
Write Kohlrausch Law and give one application for it:
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: Laws are certain kinds of rules and regulations which are universally applicable over a set of objects. Kohlrausch law is a chemical law, these are laws of nature relevant to chemistry. It is regarding the molar conductivity of electrolytes.
Complete step by step solution:
Kohlrausch Law is based on experimental data on dissociation of strong and weak electrolytes that expresses the motion of ions at infinite dilution. According to Kohlrausch Law molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte is equal to sum of molar conductivity of different ions (cation and anion) at infinite dilution. It also states that when dissociation is complete, each ion makes a definite contribution to equilibrium conductance of the electrolyte (regardless of the nature of the ion) and at the infinite dilution for any electrolyte the value of equivalent conductance is the sum of constituent ions taking part i.e., the following formula:
\[\lambda _{m}^{\infty }\] ${{\lambda }_{\infty }}_{{}}={{\lambda }_{+}}+{{\lambda }_{-}}$ .
Application of Kohlrausch Law:
Determination of molar/equivalent conductivity of a weak electrolyte at ∞(infinite) dilution.: Let use a example of a weak electrolyte Acetic Acid ($C{{H}_{3}}-COOH$).
\[\begin{align}
& NaCl\xrightarrow{{}}N{{a}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}} \\
& HCl\xrightarrow{{}}{{H}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}} \\
& C{{H}_{3}}-COONa\xrightarrow{{}}C{{H}_{3}}-CO{{O}^{-}}+N{{a}^{+}} \\
\end{align}\]
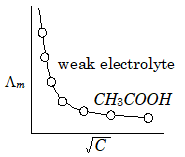
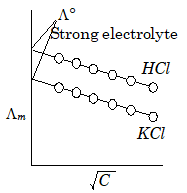
According to Kohlrausch Law
$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$NaCl$=$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$N{{a}^{+}}$+ $\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{l}^{-}}$ ……(a)
$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$HCl$=$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$${{H}^{+}}$+ $\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{l}^{-}}$ ……(b)
$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{H}_{3}}-COONa$=$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{H}_{3}}-CO{{O}^{-}}$$+ $$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$N{{a}^{+}}$ ……(c)
\[\]
Now Let equation (b)+(c)-(a) by which we get
$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$${{H}^{+}}$+$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{l}^{-}}$+$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{H}_{3}}-COONa$+$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$N{{a}^{+}}$-$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$N{{a}^{+}}$-$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{l}^{-}}$
= $\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$${{H}^{+}}$+$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{H}_{3}}-COONa$
Note: -Every Law has a fixed statement and one cannot change it, it is experimentally proved and nature is abided to it.
-At infinite dilution or near zero concentration when dissociation is 100%, each ion makes a definite contribution towards molar conductivity irrespective of the nature of the other ion.
-Do not confuse between weak and strong electrolyte.
Complete step by step solution:
Kohlrausch Law is based on experimental data on dissociation of strong and weak electrolytes that expresses the motion of ions at infinite dilution. According to Kohlrausch Law molar conductivity of a weak electrolyte is equal to sum of molar conductivity of different ions (cation and anion) at infinite dilution. It also states that when dissociation is complete, each ion makes a definite contribution to equilibrium conductance of the electrolyte (regardless of the nature of the ion) and at the infinite dilution for any electrolyte the value of equivalent conductance is the sum of constituent ions taking part i.e., the following formula:
\[\lambda _{m}^{\infty }\] ${{\lambda }_{\infty }}_{{}}={{\lambda }_{+}}+{{\lambda }_{-}}$ .
Application of Kohlrausch Law:
Determination of molar/equivalent conductivity of a weak electrolyte at ∞(infinite) dilution.: Let use a example of a weak electrolyte Acetic Acid ($C{{H}_{3}}-COOH$).
\[\begin{align}
& NaCl\xrightarrow{{}}N{{a}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}} \\
& HCl\xrightarrow{{}}{{H}^{+}}+C{{l}^{-}} \\
& C{{H}_{3}}-COONa\xrightarrow{{}}C{{H}_{3}}-CO{{O}^{-}}+N{{a}^{+}} \\
\end{align}\]


According to Kohlrausch Law
$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$NaCl$=$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$N{{a}^{+}}$+ $\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{l}^{-}}$ ……(a)
$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$HCl$=$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$${{H}^{+}}$+ $\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{l}^{-}}$ ……(b)
$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{H}_{3}}-COONa$=$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{H}_{3}}-CO{{O}^{-}}$$+ $$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$N{{a}^{+}}$ ……(c)
\[\]
Now Let equation (b)+(c)-(a) by which we get
$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$${{H}^{+}}$+$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{l}^{-}}$+$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{H}_{3}}-COONa$+$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$N{{a}^{+}}$-$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$N{{a}^{+}}$-$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{l}^{-}}$
= $\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$${{H}^{+}}$+$\lambda _{m}^{\infty }$$C{{H}_{3}}-COONa$
Note: -Every Law has a fixed statement and one cannot change it, it is experimentally proved and nature is abided to it.
-At infinite dilution or near zero concentration when dissociation is 100%, each ion makes a definite contribution towards molar conductivity irrespective of the nature of the other ion.
-Do not confuse between weak and strong electrolyte.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




