
Write the following in decimal form and say what kind of decimal expansion each has:
(i) $\dfrac{{36}}{{100}}$ (ii) $\dfrac{1}{{11}}$ (iii) $4\dfrac{1}{8}$ (iv) $\dfrac{3}{{13}}$ (v) $\dfrac{2}{{11}}$ (vi) $\dfrac{{329}}{{400}}$
Answer
596.7k+ views
Hint: We will start solving this question by dividing the numbers given. After doing division we will check whether their remainder is zero or not. With the help of their remainder, we will decide what is the type of decimal expansion.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, when we do a division, we get a quotient and a remainder. According to number systems, if we perform a division and the remainder becomes zero, then that type of decimal expansion is called terminating.
If the remainder after division never becomes zero, then it is called non-terminating decimal expansion. It is of types. If the remainder repeats after a certain stage forcing the decimal expansion to go on forever, then it is called recurring non-terminating, otherwise it is called non-terminating expansion when there is no repetition of numbers.
Now, we will start dividing the given number. First, we will divide $\dfrac{{36}}{{100}}$. On division, we get

Here, as the remainder becomes zero, so this decimal expansion is terminating.
Now, we divide $\dfrac{1}{{11}}$. On division, we get
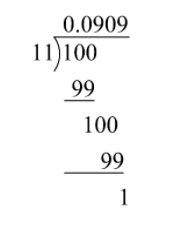
As, remainder is not zero. Also, $\dfrac{1}{{11}} = 0.0909$ which can be written as $\dfrac{1}{{11}} = 0.\overline {09} $ is repeating. So, this decimal expansion is recurring non-terminating.
Similarly dividing all the given numbers, we get
$4\dfrac{1}{8} = \dfrac{{33}}{8}$, On division, we get

$4\dfrac{1}{8} = 4.125$ terminating decimal expansion
On dividing $\dfrac{3}{{13}}$, we get

$\dfrac{3}{{13}} = 0.\overline {230769} $ recurring non-terminating decimal expansion
On dividing $\dfrac{2}{{11}}$, we get
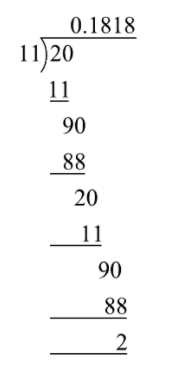
$\dfrac{2}{{11}} = 0.\overline {18} $ recurring non-terminating decimal expansion
On dividing $\dfrac{{329}}{{400}}$, we get
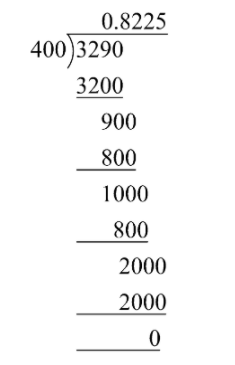
$\dfrac{{329}}{{400}} = 0.8225$ terminating decimal expansion.
Note: Whenever we come up with such types of questions, we will divide the numbers given. If the remainder comes zero, then it is a terminating decimal expansion and if the remainder is not zero, then it is a non-terminating decimal expansion. To find whether the expansion is recurring or not, we have to divide the number till we get the same numbers. If we get the same number, then it is a recurring non-terminating expansion otherwise non-recurring or known as non-terminating decimal expansion.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Now, when we do a division, we get a quotient and a remainder. According to number systems, if we perform a division and the remainder becomes zero, then that type of decimal expansion is called terminating.
If the remainder after division never becomes zero, then it is called non-terminating decimal expansion. It is of types. If the remainder repeats after a certain stage forcing the decimal expansion to go on forever, then it is called recurring non-terminating, otherwise it is called non-terminating expansion when there is no repetition of numbers.
Now, we will start dividing the given number. First, we will divide $\dfrac{{36}}{{100}}$. On division, we get

Here, as the remainder becomes zero, so this decimal expansion is terminating.
Now, we divide $\dfrac{1}{{11}}$. On division, we get
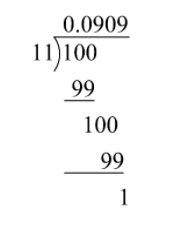
As, remainder is not zero. Also, $\dfrac{1}{{11}} = 0.0909$ which can be written as $\dfrac{1}{{11}} = 0.\overline {09} $ is repeating. So, this decimal expansion is recurring non-terminating.
Similarly dividing all the given numbers, we get
$4\dfrac{1}{8} = \dfrac{{33}}{8}$, On division, we get

$4\dfrac{1}{8} = 4.125$ terminating decimal expansion
On dividing $\dfrac{3}{{13}}$, we get

$\dfrac{3}{{13}} = 0.\overline {230769} $ recurring non-terminating decimal expansion
On dividing $\dfrac{2}{{11}}$, we get
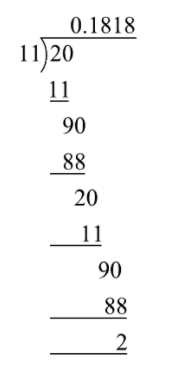
$\dfrac{2}{{11}} = 0.\overline {18} $ recurring non-terminating decimal expansion
On dividing $\dfrac{{329}}{{400}}$, we get
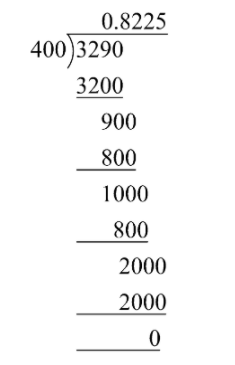
$\dfrac{{329}}{{400}} = 0.8225$ terminating decimal expansion.
Note: Whenever we come up with such types of questions, we will divide the numbers given. If the remainder comes zero, then it is a terminating decimal expansion and if the remainder is not zero, then it is a non-terminating decimal expansion. To find whether the expansion is recurring or not, we have to divide the number till we get the same numbers. If we get the same number, then it is a recurring non-terminating expansion otherwise non-recurring or known as non-terminating decimal expansion.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 9 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 9 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 9 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




