
How do you write the standard form of the equation given $\left( 2,5 \right)$ and slope undefined? ]
Answer
561.3k+ views
Hint: We recall the slope-intercept equation of line that is $y=mx+c$ and also recall for what values of $m$we get line parallel to $y-$axis. . We recall that the equation with undefined slope is given by$x=k,k\in R$. We find what is the value of $k$ with the given point$\left( 2,5 \right)$.
Complete step by step answer:
We know from the Cartesian coordinate system that every linear equation can be represented as a line. If the line is inclined with positive $x-$axis at an angle $\theta $ then its slope is given by $m=\tan \theta $ and of it cuts $y-$axis at a distance $c$ from the origin the intercept is given by $c$. The slope-intercept form of equation is given by
\[y=mx+c\]
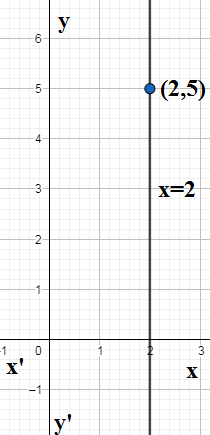
The slope $m$ here means rise over run which means to what extent the line raised itself above the positive $x-$axis with respect to the extension in the $x-$axis. We know that if the slope is undefined which means $m=\infty $ we get a line perpendicular to $x-$axis which means parallel to $y-$axis. The equation of the $y-$axis is $x=0$ and all the perpendicular lines it is given by $x=k,k\in R$.
So the equation of the required line will be in the form $x=k$ since we are given the slope of the lien undefined. We are also given the line passes through$\left( 2,5 \right)$. Since the line is parallel to the $y-$axis, its distance from $x=k$ will remain constant. So the $x-$coordinate of all the points on the line $x=k$ will remain constant. Since $\left( 2,5 \right)$ is appoint on the line whose $x-$ coordinate is 2, the equation of the given line is
\[x=2\]
Note:
We note that if the slope is $m > 0$ positive then we get a line increasing from left to right. If the slope is negative that is $m < 0$ we get a line decreasing from left to right. If $m=0$ we get a line parallel to the $x-$axis . The $x-$coordinate is the distance of the point from the $y-$axis and the $y-$coordinate is the distance of the point from the $x-$axis.
Complete step by step answer:
We know from the Cartesian coordinate system that every linear equation can be represented as a line. If the line is inclined with positive $x-$axis at an angle $\theta $ then its slope is given by $m=\tan \theta $ and of it cuts $y-$axis at a distance $c$ from the origin the intercept is given by $c$. The slope-intercept form of equation is given by
\[y=mx+c\]
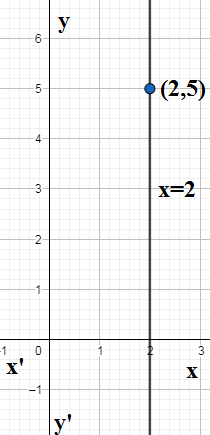
The slope $m$ here means rise over run which means to what extent the line raised itself above the positive $x-$axis with respect to the extension in the $x-$axis. We know that if the slope is undefined which means $m=\infty $ we get a line perpendicular to $x-$axis which means parallel to $y-$axis. The equation of the $y-$axis is $x=0$ and all the perpendicular lines it is given by $x=k,k\in R$.
So the equation of the required line will be in the form $x=k$ since we are given the slope of the lien undefined. We are also given the line passes through$\left( 2,5 \right)$. Since the line is parallel to the $y-$axis, its distance from $x=k$ will remain constant. So the $x-$coordinate of all the points on the line $x=k$ will remain constant. Since $\left( 2,5 \right)$ is appoint on the line whose $x-$ coordinate is 2, the equation of the given line is
\[x=2\]
Note:
We note that if the slope is $m > 0$ positive then we get a line increasing from left to right. If the slope is negative that is $m < 0$ we get a line decreasing from left to right. If $m=0$ we get a line parallel to the $x-$axis . The $x-$coordinate is the distance of the point from the $y-$axis and the $y-$coordinate is the distance of the point from the $x-$axis.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




