
Write the structural and IUPAC name of acetal.
Answer
590.7k+ views
Hint: In chemical nomenclature the IUPAC nomenclature of organic chemistry is the method of naming compounds as recommended by the International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry IUPAC. Ideally, every possible organic compound should have a name from which structural formula can be created.
Complete step by step answer:
Rules of IUPAC nomenclature:
A. Identify the longest carbon chain. This chain is called the parent chain.
B. Identify all of the substituents ( groups appending from the parent chain )
C. Number of carbons of the parent chain from the end that gives the substituents the lower numbers. When comparing a series of numbers, the series that is the lowest is the one which contains the lowest numbers at the occasion of first difference. If two or more sides chain the lowest number to the one which will come first in name.
D. If the same substance occurs more than once, the location of each point on which the substituent occurs is given. In addition, the number of times the substituent group occurs is indicated by a prefix ( di, tri, tetra, etc.)
E. If there are two or more different substituents, they are listed in alphabetical order as iso as in isopropyl or isobutyl. The prefixes sec-or tert-are not used in determining alphabetical order except when compared with each other.
F. If chain of equal length are competing for selection as the parent chain then the choice goes in series to:
(a). The chain which has the greater number of side chains.
(b). The chain whose substituents has the lowest numbers.
(c). The chain has the greatest number of carbon atoms in the smaller side of the chain .
(d). The chain has least branched size chains.
G. A cyclic (ring) hydrocarbon is designated by the prefix cyclo which appears directly in front of the base name.
Structure of Acetal $\left( {{C_6}{H_{14}}{O_2}} \right)$
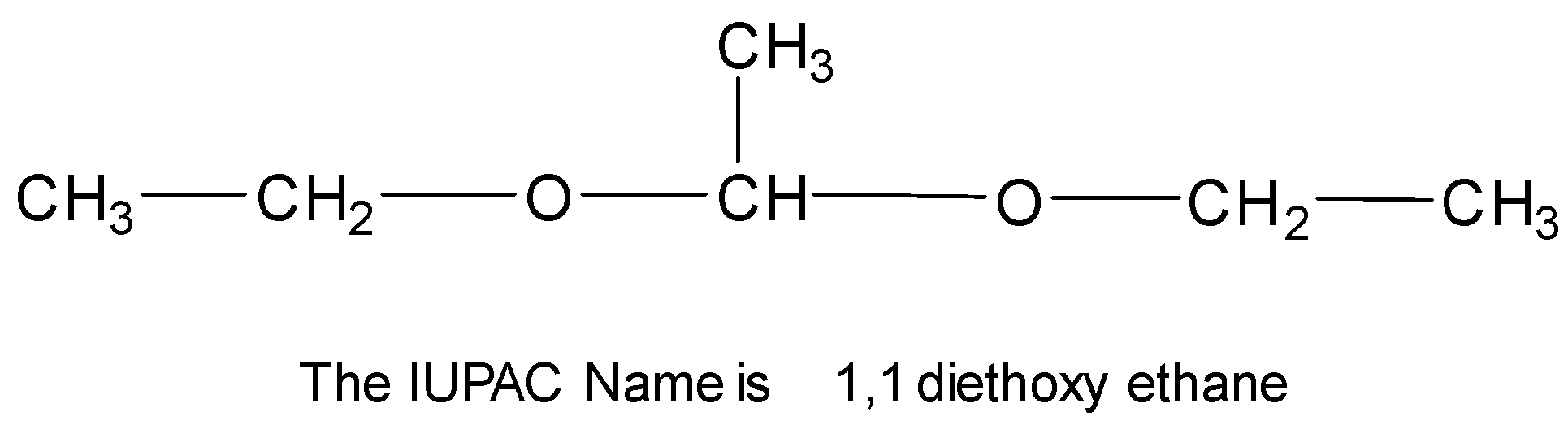
Note:
The need for the International Standard for chemistry was first addressed in $1860$ by a committee headed by German Scientist Friedrich August Kekule Von Stradonitz. This was the first international conference for an international naming system for organic compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
Rules of IUPAC nomenclature:
A. Identify the longest carbon chain. This chain is called the parent chain.
B. Identify all of the substituents ( groups appending from the parent chain )
C. Number of carbons of the parent chain from the end that gives the substituents the lower numbers. When comparing a series of numbers, the series that is the lowest is the one which contains the lowest numbers at the occasion of first difference. If two or more sides chain the lowest number to the one which will come first in name.
D. If the same substance occurs more than once, the location of each point on which the substituent occurs is given. In addition, the number of times the substituent group occurs is indicated by a prefix ( di, tri, tetra, etc.)
E. If there are two or more different substituents, they are listed in alphabetical order as iso as in isopropyl or isobutyl. The prefixes sec-or tert-are not used in determining alphabetical order except when compared with each other.
F. If chain of equal length are competing for selection as the parent chain then the choice goes in series to:
(a). The chain which has the greater number of side chains.
(b). The chain whose substituents has the lowest numbers.
(c). The chain has the greatest number of carbon atoms in the smaller side of the chain .
(d). The chain has least branched size chains.
G. A cyclic (ring) hydrocarbon is designated by the prefix cyclo which appears directly in front of the base name.
Structure of Acetal $\left( {{C_6}{H_{14}}{O_2}} \right)$

Note:
The need for the International Standard for chemistry was first addressed in $1860$ by a committee headed by German Scientist Friedrich August Kekule Von Stradonitz. This was the first international conference for an international naming system for organic compounds.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

Actinoid contraction is more than lanthanoid contraction class 11 chemistry CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction

State the laws of reflection of light




