
Write the electronic configuration of $M{n^{2 + }}$ and $F{e^{2 + }}$.
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:
We are discussing the electronic configuration of some ions mentioned above and learning how to write it by its rules. Electronic Configurations means it is a standard notation used to describe the electronic description of an atom.
Complete step by step answer:
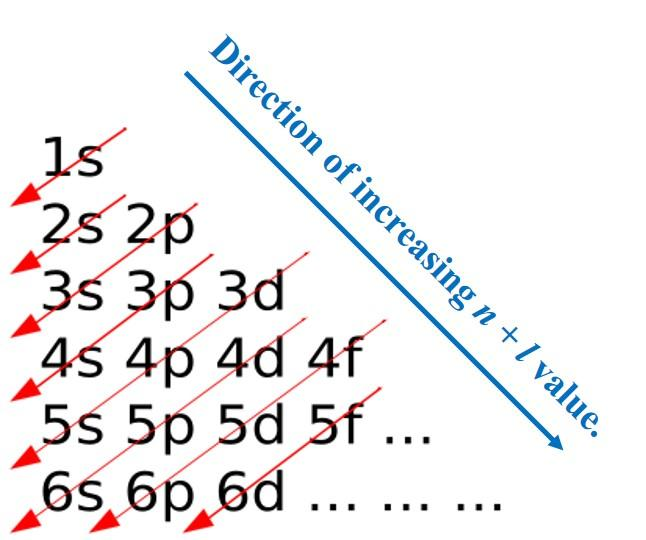
For using Electronic Configuration, Aufbau Principle (Aufbau is a German word for ‘Building-Up) is used which states that electrons occupy orbitals in order of increasing energy. The order of Energy is:
$1s < 2s < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p < 5s < 4d < 5p < 6s < 4f < 5d < 6p < 7s < 5f < 6d < 7p$
Orbital: An orbital is a space where the probability of electrons is the highest.
There are $4$ orbitals (s,p,d,f)
s is the orbital that has a maximum $2$ electrons capacity.
p is the orbital that has a maximum $6$ electrons capacity.
d is the orbital that has a maximum $10$ electrons capacity.
f is the orbital that has a maximum $14$ electrons capacity.
According to the Question,
Firstly, we can write the electronic configuration of $Mn$ first its atomic number is 25.
$1{s^2}\,2{s^2}\,2{p^6}\,3{s^2}\,3{p^6}\,4{s^2}\,3{d^5}$
After losing $2$ electrons, it will become $M{n^{2 + }}$.
Now, we can write the electronic configuration of $M{n^{2 + }}$ ion
$1{s^2}\,2{s^2}\,2{p^6}\,3{s^2}\,3{p^6}\,4{s^0}\,3{d^5}$
The electrons can be liberated from lower energy orbital (s Orbital) due to more energy gap between s orbital and p orbital and secondly, half-filled orbital and full filled orbital have higher energies and are mainly stable. So, from stable orbitals electrons cannot be released.
Now, We can write the electronic configuration of $Fe$ first its atomic number is 26.
$1{s^2}\,2{s^2}\,2{p^6}\,3{s^2}\,3{p^6}\,4{s^2}\,3{d^6}$
After losing $2$ electrons, it will become $F{e^{2 + }}$
$1{s^2}\,2{s^2}\,2{p^6}\,3{s^2}\,3{p^6}\,4{s^0}\,3{d^6}$
The electrons can be liberated from lower energy orbital (s Orbital) due to more energy gap between s orbital and p orbital.
Note: Almost all the elements follow the same trend for writing electronic configuration. Sometimes when two sub-shells differ in the energies, an electron from the lower energy moves to higher energy. The orbitals in which the subshell is exactly half-filled or completely filled are more stable because of the symmetrical distribution of electrons.
We are discussing the electronic configuration of some ions mentioned above and learning how to write it by its rules. Electronic Configurations means it is a standard notation used to describe the electronic description of an atom.
Complete step by step answer:
For using Electronic Configuration, Aufbau Principle (Aufbau is a German word for ‘Building-Up) is used which states that electrons occupy orbitals in order of increasing energy. The order of Energy is:
$1s < 2s < 3s < 3p < 4s < 3d < 4p < 5s < 4d < 5p < 6s < 4f < 5d < 6p < 7s < 5f < 6d < 7p$

Orbital: An orbital is a space where the probability of electrons is the highest.
There are $4$ orbitals (s,p,d,f)
s is the orbital that has a maximum $2$ electrons capacity.
p is the orbital that has a maximum $6$ electrons capacity.
d is the orbital that has a maximum $10$ electrons capacity.
f is the orbital that has a maximum $14$ electrons capacity.
According to the Question,
Firstly, we can write the electronic configuration of $Mn$ first its atomic number is 25.
$1{s^2}\,2{s^2}\,2{p^6}\,3{s^2}\,3{p^6}\,4{s^2}\,3{d^5}$
After losing $2$ electrons, it will become $M{n^{2 + }}$.
Now, we can write the electronic configuration of $M{n^{2 + }}$ ion
$1{s^2}\,2{s^2}\,2{p^6}\,3{s^2}\,3{p^6}\,4{s^0}\,3{d^5}$
The electrons can be liberated from lower energy orbital (s Orbital) due to more energy gap between s orbital and p orbital and secondly, half-filled orbital and full filled orbital have higher energies and are mainly stable. So, from stable orbitals electrons cannot be released.
Now, We can write the electronic configuration of $Fe$ first its atomic number is 26.
$1{s^2}\,2{s^2}\,2{p^6}\,3{s^2}\,3{p^6}\,4{s^2}\,3{d^6}$
After losing $2$ electrons, it will become $F{e^{2 + }}$
$1{s^2}\,2{s^2}\,2{p^6}\,3{s^2}\,3{p^6}\,4{s^0}\,3{d^6}$
The electrons can be liberated from lower energy orbital (s Orbital) due to more energy gap between s orbital and p orbital.
Note: Almost all the elements follow the same trend for writing electronic configuration. Sometimes when two sub-shells differ in the energies, an electron from the lower energy moves to higher energy. The orbitals in which the subshell is exactly half-filled or completely filled are more stable because of the symmetrical distribution of electrons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Accountancy: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




