
Write main differences between the properties of white phosphorus and red phosphorus.
Answer
526.1k+ views
Hint: There exist many allotropic forms of phosphorus in nature. Red phosphorus and white phosphorus are two the most common and important allotropes of phosphorus. Red phosphorus is thermally more stable than white phosphorus.
Complete answer:
Main points of difference between the properties red phosphorous and white phosphorous are tabulated below:
Note: The main point to note here is that red phosphorus exists in polymeric form and thus, is less reactive than white phosphorus. White phosphorus being less stable than red phosphorus, can be converted to red phosphorus by heating at 573K for several hours.
Complete answer:
Main points of difference between the properties red phosphorous and white phosphorous are tabulated below:
| Property | White phosphorous | Red phosphorous |
| Physical state and colour | It is a white waxy solid. It is soft and can be cut using a knife. It turns yellow in colour in exposure to light, hence, it is also called as yellow phosphorus. | It is red coloured hard crystalline solid. It is lustrous in nature. |
| Odour | It has garlic like odour. | It is odourless. |
| Physiological properties | It is poisonous in nature and prolonged working this phosphorus leads to a disease known as Phossy jaw. | It is non-poisonous in nature. |
| Structure | White phosphorus exists in ${{P}_{4}}$ tetrahedral structure. Each P-atom is $s{{p}^{3}}$ hybridized and bonded to other three P-atoms by covalent bonds.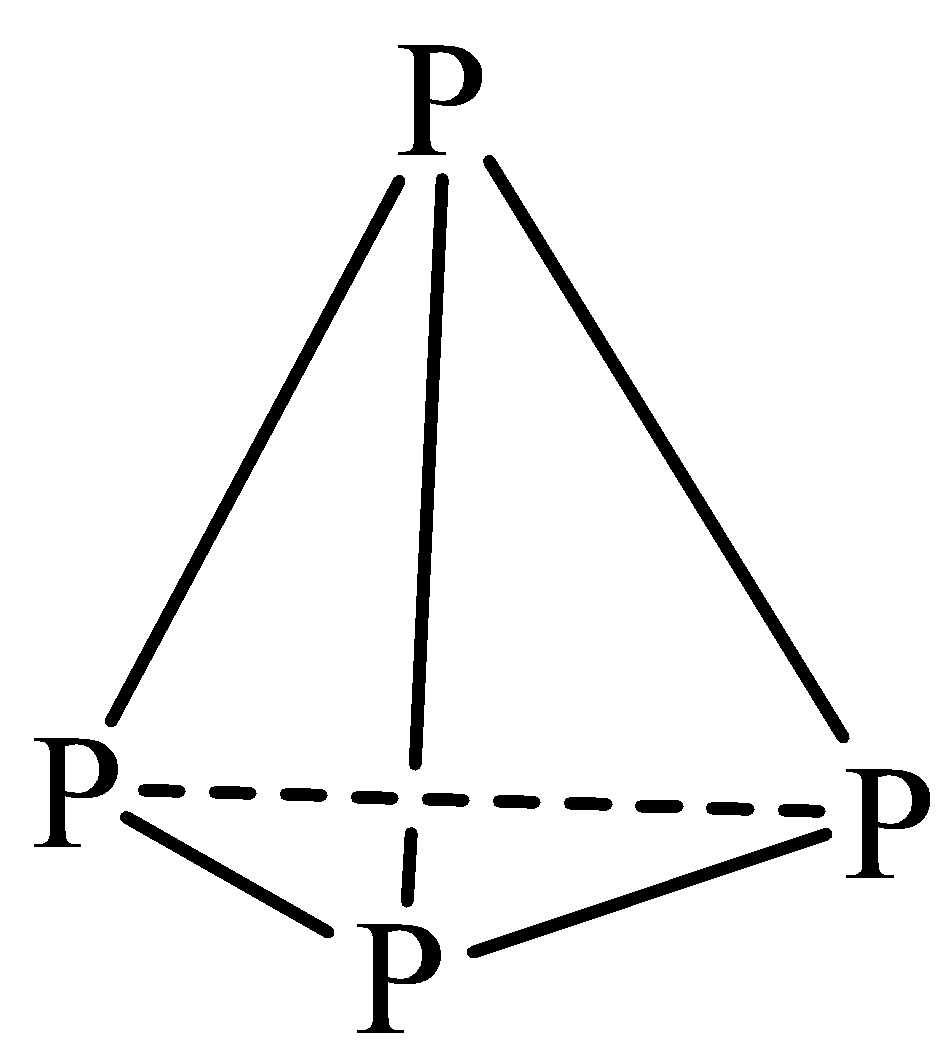
| Red phosphorus exists in polymeric form. Each ${{P}_{4}}$ tetrahedral is linked to another to form a polymer through covalent bonds. Its melting point is higher than that of white phosphorus, 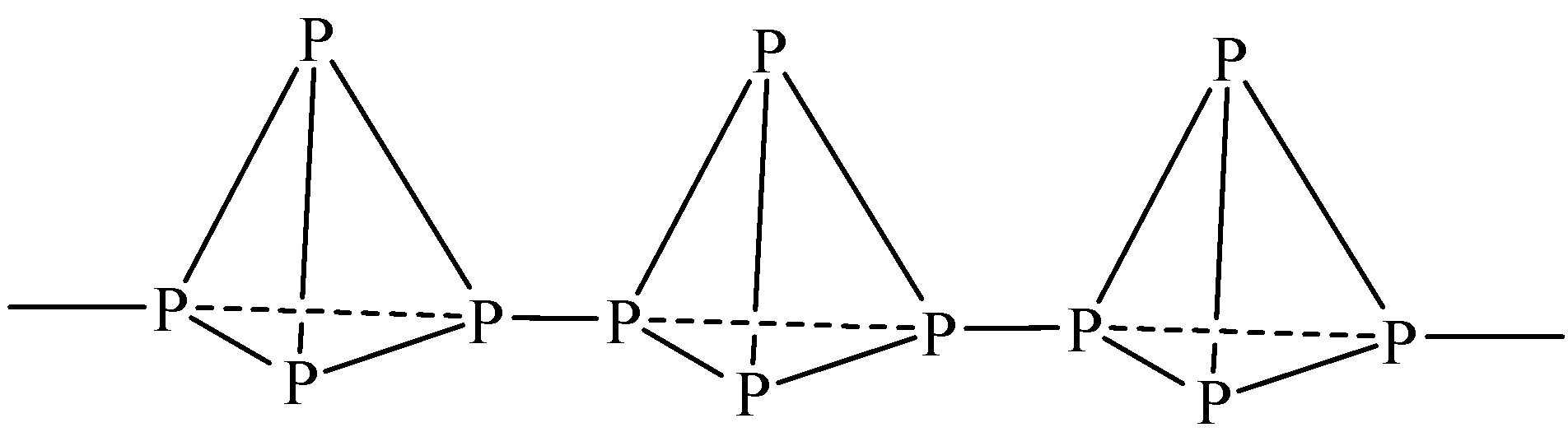
|
| Solubility | It is insoluble in water but dissolves in organic solvents for example, ether, carbon disulphide, alcohols, etc | It is not soluble in water as well as organic solvents |
| Action of air | It shows phosphorescence. Due to high angle strain, it is very reactive. It burns in air. The greenish glow is visible in the dark | It does not glow in the dark. Due to its polymeric, it is less reactive than white phosphorus. On reaction with oxygen it gives ${{P}_{4}}{{O}_{10}}$. |
| Reaction with halogens | It spontaneously burns in chlorine to form phosphorus trichloride and phosphorus pentachloride. \[{{P}_{4}}+6C{{l}_{2}}\to 4PC{{l}_{3}}\] \[{{P}_{4}}+10C{{l}_{2}}\to 4PC{{l}_{5}}\] | Being less reactive, it reacts with halogens only when heated. It forms $PC{{l}_{3}}$ followed by $PC{{l}_{5}}$. \[{{P}_{4}}+6C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\Delta }4PC{{l}_{3}}\] \[{{P}_{4}}+10C{{l}_{2}}\xrightarrow{\Delta }4PC{{l}_{5}}\] |
| Reaction with sulphur | It reacts with sulphur with violently to form a number of sulphides, i.e. ${{P}_{2}}{{S}_{3}}$, ${{P}_{2}}{{O}_{5}}$, ${{P}_{4}}{{S}_{3}}$, ${{P}_{4}}{{S}_{7}}$and ${{P}_{4}}{{S}_{10}}$. ${{P}_{4}}{{S}_{3}}$ being the most stable. \[8{{P}_{4}}+3{{S}_{8}}\to 8{{P}_{4}}{{S}_{3}}\] | It reacts with sulphur only when heated in an inert atmosphere to form sulphides. \[8{{P}_{4}}+3{{S}_{8}}\xrightarrow{453K}8{{P}_{4}}{{S}_{3}}\] |
| Reaction with metals | It reacts with metals to convert them into phosphides. | It generally does not react with metals. It may show reactions with alkali metal like Na at high temperature. |
| Reaction with base | White phosphorous when heated with solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH) solution in inert atmosphere forms phosphine ($P{{H}_{3}}$) and sodium hypophosphite ($Na{{H}_{2}}P{{O}_{2}}$). \[{{P}_{4}}+3NaOH+3{{H}_{2}}O\xrightarrow{\Delta ,C{{O}_{2}}}P{{H}_{3}}+3Na{{H}_{2}}P{{O}_{2}}\] | It does show reaction with sodium hydroxide. This property is exploited to separate red phosphorus from white phosphorus. |
Note: The main point to note here is that red phosphorus exists in polymeric form and thus, is less reactive than white phosphorus. White phosphorus being less stable than red phosphorus, can be converted to red phosphorus by heating at 573K for several hours.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




