
Write the common name and IUPAC name of the following.
A.$C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$
B. $C{H_3}COC{H_3}$
C.
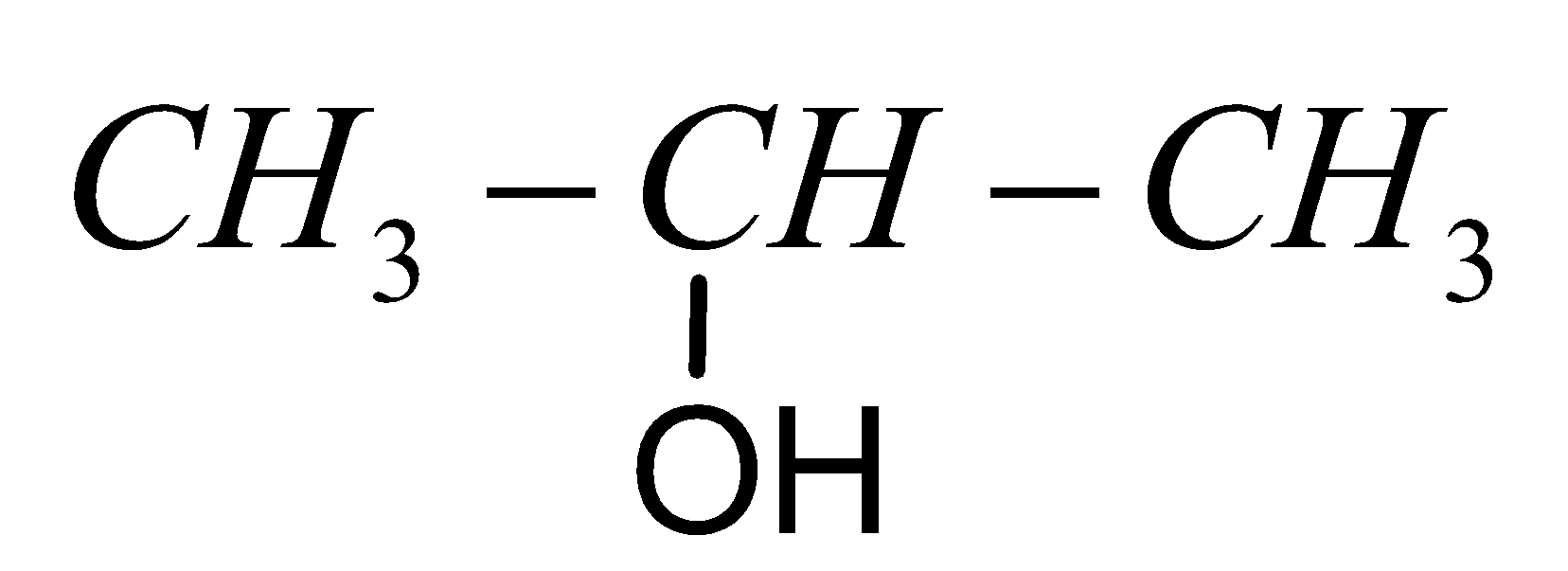
D. $C{H_3}COOH$
E. $HCHO$

Answer
569.4k+ views
Hint: International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry is abbreviated by IUPAC, standardizing nomenclature in chemistry, a set of rules to generate systematic names for chemical compound is one of the best known work for IUPAC. IUPAC is an international federation of National Adhering Organizations. Common names are what we use in our regular everyday life.
As we know that the above given compound contains single bonds and double bonds both in long carbon chains. To name this compound we will use IUPAC naming system, which is a predefined naming system for hydrocarbon compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
For acyclic compounds, the rules of IUPAC system of nomenclature:
First of all we see the number of chains lengths in the given compound. If the number of carbon atoms is one, then the compound named as \[meth - \], for two carbon atoms, the compound is given as the name \[eth - \], and for three, then called as $prop - $, etc.
Hydrocarbon chain type is saturated, unsaturated with one carbon-carbon double bond $\left( {C = C} \right)$ or unsaturated with one carbon-carbon double bond $\left( {C \equiv C} \right)$ are called $ - ane,$ $ - ene$ and $ - yne$ respectively. These are called primary suffixes. For example, methane, ethene and propyne.
Then we see the functional group present in the compound.
Alcohols$\left( { - OH} \right)$: prefix: $hydroxy - $and suffix:$ - ol$. For example:$C{H_3}C{H_2}OH$, name of the compound is ethanol and $C{H_3}OH$, IUPAC name is methan $ol$.
Carboxylic acid $\left( { - COOH} \right)$: prefix: carboxy- and suffix: -oic acid. For example: ethane $dioic$ acid $\left( {COOH - COOH} \right)$.
Ketone $C = O$: suffix: $ - one$. For example: methan $one$,${H_2}C = O$.
Alphabetical order is first considered before the parent hydrocarbon without considering the presence of a functional group.
Carbon atoms contain a functional group itself (e.g., $ - CHO,$$ - COOH,$ etc) are linked to carbon chain, such carbon should be also numbered.
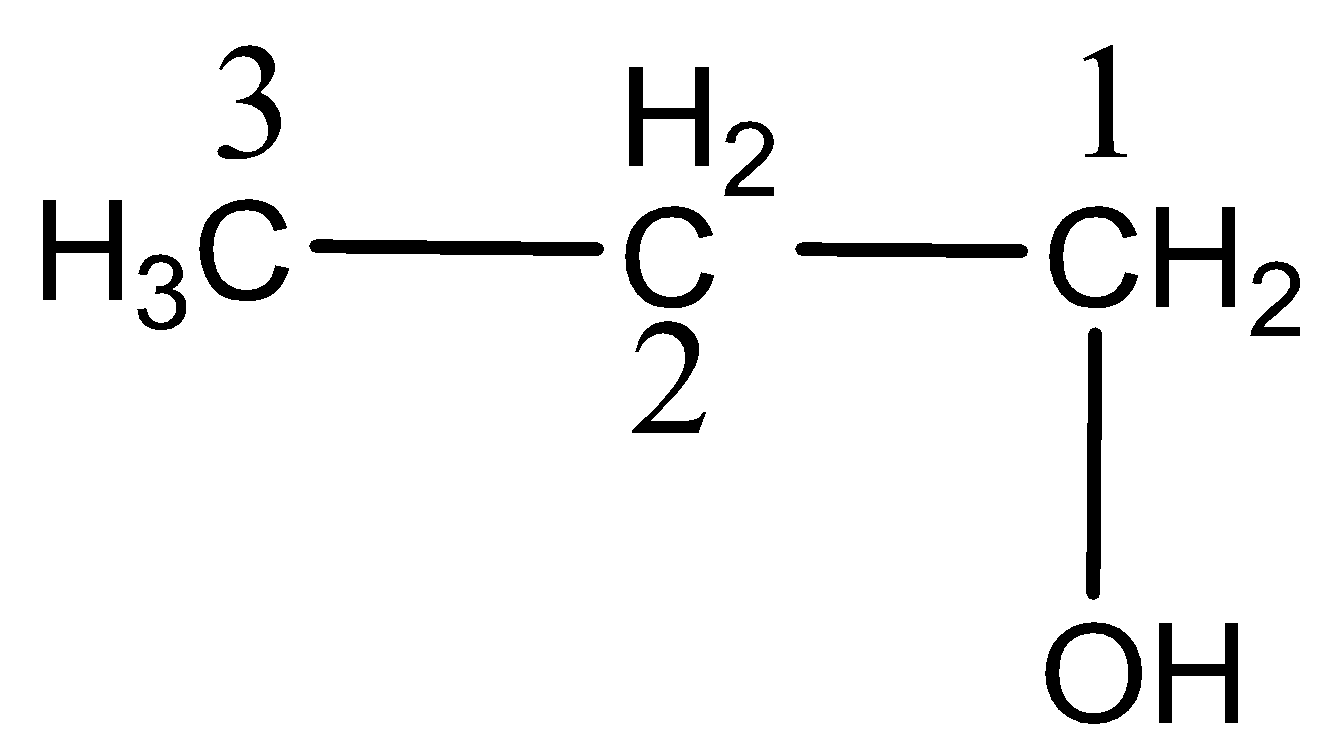
For example, , the name of the compound is \[prop - 1 - ol\].
Now we discuss about the compounds in the option as,
A.$C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$
The given compound $C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$ contains three carbon atoms. For three carbon atoms the IUPAC name for the alkane is propane, because this is a saturated compound. Then we see if any functional group contains in the compound. The functional present in the compound is aldehyde.
Common name of the compound -$propanaldehyde$.
IUPAC name of the compound is $propanal$.
Now we discuss about option (B) as,
B.$C{H_3}COC{H_3}$
The molecular formula shows three carbon atoms present in the compound and then the functional group is ketone and the ketone is present in the second carbon. This is a saturated compound. So,
Common name of the compound is acetone.
IUPAC name of the compound is $prop - 2 - one$.
Let’s we see the option C as,

The given compound contains three carbon atoms. For three carbon atoms the IUPAC name for the alkane is propane, because this is not an unsaturated compound. Then we see if any functional group contains in the compound. The functional present in the compound is alcohol.
Common name of the compound is isopropyl alcohol.
IUPAC name of the compound is $propan - 2 - ol$.
4.$C{H_3}COOH$
The above compound contains two carbon atoms, so the prefix is eth- and the functional group present in the compound is carboxylic acid.
Common name of the compound-acetic acid.
IUPAC name of the compound is ethanoic acid.
5.$HCHO$
The given compound $HCHO$ contains two carbon atoms. For two carbon atoms the IUPAC name for the alkane is ethane, because this is a saturated compound. Then we see if any functional group contains in the compound. The functional present in the compound is aldehyde.
Common name of the compound -Formaldehyde.
IUPAC name of the compound is \[methanal\]
Note: IUPAC gives a unique name to every chemical compound. IUPAC, a non-governmental organization, many global issues involving the chemical sciences are addressed by IUPAC. IUPAC was established in 1919. IUPAC also published books, fields including chemistry, biology and physics. We have to remember for a variety of compounds there are predefined IUPAC nomenclature for the naming system. The process is almost the same of every compound. The variation in the naming can be due to different functional groups present in the chain and also due to presence of higher degree of compounds as a minor branch.
As we know that the above given compound contains single bonds and double bonds both in long carbon chains. To name this compound we will use IUPAC naming system, which is a predefined naming system for hydrocarbon compounds.
Complete step by step answer:
For acyclic compounds, the rules of IUPAC system of nomenclature:
First of all we see the number of chains lengths in the given compound. If the number of carbon atoms is one, then the compound named as \[meth - \], for two carbon atoms, the compound is given as the name \[eth - \], and for three, then called as $prop - $, etc.
Hydrocarbon chain type is saturated, unsaturated with one carbon-carbon double bond $\left( {C = C} \right)$ or unsaturated with one carbon-carbon double bond $\left( {C \equiv C} \right)$ are called $ - ane,$ $ - ene$ and $ - yne$ respectively. These are called primary suffixes. For example, methane, ethene and propyne.
Then we see the functional group present in the compound.
Alcohols$\left( { - OH} \right)$: prefix: $hydroxy - $and suffix:$ - ol$. For example:$C{H_3}C{H_2}OH$, name of the compound is ethanol and $C{H_3}OH$, IUPAC name is methan $ol$.
Carboxylic acid $\left( { - COOH} \right)$: prefix: carboxy- and suffix: -oic acid. For example: ethane $dioic$ acid $\left( {COOH - COOH} \right)$.
Ketone $C = O$: suffix: $ - one$. For example: methan $one$,${H_2}C = O$.
Alphabetical order is first considered before the parent hydrocarbon without considering the presence of a functional group.
Carbon atoms contain a functional group itself (e.g., $ - CHO,$$ - COOH,$ etc) are linked to carbon chain, such carbon should be also numbered.

For example, , the name of the compound is \[prop - 1 - ol\].
Now we discuss about the compounds in the option as,
A.$C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$
The given compound $C{H_3}C{H_2}CHO$ contains three carbon atoms. For three carbon atoms the IUPAC name for the alkane is propane, because this is a saturated compound. Then we see if any functional group contains in the compound. The functional present in the compound is aldehyde.
Common name of the compound -$propanaldehyde$.
IUPAC name of the compound is $propanal$.
Now we discuss about option (B) as,
B.$C{H_3}COC{H_3}$
The molecular formula shows three carbon atoms present in the compound and then the functional group is ketone and the ketone is present in the second carbon. This is a saturated compound. So,
Common name of the compound is acetone.
IUPAC name of the compound is $prop - 2 - one$.
Let’s we see the option C as,

The given compound contains three carbon atoms. For three carbon atoms the IUPAC name for the alkane is propane, because this is not an unsaturated compound. Then we see if any functional group contains in the compound. The functional present in the compound is alcohol.
Common name of the compound is isopropyl alcohol.
IUPAC name of the compound is $propan - 2 - ol$.
4.$C{H_3}COOH$
The above compound contains two carbon atoms, so the prefix is eth- and the functional group present in the compound is carboxylic acid.
Common name of the compound-acetic acid.
IUPAC name of the compound is ethanoic acid.
5.$HCHO$
The given compound $HCHO$ contains two carbon atoms. For two carbon atoms the IUPAC name for the alkane is ethane, because this is a saturated compound. Then we see if any functional group contains in the compound. The functional present in the compound is aldehyde.
Common name of the compound -Formaldehyde.
IUPAC name of the compound is \[methanal\]
Note: IUPAC gives a unique name to every chemical compound. IUPAC, a non-governmental organization, many global issues involving the chemical sciences are addressed by IUPAC. IUPAC was established in 1919. IUPAC also published books, fields including chemistry, biology and physics. We have to remember for a variety of compounds there are predefined IUPAC nomenclature for the naming system. The process is almost the same of every compound. The variation in the naming can be due to different functional groups present in the chain and also due to presence of higher degree of compounds as a minor branch.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




