
Write the structural formula of the two isomers with the molecular formula $ {C_4}{H_8}O $ to illustrate functional group isomerism?
Answer
493.5k+ views
Hint: There can be several structures drawn with the same molecular formula. With the formula $ {C_4}{H_8}O $ also you can draw aliphatic as well as cyclic structures. In functional group isomers, the molecular formula will be the same but the functional group will be different. There will be one double bond present in both structures. First, write four carbons then add a double bond, and finally add the hydrogens. Lastly, check the number of elements with the molecular formula.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Functional group isomerism takes place when substances have the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
The molecular formula given is $ {C_4}{H_8}O $ . And with this molecular formula, we should find out two isomers having different functional groups.
In the molecular formula, there are four carbons present with eight hydrogens and one oxygen. This can be said that there will be at least one double bond present in the structure. The double bond can either be between $ C $ and $ O $ $ \left( {C = O} \right) $ or between two carbons $ \left( {C = C} \right) $ . For simplicity what can be done is just write four carbons in a single chain then add a double bond and then finally add hydrogens to complete the valency of carbon.
The two isomers that we found out with the molecular formula $ {C_4}{H_8}O $ are:
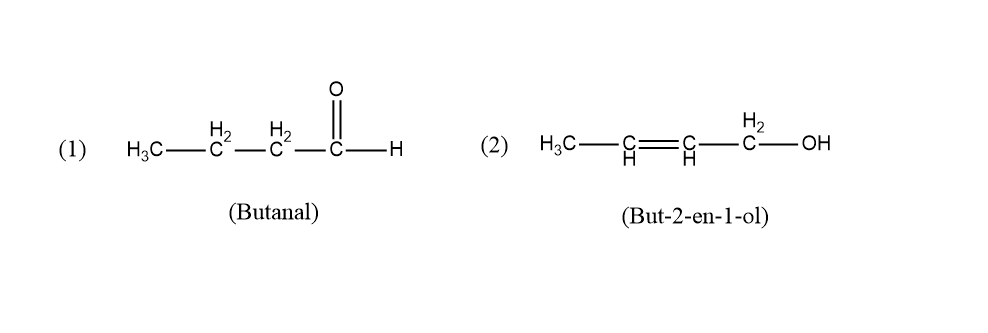
Butanal and But $ - 2 - $ en $ - 1 - $ ol are the two isomers. The functional group in Butanal is an aldehyde and in But $ - 2 - $ en $ - 1 - $ ol is alcohol. Both the functional groups are different. Hence these two structures are functional group isomers having the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
Note:
There can be many more structures drawn here using the molecular formula $ {C_4}{H_8}O $ . They can be cyclic also. The functional group isomerism is a type of structural isomerism where the molecular formula of the compounds is the same but the structures are different. There are many other types of structural isomerism such as position isomerism, chain isomerism, metamerism, tautomerism, and ring isomerism.
Complete Step By Step Answer:
Functional group isomerism takes place when substances have the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
The molecular formula given is $ {C_4}{H_8}O $ . And with this molecular formula, we should find out two isomers having different functional groups.
In the molecular formula, there are four carbons present with eight hydrogens and one oxygen. This can be said that there will be at least one double bond present in the structure. The double bond can either be between $ C $ and $ O $ $ \left( {C = O} \right) $ or between two carbons $ \left( {C = C} \right) $ . For simplicity what can be done is just write four carbons in a single chain then add a double bond and then finally add hydrogens to complete the valency of carbon.
The two isomers that we found out with the molecular formula $ {C_4}{H_8}O $ are:

Butanal and But $ - 2 - $ en $ - 1 - $ ol are the two isomers. The functional group in Butanal is an aldehyde and in But $ - 2 - $ en $ - 1 - $ ol is alcohol. Both the functional groups are different. Hence these two structures are functional group isomers having the same molecular formula but different functional groups.
Note:
There can be many more structures drawn here using the molecular formula $ {C_4}{H_8}O $ . They can be cyclic also. The functional group isomerism is a type of structural isomerism where the molecular formula of the compounds is the same but the structures are different. There are many other types of structural isomerism such as position isomerism, chain isomerism, metamerism, tautomerism, and ring isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




