
Write the structural formula for the IUPAC name: Butanone.
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: The important point one should take care about while writing the structural formula of any compound is the breaking of its IUPAC name to decipher its meaning. Ketone is the functional group in Butanone and has \[\left( { - C = O} \right)\] group in the structure.
Complete step by step answer:
Structural formula of a compound is used to identify the location of chemical bonds between the atoms of a molecule. It consists of symbols for the atoms connected by short lines. These lines represent the chemical bonds. They can be of two types- line structured and condensed structural formula.
According to IUPAC nomenclature, if organic compounds contain one principal functional group then the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having the principal functional group is selected. In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific substituents in the molecules which are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
The word root for the given compound is butane. Ketone functional group is attached at the second position of butane and therefore, the numbering starts from the carbon of the ketone functional group. The suffix of the name shows the type of functional group present on the parent chain with higher priority i.e. ketone here denoted by ‘one’ in suffix. We can also name it as butan-2-one.
Hence, the structure of the following IUPAC name butanone can be:
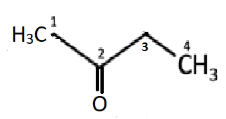
From its structure shown above, we get its condensed structural formula as \[C{H_3}C(O)C{H_2}C{H_3}\] or \[{C_4}{H_8}O\]. Its line structural formula can be written as
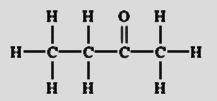
Note:
It is also known as ethyl methyl ketone. The general formula of ketone Is \[{C_n}{H_{2n}}O\] where keto group has two alkyl groups attached to it each on either side and oxygen is connected to the carbon atom with two lines in between that represent a double bond.
Complete step by step answer:
Structural formula of a compound is used to identify the location of chemical bonds between the atoms of a molecule. It consists of symbols for the atoms connected by short lines. These lines represent the chemical bonds. They can be of two types- line structured and condensed structural formula.
According to IUPAC nomenclature, if organic compounds contain one principal functional group then the longest continuous chain of carbon atoms having the principal functional group is selected. In organic chemistry, functional groups are specific substituents in the molecules which are responsible for the characteristic chemical reactions of those molecules.
The word root for the given compound is butane. Ketone functional group is attached at the second position of butane and therefore, the numbering starts from the carbon of the ketone functional group. The suffix of the name shows the type of functional group present on the parent chain with higher priority i.e. ketone here denoted by ‘one’ in suffix. We can also name it as butan-2-one.
Hence, the structure of the following IUPAC name butanone can be:

From its structure shown above, we get its condensed structural formula as \[C{H_3}C(O)C{H_2}C{H_3}\] or \[{C_4}{H_8}O\]. Its line structural formula can be written as

Note:
It is also known as ethyl methyl ketone. The general formula of ketone Is \[{C_n}{H_{2n}}O\] where keto group has two alkyl groups attached to it each on either side and oxygen is connected to the carbon atom with two lines in between that represent a double bond.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

What organs are located on the left side of your body class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of nephron and explain its structur class 11 biology CBSE

How do I convert ms to kmh Give an example class 11 physics CBSE




