
Write all organic compounds with the molecular formula ${C_3}{H_8}O$ . Mention their IUPAC names.Find out isomers from this and also mention the type of isomerism.
Answer
558.3k+ views
Hint:We know that Isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Therefore when we write all possible organic compounds with the molecular formula ${C_3}{H_8}O$ , the total number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms should remain $3,8$ and $1$ respectively. Isomerism can be of two types mainly structural isomerism and stereoisomerism.
Complete solution:
We know about isomerism. Isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers show different chemical and physical properties.
(A) Now let us write all possible organic compounds with the molecular formula ${C_3}{H_8}O$. The total number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms should be $3,8$ and $1$ respectively. The possible compounds are
1) Propanol: $C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH$
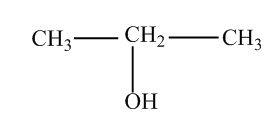
2) $propan - 2 - ol$
3) Methoxyethane
(B) Now that we know what isomerism is, we should know its types. Isomerism can be of two types that are structural and stereoisomerism. Structural isomerism is a type of isomerism in which compounds show a difference in the structural arrangement. For example, in Propanol and $propan - 2 - ol$, only position of $ - OH$ the group is different. Therefore they are structural isomers. Further, since only the position of the functional group is different, they are positional isomers. Positional isomerism is a type of structural isomerism in which the position of the substituent or functional group or double bond is different.
-Another type of structural isomerism is functional isomerism. It is a type of isomerism in which compounds have the same molecular formula but differ in the functional groups. Propanol and Methoxyethane are functional isomers.
-Alcohol and ethers are functional isomers, as discussed in the point above. Therefore, $propan - 2 - ol$ and Methoxyethane are also functional isomers. The functional group in Methoxyethane is $R - O - R$ and the functional group in alcohol is $ - OH$.
Note:As we discussed isomerism can be divided into two types that are structural and stereoisomerism. Stereoisomerism arises when compounds have the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangement of atoms. Stereoisomerism can be further subdivided into optical and geometrical isomerism.
Complete solution:
We know about isomerism. Isomerism occurs when compounds have the same molecular formula but different structural formulas. Isomers show different chemical and physical properties.
(A) Now let us write all possible organic compounds with the molecular formula ${C_3}{H_8}O$. The total number of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms should be $3,8$ and $1$ respectively. The possible compounds are
1) Propanol: $C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_2} - OH$
2) $propan - 2 - ol$

3) Methoxyethane

(B) Now that we know what isomerism is, we should know its types. Isomerism can be of two types that are structural and stereoisomerism. Structural isomerism is a type of isomerism in which compounds show a difference in the structural arrangement. For example, in Propanol and $propan - 2 - ol$, only position of $ - OH$ the group is different. Therefore they are structural isomers. Further, since only the position of the functional group is different, they are positional isomers. Positional isomerism is a type of structural isomerism in which the position of the substituent or functional group or double bond is different.
-Another type of structural isomerism is functional isomerism. It is a type of isomerism in which compounds have the same molecular formula but differ in the functional groups. Propanol and Methoxyethane are functional isomers.
-Alcohol and ethers are functional isomers, as discussed in the point above. Therefore, $propan - 2 - ol$ and Methoxyethane are also functional isomers. The functional group in Methoxyethane is $R - O - R$ and the functional group in alcohol is $ - OH$.
Note:As we discussed isomerism can be divided into two types that are structural and stereoisomerism. Stereoisomerism arises when compounds have the same molecular formula but different spatial arrangement of atoms. Stereoisomerism can be further subdivided into optical and geometrical isomerism.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




