
How do you write in simplest radical form the coordinates of point $A$ if $A$ is on the terminal side of angle in standard position whose degree measure is $\theta :OA=15,\theta ={{135}^{\circ }}$ ?
Answer
540k+ views
Hint: Here in this question we have been asked to write the coordinates of point $A$ in simplest radical form if it is given that $A$ is on the terminal side of angle in standard position whose degree measure is $\theta :OA=15,\theta ={{135}^{\circ }}$ . For answering this question we will make a reference angle inside a circle of radius $15$ and a triangle inside it.
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now considering from the question we have been asked to write the coordinates of point $A$ in simplest radical form if it is given that $A$ is on the terminal side of angle in standard position whose degree measure is $\theta :OA=15,\theta ={{135}^{\circ }}$ .
For answering this question we will make a reference angle inside a circle of radius $15$ and a triangle inside it.
The reference image will look like:
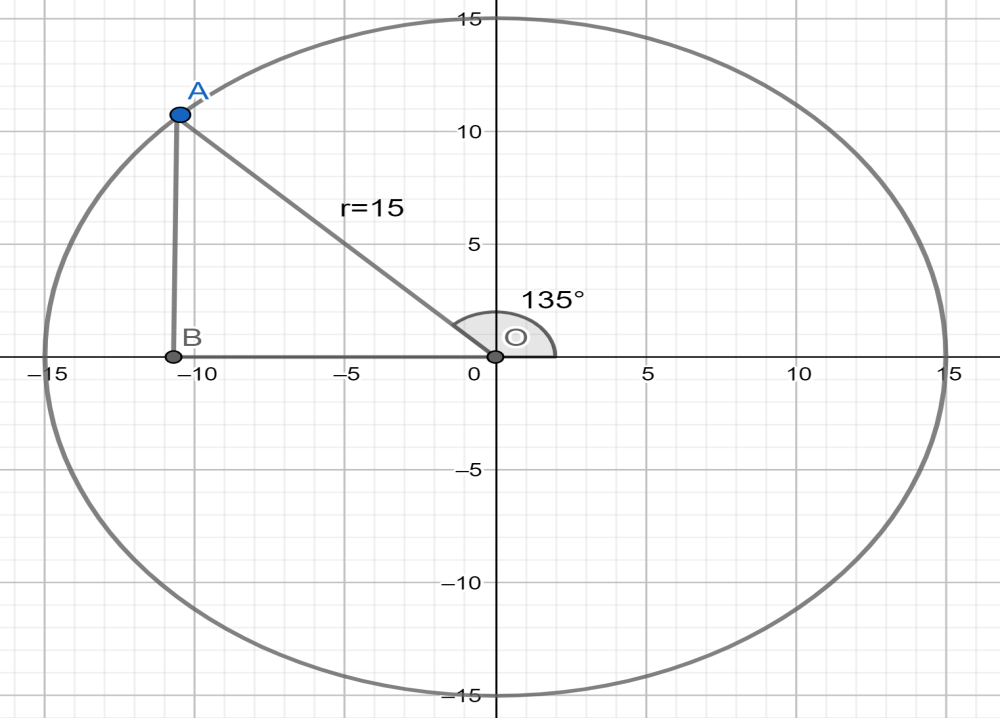
Now we can say that the inner angle of the triangle will be given as $\angle AOB={{180}^{\circ }}-{{135}^{\circ }}={{45}^{\circ }}$ .
Since we know that the coordinates of point $A$ will be given as $\left( -OB,AB \right)$ because $OB$ is the distance on the x-axis and it lies on the negative side of x-axis and $AB$ is the distance on the y-axis.
Since the reference triangle is right angle we can say that the other angle is also ${{45}^{\circ }}$ as the sum of all the angles in a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$ .
As we had assumed the radius of the circle to be $15$ we will be having $OA=15$ the length of the hypotenuse.
Since two angles are equal the sides corresponding to those angles will also be equal let us assume them to be $x$ .
From the Pythagoras theorem, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Here it will be mathematically given as ${{15}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}$ .
By simplifying this we will have
$\begin{align}
& 225=2{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\sqrt{\dfrac{225}{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{2}}\Rightarrow OB=AB \\
\end{align}$ .
Therefore we can conclude that the coordinates of $A$ in the simplest radical form when it is given that $A$ is on the terminal side of angle in standard position whose degree measure is $\theta :OA=15,\theta ={{135}^{\circ }}$ can be written as $\left( \dfrac{-15}{\sqrt{2}},\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{2}} \right)$ .
Note: While answering questions of this type we should be sure with the circular concepts that we are going to apply in the process and the calculations that we are going to perform in between. We should not forget to consider that the point lies in the second quadrant if we missed it then we will have the answer as $\left( \dfrac{15}{\sqrt{2}},\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{2}} \right)$ .
Complete step-by-step solution:
Now considering from the question we have been asked to write the coordinates of point $A$ in simplest radical form if it is given that $A$ is on the terminal side of angle in standard position whose degree measure is $\theta :OA=15,\theta ={{135}^{\circ }}$ .
For answering this question we will make a reference angle inside a circle of radius $15$ and a triangle inside it.
The reference image will look like:

Now we can say that the inner angle of the triangle will be given as $\angle AOB={{180}^{\circ }}-{{135}^{\circ }}={{45}^{\circ }}$ .
Since we know that the coordinates of point $A$ will be given as $\left( -OB,AB \right)$ because $OB$ is the distance on the x-axis and it lies on the negative side of x-axis and $AB$ is the distance on the y-axis.
Since the reference triangle is right angle we can say that the other angle is also ${{45}^{\circ }}$ as the sum of all the angles in a triangle is ${{180}^{\circ }}$ .
As we had assumed the radius of the circle to be $15$ we will be having $OA=15$ the length of the hypotenuse.
Since two angles are equal the sides corresponding to those angles will also be equal let us assume them to be $x$ .
From the Pythagoras theorem, the square of the hypotenuse is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides.
Here it will be mathematically given as ${{15}^{2}}={{x}^{2}}+{{x}^{2}}$ .
By simplifying this we will have
$\begin{align}
& 225=2{{x}^{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\sqrt{\dfrac{225}{2}} \\
& \Rightarrow x=\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{2}}\Rightarrow OB=AB \\
\end{align}$ .
Therefore we can conclude that the coordinates of $A$ in the simplest radical form when it is given that $A$ is on the terminal side of angle in standard position whose degree measure is $\theta :OA=15,\theta ={{135}^{\circ }}$ can be written as $\left( \dfrac{-15}{\sqrt{2}},\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{2}} \right)$ .
Note: While answering questions of this type we should be sure with the circular concepts that we are going to apply in the process and the calculations that we are going to perform in between. We should not forget to consider that the point lies in the second quadrant if we missed it then we will have the answer as $\left( \dfrac{15}{\sqrt{2}},\dfrac{15}{\sqrt{2}} \right)$ .
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




