
Write an equation to show that 2,3-dimethylbutane may be prepared from each of the following compounds. (i) an alkene (ii) a grignard reagent (iii) a haloalkane (iv) a sodium alkanoate?
Answer
531.6k+ views
Hint: 2,3-dimethylbutane is generally a form of alkane which consist of long chain of 4 carbon atoms known as the name butane and branching of two methyl groups are present at position 2 and 3 which termed as dimethyl.
Complete answer:
(i) An alkene: Alkene contains unsaturation in it i.e. double bond is present in alkenes. The equation can be written as:
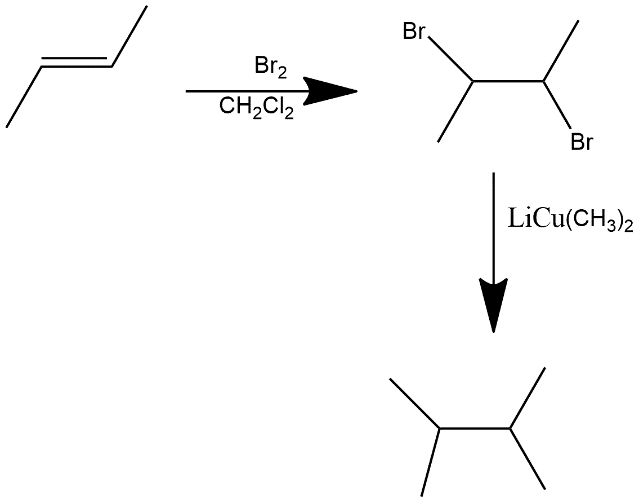
In first step bromination is done and then two equivalents of $LiCu{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}$gives us the 2,3-dimethylbutane.
(ii) a grignard reagent: This can be shown as follows:

Water gets rid by the magnesium bromide substituent and substitutes it with a hydrogen, then Hydroboration adds a hydroxide on the carbon where the magnesium bromide is added according to anti-Markovnikov rule and $PB{{r}_{3}}$ substitutes the hydroxide with a bromide group then$MgS{{O}_{4}}$ acts as a drying agent to clear the reaction vessel of any water remaining from steps 1 and 2, $LiCu{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}$ substitutes a methyl group in place of the bromide group.
(iii) a haloalkane:

This is the same as alkene.
(iv) a sodium alkanoate
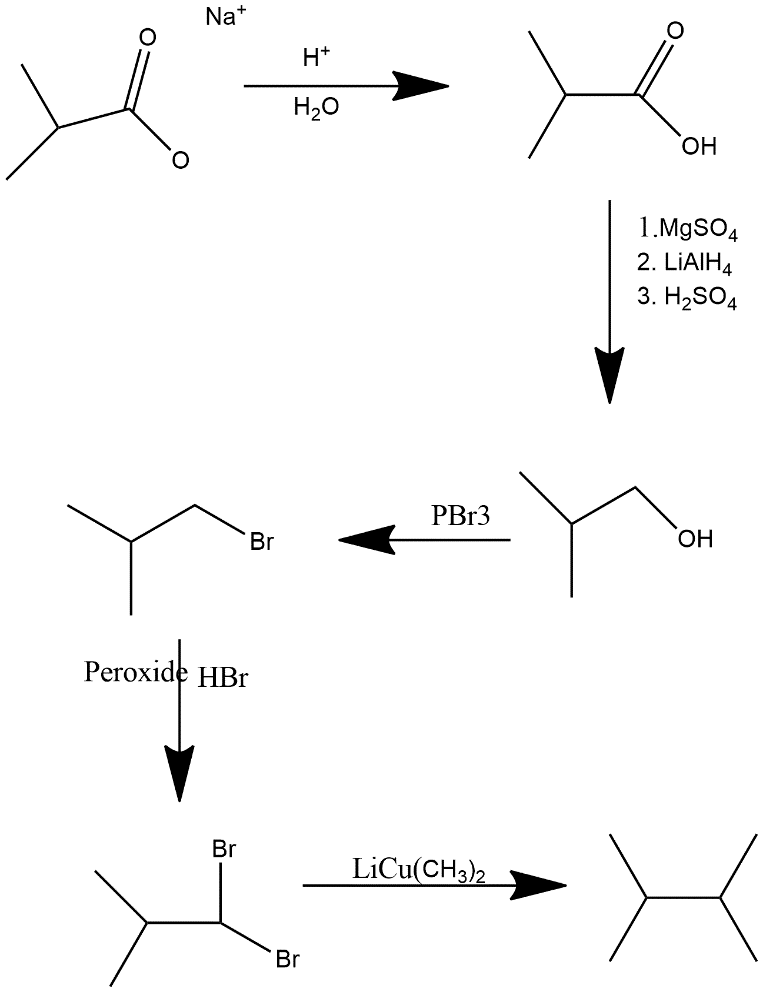
In first step strong acid protonated the alkanoate and make it carboxylic acid then $MgS{{O}_{4}}$ $MgS{{O}_{4}}$, $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ and dilute sulfuric acid acts as reducing agent turns acid in alcoholic group after that same step occurs as in equation i.
Note:
Alkyl halides are also known by the name halo alkanes or halogen alkanes. These are chemical compounds which are derived from alkanes which contains one or more halogen atoms. These are also known as these are a subset of the general class of halocarbons.
Complete answer:
(i) An alkene: Alkene contains unsaturation in it i.e. double bond is present in alkenes. The equation can be written as:

In first step bromination is done and then two equivalents of $LiCu{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}$gives us the 2,3-dimethylbutane.
(ii) a grignard reagent: This can be shown as follows:

Water gets rid by the magnesium bromide substituent and substitutes it with a hydrogen, then Hydroboration adds a hydroxide on the carbon where the magnesium bromide is added according to anti-Markovnikov rule and $PB{{r}_{3}}$ substitutes the hydroxide with a bromide group then$MgS{{O}_{4}}$ acts as a drying agent to clear the reaction vessel of any water remaining from steps 1 and 2, $LiCu{{(C{{H}_{3}})}_{2}}$ substitutes a methyl group in place of the bromide group.
(iii) a haloalkane:

This is the same as alkene.
(iv) a sodium alkanoate

In first step strong acid protonated the alkanoate and make it carboxylic acid then $MgS{{O}_{4}}$ $MgS{{O}_{4}}$, $LiAl{{H}_{4}}$ and dilute sulfuric acid acts as reducing agent turns acid in alcoholic group after that same step occurs as in equation i.
Note:
Alkyl halides are also known by the name halo alkanes or halogen alkanes. These are chemical compounds which are derived from alkanes which contains one or more halogen atoms. These are also known as these are a subset of the general class of halocarbons.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




