
Write the formula for finding volume of a frustum of a cone.
Answer
617.1k+ views
Hint: Find the frustum of a cone’s shape. From that you can observe the shape’s volume. So, subtracting the volume of the small cone from the volume of the total cone we can get the volume of frustum of the cone. Use normal geometry, find the relation between the angles in the cone. From that relate the volumes of both the cones. From that relation try to find differences between them. From the shape of frustum, you can say that the difference between volumes is nothing but volume of frustum.
Complete step-by-step answer:
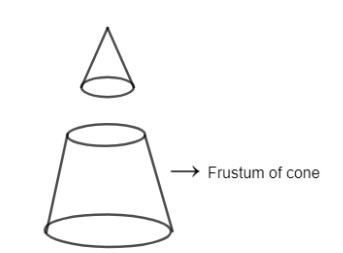
When a solid is cut in such a manner that the base of the solid and the plane cutting the solid are parallel to each other, part of the solid which remains between the parallel cutting planes is known as frustum.
Frustum of cone is shown below.
Volume of frustum
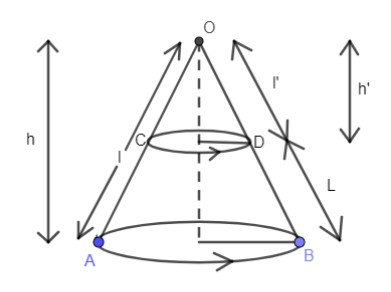
Let the large cone which has a height equal to h units, slant height as l units and radius as r units be named as cone 1 and smaller right cone be names as cone 2, whose height is given as h’ units, radius as r’ units, slant height is given as l’ units.
The height of Frustum is H and its slant height is L.
The volume of right circular cone 1 $=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Volume of right circular cone 2 $=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi r{{'}^{2}}h'$
Volume of frustum of cone is given by subtracting total volume of cone and small right circular cone.
i.e Volume of cone 1-Volume of cone 2
Volume of frustum $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{r}^{2}}h-r{{'}^{2}}h' \right)$
From figure $\Delta OO'D$ , $\Delta OPB$ are similar from AA criterion.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{h'}{h}=\dfrac{r'}{r}$ . By substituting this into volume equation, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{r}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{h'r}{r'} \right)-r{{'}^{2}}h' \right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi h'\left( \dfrac{{{r}^{3}}-r{{'}^{3}}}{r'} \right)$
We know $h=H+h'$
Substituting this, we get:
$\dfrac{h'}{H+h'}=\dfrac{r'}{r}$
$\dfrac{h'}{H}=\dfrac{r'}{r-r'}$
$h'=H\left( \dfrac{r'}{r-r'} \right)$
Substituting the value of h’ in volume equation, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi H\left( \dfrac{r'}{r-r'} \right)\left( \dfrac{{{r}^{3}}-r{{'}^{3}}}{r'} \right)$
By cancelling the common terms in the above equation, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi H\left( \dfrac{{{r}^{3}}-r{{'}^{3}}}{r-r'} \right)$
By using general algebraic identity:
\[{{a}^{3}}-{{b}^{3}}=\left( a-b \right)\left( {{a}^{2}}+ab+{{b}^{2}} \right)\]
By substituting above equation, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi H\left( \dfrac{\left( r-r' \right)\left( {{r}^{2}}+r'r+r{{'}^{2}} \right)}{r-r'} \right)$
By cancelling common terms, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi H\left( {{r}^{2}}+r'r+r{{'}^{2}} \right)$
This gives the required volume of frustum of cone.
Note: Be careful in definition of frustum of cone, it is the part below not the cone part above. Be careful while getting relation between the H, h’ as this turns the volume simpler. If you miss the $'-'$ sign $r-r'$ will not get canceled and the answer may look very large. As here we don’t know the final answer each step must be calculated carefully. While finding the volume of a smaller cone take care of height and radius correspondingly.
Complete step-by-step answer:
When a solid is cut in such a manner that the base of the solid and the plane cutting the solid are parallel to each other, part of the solid which remains between the parallel cutting planes is known as frustum.
Frustum of cone is shown below.

Volume of frustum

Let the large cone which has a height equal to h units, slant height as l units and radius as r units be named as cone 1 and smaller right cone be names as cone 2, whose height is given as h’ units, radius as r’ units, slant height is given as l’ units.
The height of Frustum is H and its slant height is L.
The volume of right circular cone 1 $=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi {{r}^{2}}h$
Volume of right circular cone 2 $=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi r{{'}^{2}}h'$
Volume of frustum of cone is given by subtracting total volume of cone and small right circular cone.
i.e Volume of cone 1-Volume of cone 2
Volume of frustum $\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{r}^{2}}h-r{{'}^{2}}h' \right)$
From figure $\Delta OO'D$ , $\Delta OPB$ are similar from AA criterion.
$\Rightarrow \dfrac{h'}{h}=\dfrac{r'}{r}$ . By substituting this into volume equation, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi \left( {{r}^{2}}\left( \dfrac{h'r}{r'} \right)-r{{'}^{2}}h' \right)=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi h'\left( \dfrac{{{r}^{3}}-r{{'}^{3}}}{r'} \right)$
We know $h=H+h'$
Substituting this, we get:
$\dfrac{h'}{H+h'}=\dfrac{r'}{r}$
$\dfrac{h'}{H}=\dfrac{r'}{r-r'}$
$h'=H\left( \dfrac{r'}{r-r'} \right)$
Substituting the value of h’ in volume equation, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi H\left( \dfrac{r'}{r-r'} \right)\left( \dfrac{{{r}^{3}}-r{{'}^{3}}}{r'} \right)$
By cancelling the common terms in the above equation, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi H\left( \dfrac{{{r}^{3}}-r{{'}^{3}}}{r-r'} \right)$
By using general algebraic identity:
\[{{a}^{3}}-{{b}^{3}}=\left( a-b \right)\left( {{a}^{2}}+ab+{{b}^{2}} \right)\]
By substituting above equation, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi H\left( \dfrac{\left( r-r' \right)\left( {{r}^{2}}+r'r+r{{'}^{2}} \right)}{r-r'} \right)$
By cancelling common terms, we get:
$V=\dfrac{1}{3}\pi H\left( {{r}^{2}}+r'r+r{{'}^{2}} \right)$
This gives the required volume of frustum of cone.
Note: Be careful in definition of frustum of cone, it is the part below not the cone part above. Be careful while getting relation between the H, h’ as this turns the volume simpler. If you miss the $'-'$ sign $r-r'$ will not get canceled and the answer may look very large. As here we don’t know the final answer each step must be calculated carefully. While finding the volume of a smaller cone take care of height and radius correspondingly.
Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




