
How do you write the expression for the area given the length \[(x+6)\] and width \[(x-3)\]?
Answer
558k+ views
Hint: As we have directly given the length and width, we will assume that the region of which area is to be found is a rectangle of length \[(x+6)\], and width \[(x-3)\]. As we know that the area of a rectangle is \[length\times width\]. We should also know that the expansion of \[\left( a+b \right)\left( c+d \right)\] is \[ac+ad+bc+bd\].
Complete step by step answer:
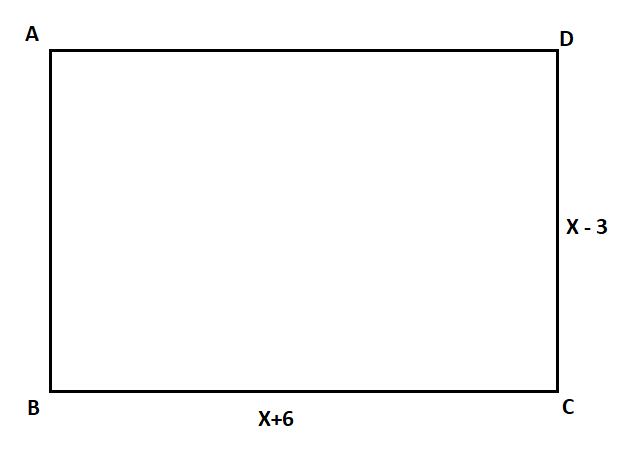
The rectangle given in the above figure has a length of \[(x+6)\], and width of \[(x-3)\]. We need to find the area of the above rectangle. We know that the area of the rectangle is the product of length and its width,
\[\Rightarrow length\times width\]
Here we are given that the length is \[(x+6)\], and width is \[(x-3)\]. Substituting the values in the above formula, we get
Area of rectangle \[=length\times width\]
\[\Rightarrow \left( x+6 \right)\times \left( x-3 \right)\]
Here the above area expression is of the form \[\left( a+b \right)\left( c+d \right)\], here we have \[a=c=x,b=6\And d=-3\]. We know that the expansion of \[\left( a+b \right)\left( c+d \right)\] is \[ac+ad+bc+bd\]. Substituting the values in this expansion, we get
\[\Rightarrow x\times x+x(-3)+6\times x+6\times (-3)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-3x+6x-18\]
Simplifying the above expression, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+3x-18\]
We should note that \[\left( x+6 \right)\] and \[\left( x-3 \right)\], are dimensions of the given rectangle. Dimensions of any region are always positive; hence we should apply this condition on these also.
For the length of the rectangle, as the length is \[\left( x+6 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow x+6>0\]
subtracting 6 from both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow x+6-6>0-6\]
\[\Rightarrow x>-6\]
For the width of the rectangle, as the width is \[\left( x-3 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow x-3>0\]
Adding 3 to both sides, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x-3+3>0+3 \\
& \Rightarrow x>3 \\
\end{align}\]
We have to conditions on \[x\] first is \[x>-6\], and second is \[x>3\], as we want both to be satisfied we take the intersection of both, by doing this we get \[x>3\] as the common condition for length and width to be positive.
So, the final answer is \[{{x}^{2}}+3x-18\], for \[x\in \left( 3,\infty \right)\].
Note: Here one may think that as the expression for the area is quadratic, so it must have two roots for which the area becomes zero. But, as we already put the conditions on dimensions to be positive, their product in other words the area of the rectangle will also be positive always.
Complete step by step answer:

The rectangle given in the above figure has a length of \[(x+6)\], and width of \[(x-3)\]. We need to find the area of the above rectangle. We know that the area of the rectangle is the product of length and its width,
\[\Rightarrow length\times width\]
Here we are given that the length is \[(x+6)\], and width is \[(x-3)\]. Substituting the values in the above formula, we get
Area of rectangle \[=length\times width\]
\[\Rightarrow \left( x+6 \right)\times \left( x-3 \right)\]
Here the above area expression is of the form \[\left( a+b \right)\left( c+d \right)\], here we have \[a=c=x,b=6\And d=-3\]. We know that the expansion of \[\left( a+b \right)\left( c+d \right)\] is \[ac+ad+bc+bd\]. Substituting the values in this expansion, we get
\[\Rightarrow x\times x+x(-3)+6\times x+6\times (-3)\]
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}-3x+6x-18\]
Simplifying the above expression, we get
\[\Rightarrow {{x}^{2}}+3x-18\]
We should note that \[\left( x+6 \right)\] and \[\left( x-3 \right)\], are dimensions of the given rectangle. Dimensions of any region are always positive; hence we should apply this condition on these also.
For the length of the rectangle, as the length is \[\left( x+6 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow x+6>0\]
subtracting 6 from both sides, we get
\[\Rightarrow x+6-6>0-6\]
\[\Rightarrow x>-6\]
For the width of the rectangle, as the width is \[\left( x-3 \right)\]
\[\Rightarrow x-3>0\]
Adding 3 to both sides, we get
\[\begin{align}
& \Rightarrow x-3+3>0+3 \\
& \Rightarrow x>3 \\
\end{align}\]
We have to conditions on \[x\] first is \[x>-6\], and second is \[x>3\], as we want both to be satisfied we take the intersection of both, by doing this we get \[x>3\] as the common condition for length and width to be positive.
So, the final answer is \[{{x}^{2}}+3x-18\], for \[x\in \left( 3,\infty \right)\].
Note: Here one may think that as the expression for the area is quadratic, so it must have two roots for which the area becomes zero. But, as we already put the conditions on dimensions to be positive, their product in other words the area of the rectangle will also be positive always.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 8 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 8 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Master Class 8 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 8 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 7 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Difference Between Plant Cell and Animal Cell

Fill the blanks with the suitable prepositions 1 The class 9 english CBSE

Who is eligible for RTE class 9 social science CBSE

Which places in India experience sunrise first and class 9 social science CBSE

What is pollution? How many types of pollution? Define it

Name 10 Living and Non living things class 9 biology CBSE




