
Write structure and function of cell membrane?
Answer
591.3k+ views
Hint: Cell is the basic structural, functional and biological unit of life.
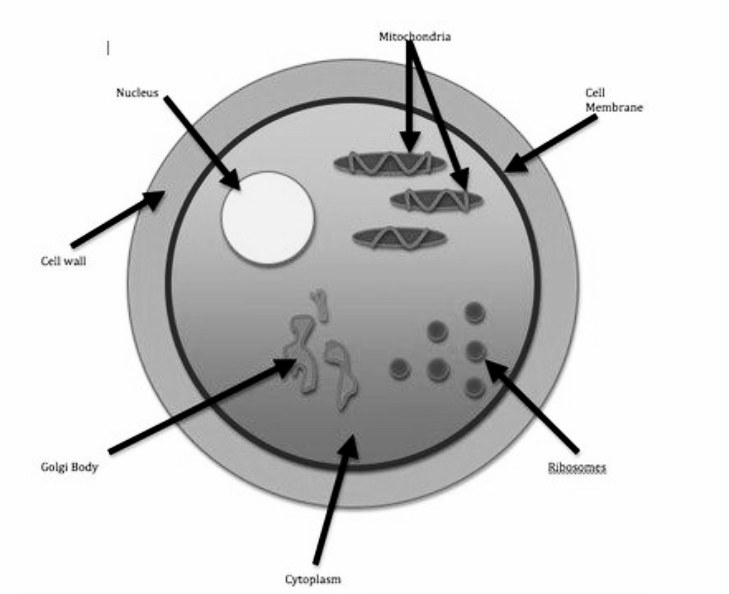
The living cell consists of an outer layer which includes a cell wall and plasma membrane or cell membrane. Cell membrane or plasma membrane is the outermost layer in the animal cell and second outermost layer in the plant cell after the cell wall. Cell membrane is lipid bilayer; contain some proteins and carbohydrates,
Complete answer:
Cell membrane: The double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell and separates the cytoplasm from the external environment is known as cell membrane or plasma membrane. In 1972, Singer and Nicolson proposed a model of the plasma membrane known as fluid mosaic model. The model states that plasma membrane is made of a bilayer of phospholipids with carbohydrates, proteins, glycolipids, and glycoprotein embedded inside it. A phospholipid molecule has its head (the phosphate-containing group), which has a polar character or negative charge, and an area called the tail which consists of fatty acids has no charge. A molecule with this arrangement of a positively or negatively charged is called dual-loving. Both surfaces of the plasma membrane are hydrophilic.
In contrast, the interior of the membrane is a hydrophobic or nonpolar region.
> Proteins: They are the second most abundant component of cell membranes.
Structural proteins help to give the cell support and shape.
Integral proteins are embedded and serve as channels to move materials into or out of the cell.
Peripheral proteins are present on the exterior or interior surfaces of membranes.
Both integral and peripheral proteins may serve as enzymes.
> Carbohydrates: They are the third major component of plasma membranes.
They are bound either to proteins forming glycoproteins or to lipids forming glycoproteins and glycolipids respectively.
Functions of the Cell Membrane are:
- It is responsible for the structure of the cell.
- It protects cells both mechanically and chemically.
- It maintains the differences in the concentration both inside and outside the membrane.
- It regulates transport of substances through selective permeable barrier
- It receives extra cellular signals and transfers it inside the cell.
- It interacts with other cells for tissue formation.
Note:
- Prokaryotic cells: cells that lack a membrane bound organelle (nucleus).
Organisms with prokaryotic cells are abundant and make up much of Earth's biomass.
For example: bacteria’s.
- Eukaryotic cells: cells which contain the membrane bound organelle (nucleus).
These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.
For example: Fungi, Protozoa, plants and animals.
The living cell consists of an outer layer which includes a cell wall and plasma membrane or cell membrane. Cell membrane or plasma membrane is the outermost layer in the animal cell and second outermost layer in the plant cell after the cell wall. Cell membrane is lipid bilayer; contain some proteins and carbohydrates,
Complete answer:
Cell membrane: The double layer of lipids and proteins that surrounds a cell and separates the cytoplasm from the external environment is known as cell membrane or plasma membrane. In 1972, Singer and Nicolson proposed a model of the plasma membrane known as fluid mosaic model. The model states that plasma membrane is made of a bilayer of phospholipids with carbohydrates, proteins, glycolipids, and glycoprotein embedded inside it. A phospholipid molecule has its head (the phosphate-containing group), which has a polar character or negative charge, and an area called the tail which consists of fatty acids has no charge. A molecule with this arrangement of a positively or negatively charged is called dual-loving. Both surfaces of the plasma membrane are hydrophilic.
In contrast, the interior of the membrane is a hydrophobic or nonpolar region.
> Proteins: They are the second most abundant component of cell membranes.
Structural proteins help to give the cell support and shape.
Integral proteins are embedded and serve as channels to move materials into or out of the cell.
Peripheral proteins are present on the exterior or interior surfaces of membranes.
Both integral and peripheral proteins may serve as enzymes.
> Carbohydrates: They are the third major component of plasma membranes.
They are bound either to proteins forming glycoproteins or to lipids forming glycoproteins and glycolipids respectively.

Functions of the Cell Membrane are:
- It is responsible for the structure of the cell.
- It protects cells both mechanically and chemically.
- It maintains the differences in the concentration both inside and outside the membrane.
- It regulates transport of substances through selective permeable barrier
- It receives extra cellular signals and transfers it inside the cell.
- It interacts with other cells for tissue formation.
Note:
- Prokaryotic cells: cells that lack a membrane bound organelle (nucleus).
Organisms with prokaryotic cells are abundant and make up much of Earth's biomass.
For example: bacteria’s.
- Eukaryotic cells: cells which contain the membrane bound organelle (nucleus).
These organisms are grouped into the biological domain Eukaryota.
For example: Fungi, Protozoa, plants and animals.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




