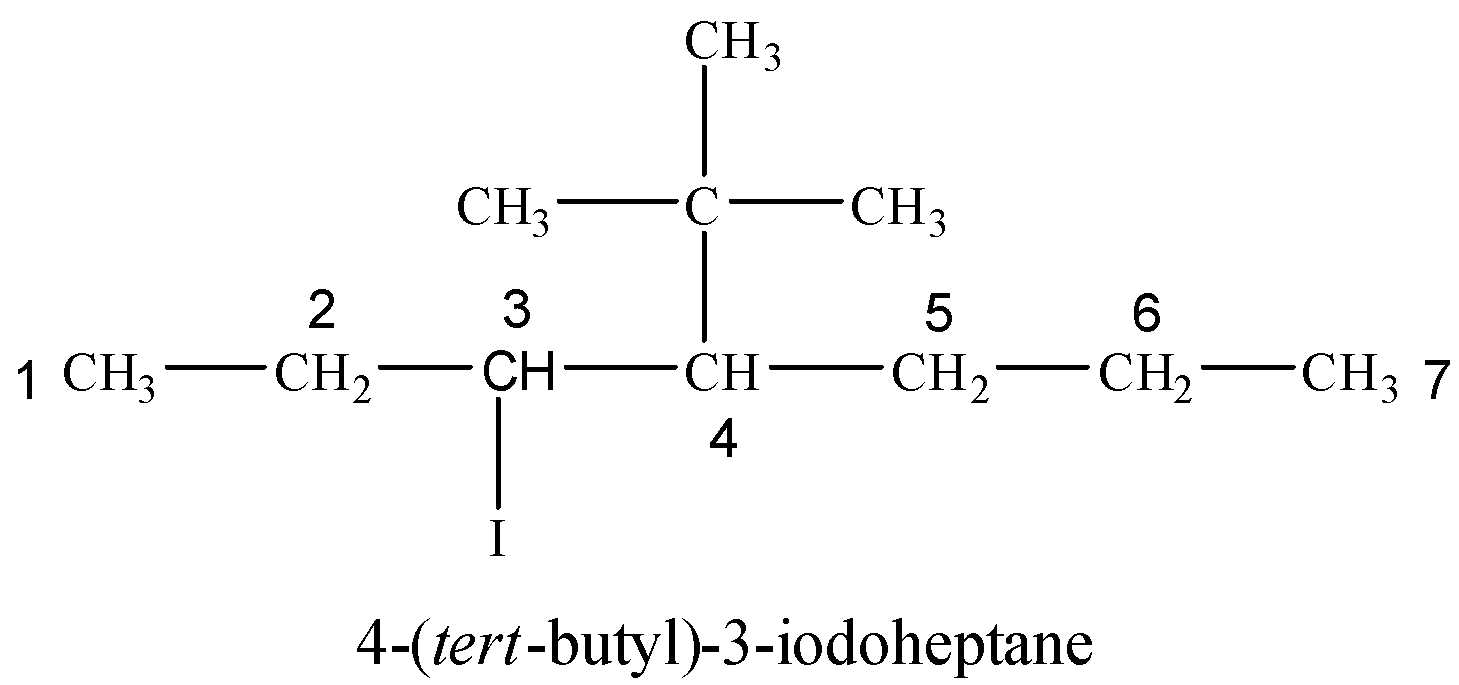
(vi) 4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
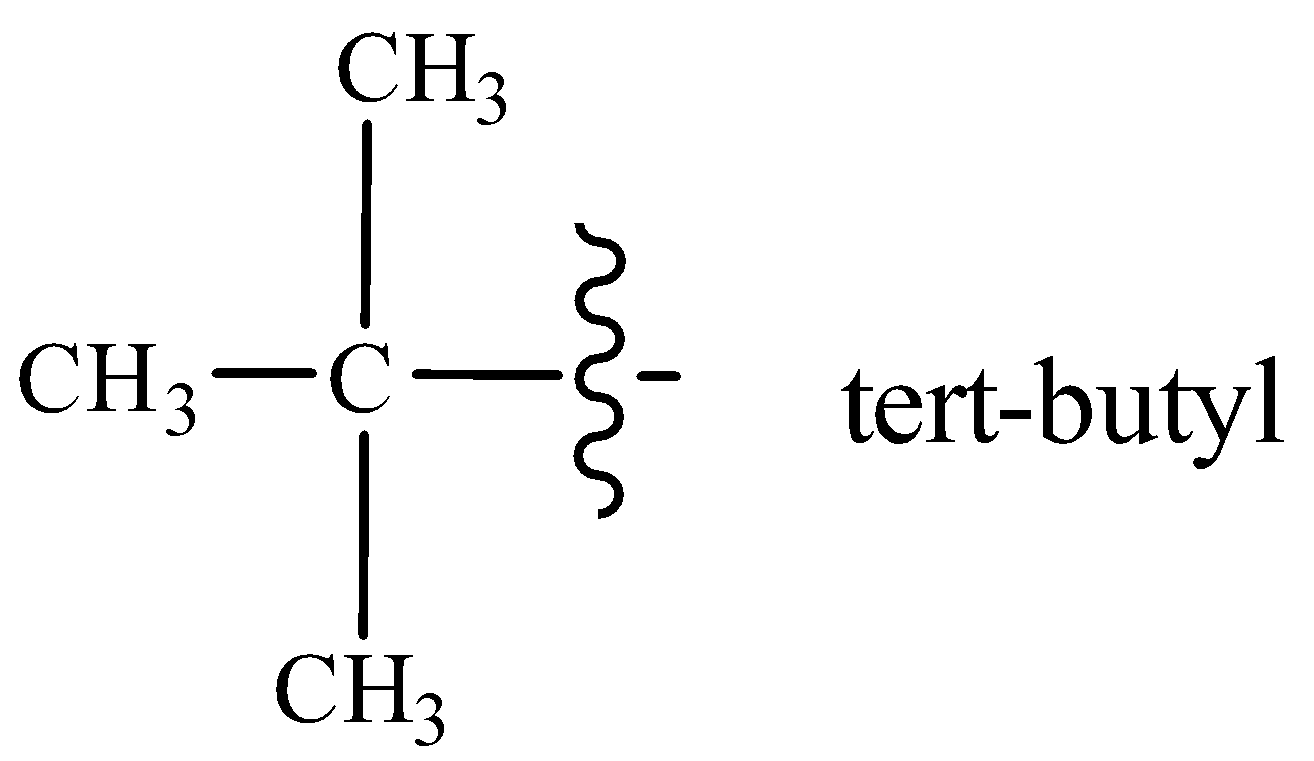
Tert-butyl group is attached at 4-position with respect to I at 3-position on a seven carbon hydrocarbon chain.
(vii) 1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene
On the benzene ring Br, methyl and secondary butyl groups are present at 1, 2 and 4-positions, respectively. Secondary carbon is the carbon atom attached to two other carbon chains.

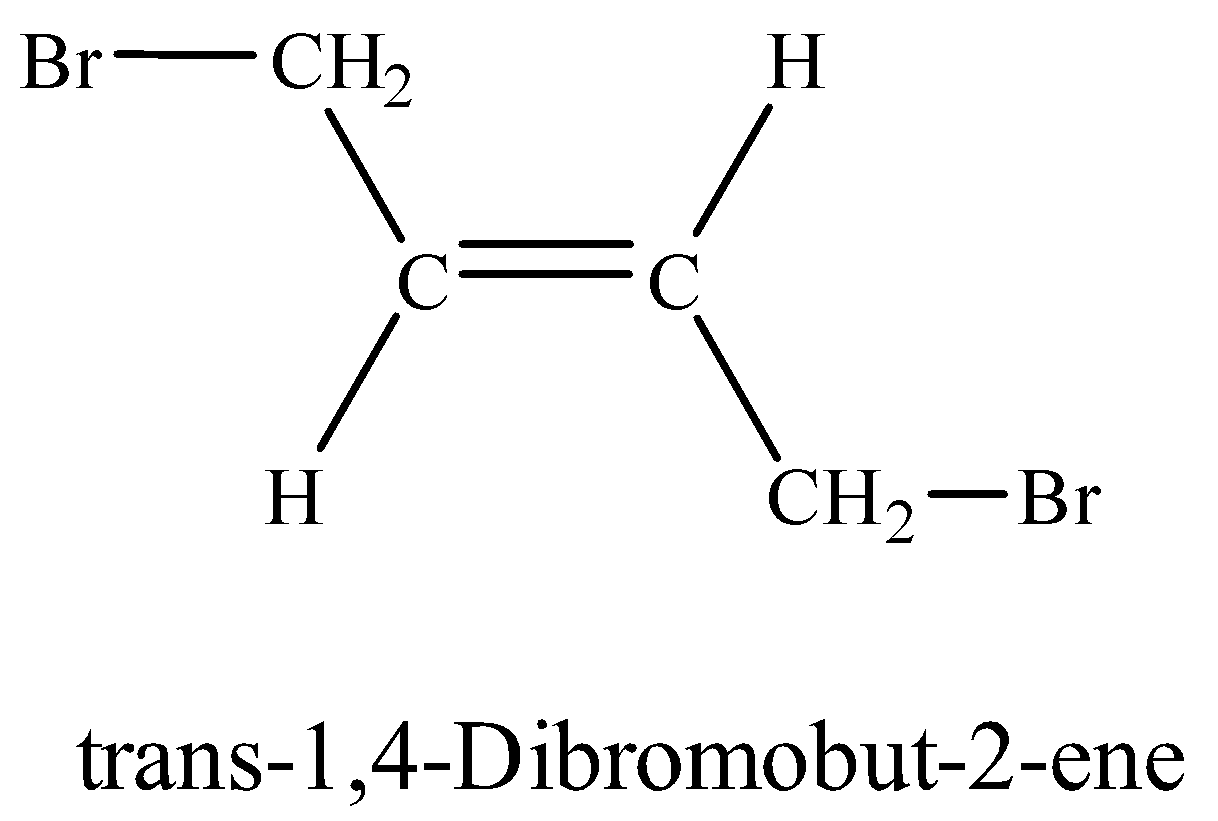
(viii) 1, 4-Dibromobut-2-ene

Additional Information: Two geometrical isomers exist for 1, 4-Dibromobut-2-ene. i.e. cis and trans. When the same groups are on the same side of the double, the isomer is cis-isomer whereas trans-isomer has same groups on opposite side. Trans-isomer is energetically more stable than cis-isomer.

Note: Read carefully the name of the compound given before writing its structure. If a compound contains more and large groups, then try to write the structure of each substituent and then attach the substituent at their respective positions on the main largest carbon chain.
Complete answer:
Let us write the structure of the given organic halogen compounds one by one:
(i) 2-Chloro-3-methylpentane
Numbering on the longest carbon chain starts from the end in which Cl gets a lower number than methyl-group.

(ii) p-Bromochlorobenzene
p-Bromochlorobenzene is the common or trivial name of 1-bromo-4-chlorobenzene.
Br is present at the para-position with respect to the Cl on the benzene ring.

(iii) 1-Chloro-4-ethylcyclohexane
Cyclohexane is a six membered aliphatic ring. Ethyl ($C{{H}_{3}}C{{H}_{2}}-$) group is present at the 4-position with respect to Cl on the cyclohexane.

(iv) 2-(2-chlorophenyl)-1-iodooctane
Hydrocarbon chain having eight carbon atoms is called octane. On the 2-position with respect to I, a phenyl group containing Cl at 2’-position is attached.


(v) 2-Bromobutane
Br is attached to a four carbon chain at 2-position.

(vi) 4-tert-Butyl-3-iodoheptane
Tert-butyl group is attached at 4-position with respect to I at 3-position on a seven carbon hydrocarbon chain.


(vii) 1-Bromo-4-sec-butyl-2-methylbenzene
On the benzene ring Br, methyl and secondary butyl groups are present at 1, 2 and 4-positions, respectively. Secondary carbon is the carbon atom attached to two other carbon chains.

(viii) 1, 4-Dibromobut-2-ene

Additional Information: Two geometrical isomers exist for 1, 4-Dibromobut-2-ene. i.e. cis and trans. When the same groups are on the same side of the double, the isomer is cis-isomer whereas trans-isomer has same groups on opposite side. Trans-isomer is energetically more stable than cis-isomer.


Note: Read carefully the name of the compound given before writing its structure. If a compound contains more and large groups, then try to write the structure of each substituent and then attach the substituent at their respective positions on the main largest carbon chain.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




