
Write the structures of all enantiomers possible for lactic acid.
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint: Enantiomers are a pair of molecules that exist in two forms that are mirror images of one another but cannot be superimposed one upon the other. They are basically non-superimposable mirror images of one another.
Complete step by step solution:
- An enantiomer can be defined as one of the two stereoisomers of a compound that is a non-superimposable mirror image of another stereoisomer of the same compound.
- Moreover, the chemical compounds that exhibit stereoisomerism and have multiple enantiomeric structures are known to often participate in chemical reactions with other enantiomeric compounds.
- Further, lactic acid is an organic acid with chemical formula ${C_3}{H_6}{O_3}$. It is also known as milk acid and it further consists of two enantiomers. The first enantiomer is \[L\left( + \right)\] lactic and the second enantiomer is \[D\left( - \right)\] lactic acid. Both the enantiomers are as shown:
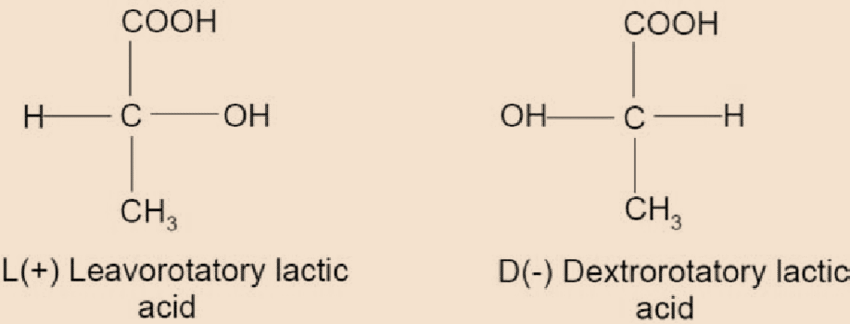
Moreover, enantiomers can be classified as special types of optical isomers. It is important to note that two enantiomers of a compound must be non-superimposable. Each of the possible structures is known as enantiomorph. Hence, the structural property of a chemical compound that allows it to have two different possible enantiomorphs is known as enantiomorphism.
Note: Many biological molecules are known to be enantiomers. Two different enantiomers of the same chemical compound can have completely different effects on many organisms. This phenomenon is widely observed in the effects of different drugs on human beings. In most cases, only one enantiomer of a drug will have the ability to bring about the desired physiological change whereas the other enantiomer is often not as active.
Complete step by step solution:
- An enantiomer can be defined as one of the two stereoisomers of a compound that is a non-superimposable mirror image of another stereoisomer of the same compound.
- Moreover, the chemical compounds that exhibit stereoisomerism and have multiple enantiomeric structures are known to often participate in chemical reactions with other enantiomeric compounds.
- Further, lactic acid is an organic acid with chemical formula ${C_3}{H_6}{O_3}$. It is also known as milk acid and it further consists of two enantiomers. The first enantiomer is \[L\left( + \right)\] lactic and the second enantiomer is \[D\left( - \right)\] lactic acid. Both the enantiomers are as shown:

Moreover, enantiomers can be classified as special types of optical isomers. It is important to note that two enantiomers of a compound must be non-superimposable. Each of the possible structures is known as enantiomorph. Hence, the structural property of a chemical compound that allows it to have two different possible enantiomorphs is known as enantiomorphism.
Note: Many biological molecules are known to be enantiomers. Two different enantiomers of the same chemical compound can have completely different effects on many organisms. This phenomenon is widely observed in the effects of different drugs on human beings. In most cases, only one enantiomer of a drug will have the ability to bring about the desired physiological change whereas the other enantiomer is often not as active.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




