
How do you write the polar equation $r = 6$ in rectangular form?
Answer
556.5k+ views
Hint: In order to express the polar form into rectangular form, we need to express the value in terms of $x$ and $y$. As we know that ${r^2} = {x^2} + {y^2}$, we simply substitute the value of ${r^2}$, in the given equation to get our required answer.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this question, we are asked to express the given polar form into rectangular form.
As we know that in a right-angled triangle, according to Pythagoras theorem:
${\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}{\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}$
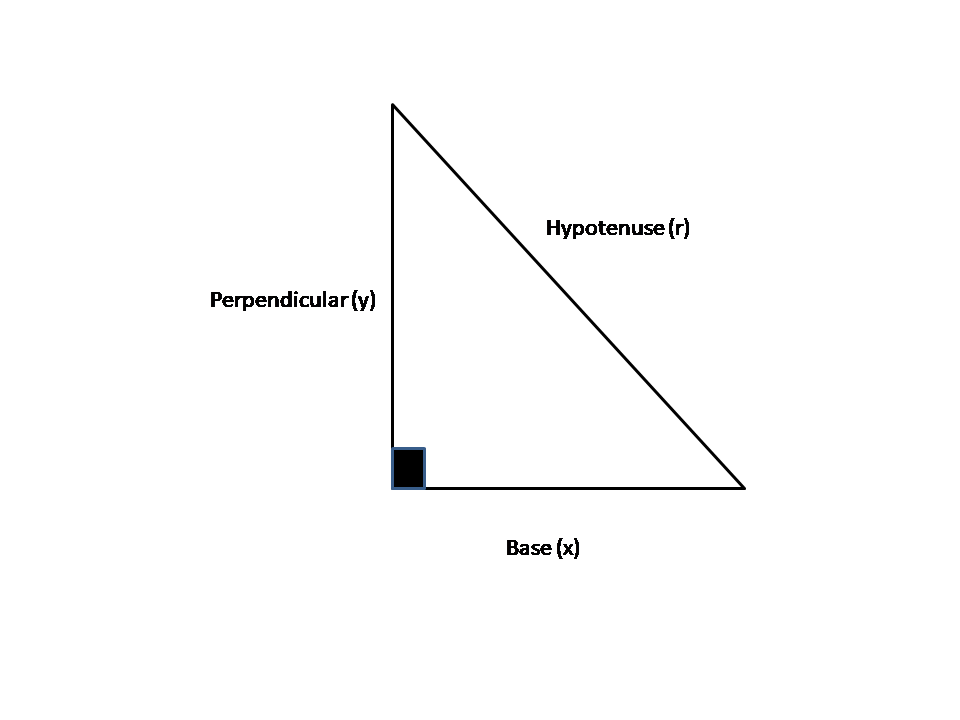
That is, ${r^2} = {x^2} + {y^2}$
In polar form, we express the values in terms of $r$ and $\theta $ , while in rectangular form, we express the values in terms of $x$ and $y$
In the given we have: $r = 6$
On taking the square value on both sides, we get:
Therefore, ${r^2} = {6^2} = 36$
Rectangular form is given as: ${x^2} + {y^2} = r$
Therefore,${x^2} + {y^2} = 36$
Thus we have our required answer.
Note: Polar form of a complex number can also be defined as expressing that particular number with both its magnitude and direction. For example, when we say “3000miles, northwest” – we are saying both the distance and the direction. The distance is the magnitude and the direction is the angle. The angle is denoted by the symbol ‘$\angle $’. These values are also known as vector values.
Rectangular form is when we express the said vector values in terms of its coordinates. The coordinates are expressed in terms of x-coordinate and y-coordinates. That is, the angled vector can also be taken to be the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle, and expressed with its help along with the base and the perpendicular side.
Complete Step by Step Solution:
In this question, we are asked to express the given polar form into rectangular form.
As we know that in a right-angled triangle, according to Pythagoras theorem:
${\left( {{\text{hypotenuse}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ = }}{\left( {{\text{base}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}{\text{ + }}{\left( {{\text{perpendicular}}} \right)^{\text{2}}}$

That is, ${r^2} = {x^2} + {y^2}$
In polar form, we express the values in terms of $r$ and $\theta $ , while in rectangular form, we express the values in terms of $x$ and $y$
In the given we have: $r = 6$
On taking the square value on both sides, we get:
Therefore, ${r^2} = {6^2} = 36$
Rectangular form is given as: ${x^2} + {y^2} = r$
Therefore,${x^2} + {y^2} = 36$
Thus we have our required answer.
Note: Polar form of a complex number can also be defined as expressing that particular number with both its magnitude and direction. For example, when we say “3000miles, northwest” – we are saying both the distance and the direction. The distance is the magnitude and the direction is the angle. The angle is denoted by the symbol ‘$\angle $’. These values are also known as vector values.
Rectangular form is when we express the said vector values in terms of its coordinates. The coordinates are expressed in terms of x-coordinate and y-coordinates. That is, the angled vector can also be taken to be the hypotenuse of a right angled triangle, and expressed with its help along with the base and the perpendicular side.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




