
Write the structural formula of the following:
a.Butene
b.Ethyne
c.Benzene
d.cyclohexane
Answer
469.2k+ views
Hint: The IUPAC name of the given compounds gives a lot of information about its structural features like the type of bonds present in it, the substituents and functional groups attached (along with their positions) and the total number of carbon atoms present in it.
Complete step by step answer:
The structural formula of any compound reveals the types of bonds present in it and their arrangement.
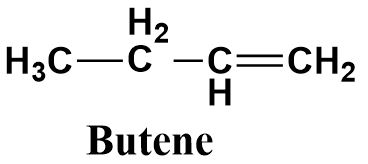
Butene is an unsaturated compound containing a double bond (as suggested by its suffix ‘ene’) between the terminal carbon atom and the adjacent carbon atom. It consists of four carbon atoms as suggested from its prefix ‘but’. Hence it’s a four membered alkene with the following structure:
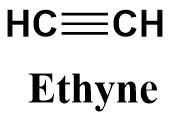
Ethyne belongs to the alkyne family and consists of two carbon atoms (as suggested from the prefix ‘eth’) linked to each other through a triple bond as suggested from the suffix ‘yne’. It’s structure can be written as follows:
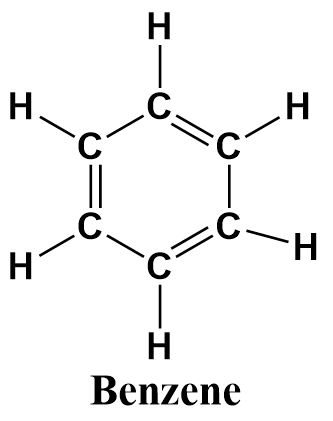
Benzene is a six membered aromatic hydrocarbon containing alternating double bonds that delocalize through the hexagonal ring formed by the six carbon atoms. It’s structure can be written as follows:
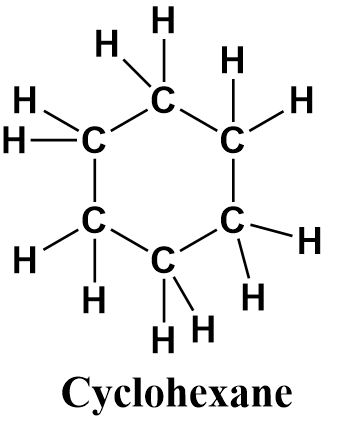
Cyclohexane is a cyclic compound containing six carbon atoms (as suggested from the prefix ‘hex’) bonded to each other through single bonds. It is therefore a saturated and ringed hydrocarbon. It’s structure can be written as follows:
Note:
Though the structures of cyclohexane and benzene look alike as both of them consist of hexagonal rings of six carbon atoms, yet they are not the same. Benzene has aromatic character due to the presence of double bonds and cyclohexane is a non-planar molecule with single bonds only.
Complete step by step answer:
The structural formula of any compound reveals the types of bonds present in it and their arrangement.
Butene is an unsaturated compound containing a double bond (as suggested by its suffix ‘ene’) between the terminal carbon atom and the adjacent carbon atom. It consists of four carbon atoms as suggested from its prefix ‘but’. Hence it’s a four membered alkene with the following structure:

Ethyne belongs to the alkyne family and consists of two carbon atoms (as suggested from the prefix ‘eth’) linked to each other through a triple bond as suggested from the suffix ‘yne’. It’s structure can be written as follows:

Benzene is a six membered aromatic hydrocarbon containing alternating double bonds that delocalize through the hexagonal ring formed by the six carbon atoms. It’s structure can be written as follows:

Cyclohexane is a cyclic compound containing six carbon atoms (as suggested from the prefix ‘hex’) bonded to each other through single bonds. It is therefore a saturated and ringed hydrocarbon. It’s structure can be written as follows:

Note:
Though the structures of cyclohexane and benzene look alike as both of them consist of hexagonal rings of six carbon atoms, yet they are not the same. Benzene has aromatic character due to the presence of double bonds and cyclohexane is a non-planar molecule with single bonds only.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




