
How do you write the equation of a circle with the center $\left( {2a,a} \right)$ and touching the y-axis?
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint: First find the radius of the circle by using the horizontal distance from center to y-axis. After that, use the standard equation of the circle with the center $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and radius of length ‘r’, which is given
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
Now put the value of $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and r to the above equation to get the required equation of the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know the standard equation of a circle is given
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)^2} = {r^2}$ ….. (1)
Where $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ is the center of the circle and ‘r’ is the radius of the circle and it is shown with the help of a diagram as,
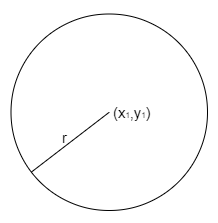
Now, coming to the question, we are given the center of a circle as (2a, a) and touching the y-axis and hence, we need to determine the equation of the circle.
If the circle touches the y-axis then the radius of the circle is equal to the horizontal distance from the y-axis to the center of the circle.
The distance from the y-axis to the center of the circle is the x coordinate of the center of the circle.
So, in this case the radius is 2a.
So, equation (1) is representing the standard equation of a circle, with center $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and radius ‘r’. So, we can put $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ as $\left( {2a,a} \right)$ and r as 2a to the equation (1). So, we get the equation of the circle.
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 2a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - a} \right)^2} = {\left( {2a} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 2a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - a} \right)^2} = 4{a^2}$
Now, we can use the algebraic identity of ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2}$ , which are given
\[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\]
Hence, we can write the above equation as,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 4ax + 4{a^2} + {y^2} - 2ay + {a^2} = 4{a^2}$
Move all terms on the left side,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 4ax + 4{a^2} + {y^2} - 2ay + {a^2} - 4{a^2} = 0$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 4ax - 2ay + {a^2} = 0$
Hence, the equation of the circle with the given criteria is given ${x^2} + {y^2} - 4ax - 2ay + {a^2} = 0$.
Note:
Another approach to solving the question would be that we can use another standard equation of a circle given
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0$
Where $\left( { - g, - f} \right)$ is the center of the circle and $\sqrt {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} $ is the radius of the circle.
So, we can put $\left( { - g, - f} \right)$ as $\left( {2, - 1} \right)$ to get ‘g’ and ‘f’ and equating $\sqrt {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} $ to 4 (radius), we can get the value of ‘c’. So, it can be another approach.
One may prove the standard equation of the circle by the distance formula between two points. It is given
$ \Rightarrow D = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)}^2}} $
Suppose general point on a circle as $\left( {x,y} \right)$ and center as $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and radius as ‘r’ and hence, use the above equation. So, get
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
Now put the value of $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and r to the above equation to get the required equation of the circle.
Complete step-by-step answer:
As we know the standard equation of a circle is given
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)^2} = {r^2}$ ….. (1)
Where $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ is the center of the circle and ‘r’ is the radius of the circle and it is shown with the help of a diagram as,

Now, coming to the question, we are given the center of a circle as (2a, a) and touching the y-axis and hence, we need to determine the equation of the circle.
If the circle touches the y-axis then the radius of the circle is equal to the horizontal distance from the y-axis to the center of the circle.
The distance from the y-axis to the center of the circle is the x coordinate of the center of the circle.
So, in this case the radius is 2a.
So, equation (1) is representing the standard equation of a circle, with center $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and radius ‘r’. So, we can put $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ as $\left( {2a,a} \right)$ and r as 2a to the equation (1). So, we get the equation of the circle.
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 2a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - a} \right)^2} = {\left( {2a} \right)^2}$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - 2a} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - a} \right)^2} = 4{a^2}$
Now, we can use the algebraic identity of ${\left( {a - b} \right)^2}$ , which are given
\[{\left( {a - b} \right)^2} = {a^2} + {b^2} - 2ab\]
Hence, we can write the above equation as,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 4ax + 4{a^2} + {y^2} - 2ay + {a^2} = 4{a^2}$
Move all terms on the left side,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} - 4ax + 4{a^2} + {y^2} - 2ay + {a^2} - 4{a^2} = 0$
Simplify the terms,
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} - 4ax - 2ay + {a^2} = 0$
Hence, the equation of the circle with the given criteria is given ${x^2} + {y^2} - 4ax - 2ay + {a^2} = 0$.
Note:
Another approach to solving the question would be that we can use another standard equation of a circle given
$ \Rightarrow {x^2} + {y^2} + 2gx + 2fy + c = 0$
Where $\left( { - g, - f} \right)$ is the center of the circle and $\sqrt {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} $ is the radius of the circle.
So, we can put $\left( { - g, - f} \right)$ as $\left( {2, - 1} \right)$ to get ‘g’ and ‘f’ and equating $\sqrt {{g^2} + {f^2} - c} $ to 4 (radius), we can get the value of ‘c’. So, it can be another approach.
One may prove the standard equation of the circle by the distance formula between two points. It is given
$ \Rightarrow D = \sqrt {{{\left( {{x_1} - {x_2}} \right)}^2} + {{\left( {{y_1} - {y_2}} \right)}^2}} $
Suppose general point on a circle as $\left( {x,y} \right)$ and center as $\left( {{x_1},{y_1}} \right)$ and radius as ‘r’ and hence, use the above equation. So, get
$ \Rightarrow {\left( {x - {x_1}} \right)^2} + {\left( {y - {y_1}} \right)^2} = {r^2}$
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Class 11 Question and Answer - Your Ultimate Solutions Guide

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

10 examples of friction in our daily life




