
Write the principle behind the froth floatation. What is the role of collectors in this process?
Answer
586.5k+ views
Hint: Try to recall that froth flotation is a method which is used for the concentration of sulphide ores with the help of froth stabilisers and collectors. It is based on the principle of difference in wetting properties of ore and gangue particles with oil and water. Now, by using this you can easily answer the given question.
Complete step by step answer:
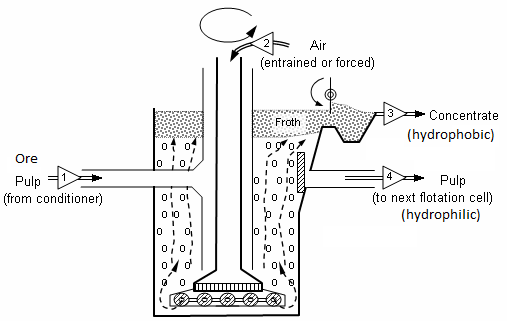
- It is known to you that froth floatation is a metallurgical process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. It is based on the principle of difference in wetting properties of the ore and gangue particles with water.
- It is used for the extraction of those metals in which the ore particles are preferentially wetted by oil and gangue particles by water.
- This method has been used for removing gangue from sulphide ores. Example: Galena ($PbS$), zinc blende ($ZnS$), etc.
- In this method, a suspension of powdered ore is made with water. To this suspension small quantities of collectors and froth stabilizers are added.
- The role of collectors (e.g. pine oil, eucalyptus, fatty acids, xanthates, etc.) is to enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles and froth stabilisers (e.g. cresols, aniline) help in stabilization of the froth.
Note: Note that froth floatation process is also used for the separation of two sulphide ores by adjusting proportion of oil to water or by using ‘depressants’. Also, you should remember that sodium cyanide is used as a depressant in the separation of zinc sulphide ore ($ZnS$) and lead sulphide ore ($PbS$).
Complete step by step answer:
- It is known to you that froth floatation is a metallurgical process for selectively separating hydrophobic materials from hydrophilic. It is based on the principle of difference in wetting properties of the ore and gangue particles with water.
- It is used for the extraction of those metals in which the ore particles are preferentially wetted by oil and gangue particles by water.
- This method has been used for removing gangue from sulphide ores. Example: Galena ($PbS$), zinc blende ($ZnS$), etc.
- In this method, a suspension of powdered ore is made with water. To this suspension small quantities of collectors and froth stabilizers are added.
- The role of collectors (e.g. pine oil, eucalyptus, fatty acids, xanthates, etc.) is to enhance non-wettability of the mineral particles and froth stabilisers (e.g. cresols, aniline) help in stabilization of the froth.

Note: Note that froth floatation process is also used for the separation of two sulphide ores by adjusting proportion of oil to water or by using ‘depressants’. Also, you should remember that sodium cyanide is used as a depressant in the separation of zinc sulphide ore ($ZnS$) and lead sulphide ore ($PbS$).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




