
Write the structure of $\alpha - D - ( + ) -$glucopyranose and $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$.
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: The $\alpha - D - ( + ) -$ glucopyranose and $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$ are the two cyclic hemiacetal structural forms of glucose which differ from each other in the presence of hydroxyl group at the anomeric carbon.
Complete step by step answer:
The pyranose ring of glucose is formed by treating the hydroxyl group available in the fifth position of carbon (C-5) of the glucose molecule with the aldehydic group available at the first position of the carbon (C-1) of the same glucose molecule. This results in the formation of intramolecular hemiacetal molecules.
The structure of the pyranose ring of glucose is shown below.
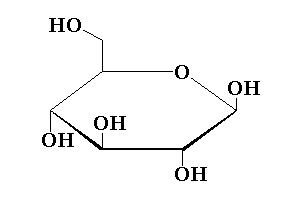
In this pyranose ring structure of glucose, five carbon atoms are present and one oxygen atom is present forming a six membered ring structure.
The pyranose ring structure of glucose is divided in two forms one is $\alpha - D - ( + ) -$glucopyranose and other is $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$.
Both the structures differ from each other by their three dimensional configuration of atoms or groups present at one or more than one position.
The structure of $\alpha - D - ( + ) -$glucopyranose is shown below.
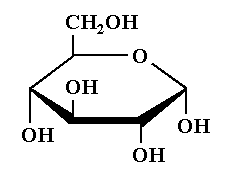
In $\alpha - D - ( + ) -$glucopyranose, $\alpha$- means that the hydroxyl group is attached to the carbon 1 and the $- C{H_2}OH$ group is attached at the carbon 5 position is present at the opposite sides of the plane of ring. It is the trans arrangement.
The structure of $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$ is shown below.
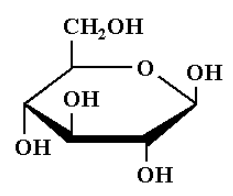
In $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$, $\beta$-means, the hydroxyl group is attached to the carbon 1 and the $- C{H_2}OH$ group is attached at the carbon 5 position is present on the same sides of the plane of ring. It is the cis arrangement.
Note:
The pyranose name of glucose is taken from the heterocyclic compound which contains an oxygen atom with five carbon atoms generating a cyclic structure called pyran. Both structures are almost the same except in the .. glucopyranose, the hydroxyl group is present far right is down and in $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$, the hydroxyl is present far right is up.
Complete step by step answer:
The pyranose ring of glucose is formed by treating the hydroxyl group available in the fifth position of carbon (C-5) of the glucose molecule with the aldehydic group available at the first position of the carbon (C-1) of the same glucose molecule. This results in the formation of intramolecular hemiacetal molecules.
The structure of the pyranose ring of glucose is shown below.

In this pyranose ring structure of glucose, five carbon atoms are present and one oxygen atom is present forming a six membered ring structure.
The pyranose ring structure of glucose is divided in two forms one is $\alpha - D - ( + ) -$glucopyranose and other is $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$.
Both the structures differ from each other by their three dimensional configuration of atoms or groups present at one or more than one position.
The structure of $\alpha - D - ( + ) -$glucopyranose is shown below.

In $\alpha - D - ( + ) -$glucopyranose, $\alpha$- means that the hydroxyl group is attached to the carbon 1 and the $- C{H_2}OH$ group is attached at the carbon 5 position is present at the opposite sides of the plane of ring. It is the trans arrangement.
The structure of $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$ is shown below.

In $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$, $\beta$-means, the hydroxyl group is attached to the carbon 1 and the $- C{H_2}OH$ group is attached at the carbon 5 position is present on the same sides of the plane of ring. It is the cis arrangement.
Note:
The pyranose name of glucose is taken from the heterocyclic compound which contains an oxygen atom with five carbon atoms generating a cyclic structure called pyran. Both structures are almost the same except in the .. glucopyranose, the hydroxyl group is present far right is down and in $\beta - D - ( + ) - glucopyranose$, the hydroxyl is present far right is up.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




