
Write any two differences between the transverse and the longitudinal wave.
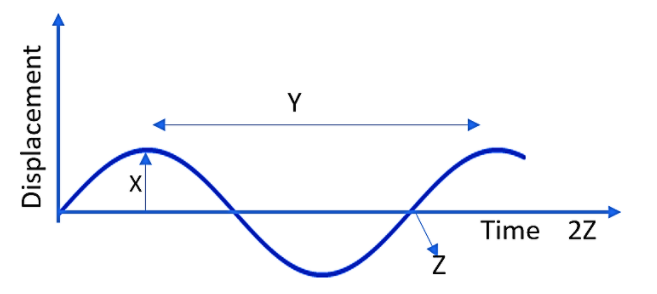

Answer
523.5k+ views
Hint: Transverse waves consist of crest and trough where the particles vibrate in the perpendicular motion. Whereas, longitudinal waves are having compression and rarefaction which will vibrate the particle in the medium in the same direction of propagation of wave.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all let us define the longitudinal and transverse wave. A longitudinal wave is the kind of wave which is moving in the direction that it started. It is having the compression which depicts the increased intensity of the medium particles and a rarefaction depicting a reduction in the intensity. A transverse wave is the kind of wave which traverses in a perpendicular direction to the direction it was started.
Now let us discuss the differences between them.
First of all, the movement of the medium is different for the two waves. In the longitudinal wave, the medium moves parallel, while in the transverse wave, the medium motion is perpendicular. Longitudinal waves consist of wave compression and rarefaction. By the way, the transverse wave is having a crest and a trough. Longitudinal waves have a pressure variation unless that of the transverse wave. Longitudinal waves are able to propagate in solids, liquids and also in gases, where the transverse waves can propagate only in solids and also on the surfaces of liquids. Longitudinal waves include the change in density throughout the medium, but the transverse waves are not affected by the change in intensity.
In short, transverses are travelling by moving the medium perpendicular to the wave propagation, while longitudinal waves by moving the medium parallel to the wave propagation. The transverse wave consists of crest and trough while longitudinal waves are having compression and rarefaction.
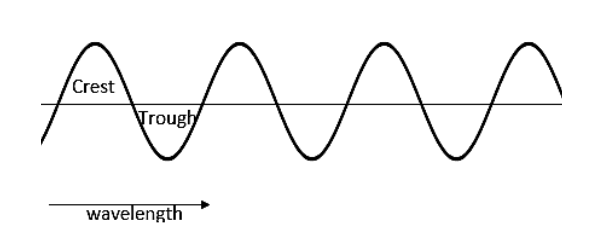
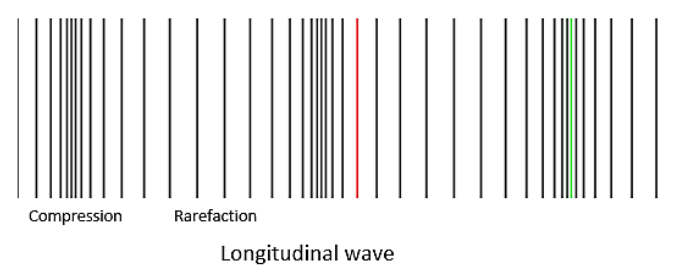
Note: A most general example for a longitudinal wave is a sound wave. Shock waves are another example. The examples for the transverse waves are a string on a guitar vibrating, and the ripples forming on the surface of water. Light wave is the most general example of transverse wave.
Complete step-by-step answer:
First of all let us define the longitudinal and transverse wave. A longitudinal wave is the kind of wave which is moving in the direction that it started. It is having the compression which depicts the increased intensity of the medium particles and a rarefaction depicting a reduction in the intensity. A transverse wave is the kind of wave which traverses in a perpendicular direction to the direction it was started.
Now let us discuss the differences between them.
First of all, the movement of the medium is different for the two waves. In the longitudinal wave, the medium moves parallel, while in the transverse wave, the medium motion is perpendicular. Longitudinal waves consist of wave compression and rarefaction. By the way, the transverse wave is having a crest and a trough. Longitudinal waves have a pressure variation unless that of the transverse wave. Longitudinal waves are able to propagate in solids, liquids and also in gases, where the transverse waves can propagate only in solids and also on the surfaces of liquids. Longitudinal waves include the change in density throughout the medium, but the transverse waves are not affected by the change in intensity.
In short, transverses are travelling by moving the medium perpendicular to the wave propagation, while longitudinal waves by moving the medium parallel to the wave propagation. The transverse wave consists of crest and trough while longitudinal waves are having compression and rarefaction.


Note: A most general example for a longitudinal wave is a sound wave. Shock waves are another example. The examples for the transverse waves are a string on a guitar vibrating, and the ripples forming on the surface of water. Light wave is the most general example of transverse wave.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




