
Write the structure of an isomer of compound \[{C_4}{H_9}Br\],which is most reactive towards \[{S_N}1\] reaction.
Answer
588k+ views
Hint: In order to solve this question, go through the following steps: Identify the rules for the order of the reactivity for different types of haloalkanes. Compare them with the isomers that we may obtain from \[{C_4}{H_9}Br\]. Then select the isomer that provides the maximum reactivity according to the rules of \[{S_N}1\] reaction.
Complete step by step answer:
\[{S_N}\] reactions stand for Nucleophilic Substitution reactions. To further classify this concept, there are 2 types of \[{S_N}\] reactions, namely \[{S_N}1\] and \[{S_N}2\] reactions.
Of these, the \[{S_N}1\] reaction be characterized as follows:
\[{S_N}1\] reaction basically means that the given reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction where
The rate determining step of the reaction involves only 1 component. Some common rules to be followed for determining if the given reaction is \[{S_N}1\]:
1.These reactions are unimolecular, i.e. require only 1 component for completion, which proceeds through a carbocation.
2.\[{S_N}1\]reactions result in racemization of stereochemistry at the centre of the rection
3.The first step of the reaction is usually slower and hence it is the one that determines the rate of the reaction.
4.Participation of neighbouring groups is important in \[{S_N}1\] reactions.
Now, \[{C_4}{H_9}Br\] can be identified as a haloalkane. The concentration of haloalkanes determines the rate of the reaction, not the nucleophile. The reason for this is that breaking the Carbon – halogen bond is the slowest step, and hence is the rate determining step of the reaction. Now, another observed trend in haloalkanes is that the reactivity order is \[3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ > methyl\].
In the given compound, the only \[3^\circ \] isomer possible is:
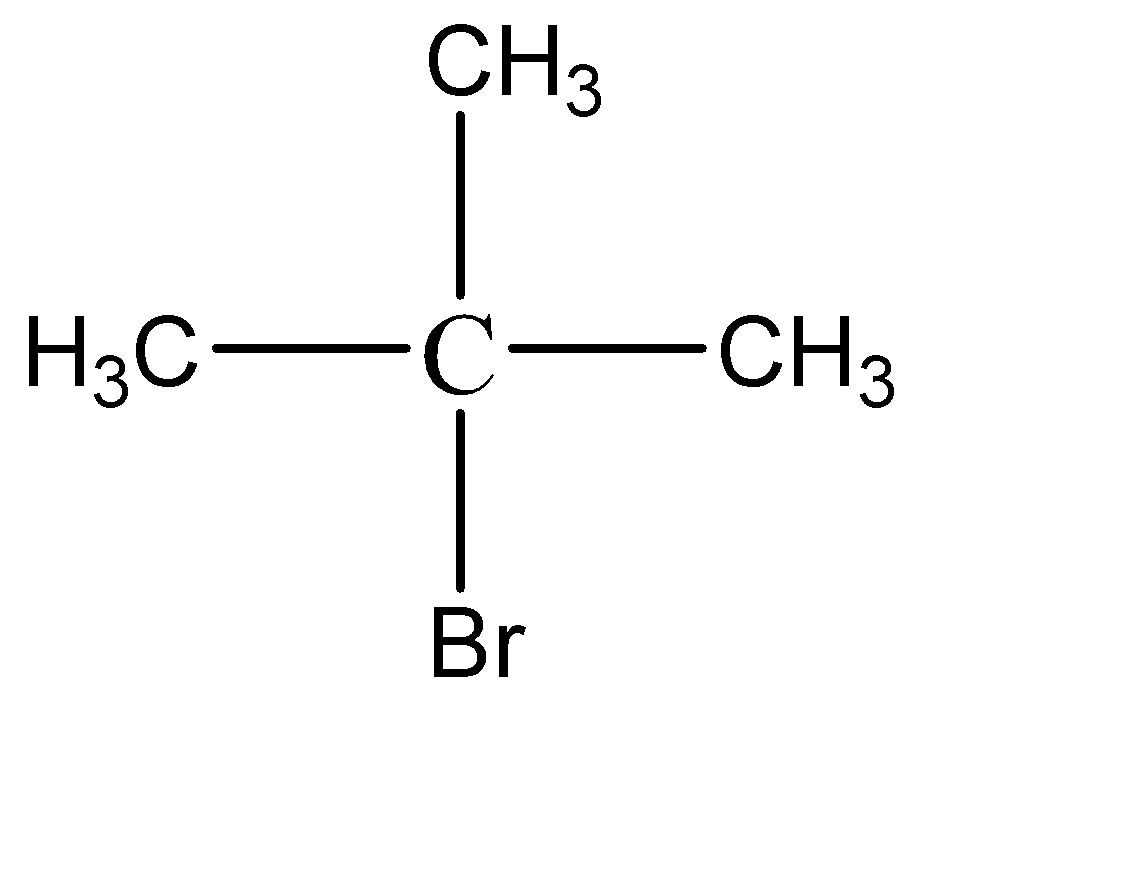
Hence, this is the structure of an isomer of compound \[{C_4}{H_9}Br\] ,which is most reactive towards \[{S_N}1\] reaction.
Note:
The reactivity order of alkyl halides in the case of SN1 reaction is\[3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ > methyl\].The same reason is responsible for more reactivity of compounds such as benzylic halide and allylic halides towards \[{S_N}1\] reaction because it leads to the formation of highly stable resonance structures of carbocation intermediates.
Complete step by step answer:
\[{S_N}\] reactions stand for Nucleophilic Substitution reactions. To further classify this concept, there are 2 types of \[{S_N}\] reactions, namely \[{S_N}1\] and \[{S_N}2\] reactions.
Of these, the \[{S_N}1\] reaction be characterized as follows:
\[{S_N}1\] reaction basically means that the given reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction where
The rate determining step of the reaction involves only 1 component. Some common rules to be followed for determining if the given reaction is \[{S_N}1\]:
1.These reactions are unimolecular, i.e. require only 1 component for completion, which proceeds through a carbocation.
2.\[{S_N}1\]reactions result in racemization of stereochemistry at the centre of the rection
3.The first step of the reaction is usually slower and hence it is the one that determines the rate of the reaction.
4.Participation of neighbouring groups is important in \[{S_N}1\] reactions.
Now, \[{C_4}{H_9}Br\] can be identified as a haloalkane. The concentration of haloalkanes determines the rate of the reaction, not the nucleophile. The reason for this is that breaking the Carbon – halogen bond is the slowest step, and hence is the rate determining step of the reaction. Now, another observed trend in haloalkanes is that the reactivity order is \[3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ > methyl\].
In the given compound, the only \[3^\circ \] isomer possible is:

Hence, this is the structure of an isomer of compound \[{C_4}{H_9}Br\] ,which is most reactive towards \[{S_N}1\] reaction.
Note:
The reactivity order of alkyl halides in the case of SN1 reaction is\[3^\circ > 2^\circ > 1^\circ > methyl\].The same reason is responsible for more reactivity of compounds such as benzylic halide and allylic halides towards \[{S_N}1\] reaction because it leads to the formation of highly stable resonance structures of carbocation intermediates.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




