
Write the electronic configuration of the Boron.
Answer
597.3k+ views
Hint: Boron belongs to the group no. 13 and it’s atomic no. is 5. So, it has 5 electrons. General valence electronic configuration of group 13 elements is $n{s^2}n{p^1}$. To write the electronic configuration of boron, fill its 5 electrons in the orbitals arranged in order of increasing energies, according to Aufbau Principle.
Complete step by step solution:
An electron in an atom is characterised by 4 quantum numbers, and the principal quantum number $(n)$ defines the main energy level known as the shell. Each shell consists of one or more subshells or sub-levels. Each subshell is assigned by azimuthal quantum no. ($l$) and $l$have values from 0 to $n - 1$ Also, each subshell has orbitals equal to \[2l + 1\] . The distribution of electrons into orbitals of an atom is called its electronic configuration.
Boron has atomic no. 5 and it is represented by symbol the B. It belongs to group 13 of p-block. Group 13 elements outermost or valence electronic configuration is \[\left[ E \right]n{s^2}n{p^1}\], where E is an inert gas configuration).
To find the electronic configuration of boron, fill 5 electrons of boron in orbitals according to Aufbau principle. Consequently, electronic configuration of boron will be :\[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^1}\].
Now, to write the noble gas electronic configuration of boron, we need to find the noble gas that comes before boron in the periodic table and it is helium ( electronic configuration of helium is \[1{s^2}\]).
Therefore, the noble gas electronic configuration of boron is \[\left[ {He} \right]2{s^2}2{p^1}\]. The 2 in $2{s^2}and\,2{p^2}$ denotes the shell no (n) and shell number denotes the period no. to which the element belongs. Thus, boron belongs to period 2 of the periodic table.
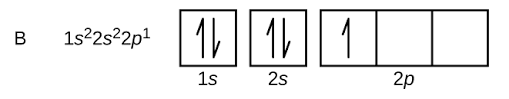
Note: The orbital picture of boron can be represented as :
$s$- orbital can hold up maximum 2 electrons, $p$-orbitals can hold maximum 6 electrons.
Complete step by step solution:
An electron in an atom is characterised by 4 quantum numbers, and the principal quantum number $(n)$ defines the main energy level known as the shell. Each shell consists of one or more subshells or sub-levels. Each subshell is assigned by azimuthal quantum no. ($l$) and $l$have values from 0 to $n - 1$ Also, each subshell has orbitals equal to \[2l + 1\] . The distribution of electrons into orbitals of an atom is called its electronic configuration.
Boron has atomic no. 5 and it is represented by symbol the B. It belongs to group 13 of p-block. Group 13 elements outermost or valence electronic configuration is \[\left[ E \right]n{s^2}n{p^1}\], where E is an inert gas configuration).
To find the electronic configuration of boron, fill 5 electrons of boron in orbitals according to Aufbau principle. Consequently, electronic configuration of boron will be :\[1{s^2}2{s^2}2{p^1}\].
Now, to write the noble gas electronic configuration of boron, we need to find the noble gas that comes before boron in the periodic table and it is helium ( electronic configuration of helium is \[1{s^2}\]).
Therefore, the noble gas electronic configuration of boron is \[\left[ {He} \right]2{s^2}2{p^1}\]. The 2 in $2{s^2}and\,2{p^2}$ denotes the shell no (n) and shell number denotes the period no. to which the element belongs. Thus, boron belongs to period 2 of the periodic table.
Note: The orbital picture of boron can be represented as :
$s$- orbital can hold up maximum 2 electrons, $p$-orbitals can hold maximum 6 electrons.

Recently Updated Pages
Basicity of sulphurous acid and sulphuric acid are

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE

State and prove Bernoullis theorem class 11 physics CBSE

What steps did the French revolutionaries take to create class 11 social science CBSE

The transition element that has lowest enthalpy of class 11 chemistry CBSE

Can anyone list 10 advantages and disadvantages of friction




