
Write a short note on the solar spectrum or continuous spectrum.
Answer
582.3k+ views
Hint: The term continuous spectrum involves light and colours and their electromagnetic spectrum. Its best example is rainbow. If the rainbow has all the colours and no gaps between them it can be referred to as a continuous spectrum.
Complete step by step answer:
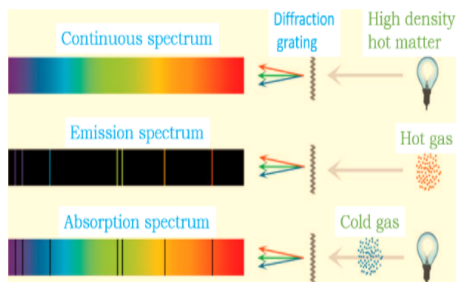
-Spectra helps us to understand how atoms absorb different light energies to provide the colour we see. There are two types of spectra: continuous and line spectra. Sun’s light contains continuous spectra. This can be explained as when white light is passed through a prism, it produces a rainbow of colours because of the different wavelengths that bend at different angles when passed through the prism.
-It is possible to obtain continuous spectra when we heat up different materials until they glow. Rainbow is a continuous spectrum when it has all the colours from red to violet and has no gaps between them. This was experimentally proven by Newton as he noted that the sun produces a rainbow of colours.
-Continuous spectrum can also be obtained from a hot solid, for example, light produced by incandescent light bulbs. These bulbs give off light by a very thin coil of metal or filament, get extremely hot when electric current passes through them. On getting thousands of degrees filament gives off light.
-Continuous spectrum has all the wavelengths and occurs when both absorption and emission spectra of a single species are put together. An emission spectrum is the exact opposite of an absorption spectra. An absorption spectrum shows few wavelengths with some particular colours missing whereas an emission spectrum shows the colours which are missing in an absorption spectrum. Therefore, their combination would give all the wavelength that forms a continuous spectrum.
Note:
The continuous spectrum from hot objects like stars, planets or moons is called a thermal spectrum because they emit electromagnetic radiation at all wavelengths. The shape of a continuous spectrum depends only on the temperature of the object and not on its chemical composition.
Complete step by step answer:
-Spectra helps us to understand how atoms absorb different light energies to provide the colour we see. There are two types of spectra: continuous and line spectra. Sun’s light contains continuous spectra. This can be explained as when white light is passed through a prism, it produces a rainbow of colours because of the different wavelengths that bend at different angles when passed through the prism.
-It is possible to obtain continuous spectra when we heat up different materials until they glow. Rainbow is a continuous spectrum when it has all the colours from red to violet and has no gaps between them. This was experimentally proven by Newton as he noted that the sun produces a rainbow of colours.
-Continuous spectrum can also be obtained from a hot solid, for example, light produced by incandescent light bulbs. These bulbs give off light by a very thin coil of metal or filament, get extremely hot when electric current passes through them. On getting thousands of degrees filament gives off light.
-Continuous spectrum has all the wavelengths and occurs when both absorption and emission spectra of a single species are put together. An emission spectrum is the exact opposite of an absorption spectra. An absorption spectrum shows few wavelengths with some particular colours missing whereas an emission spectrum shows the colours which are missing in an absorption spectrum. Therefore, their combination would give all the wavelength that forms a continuous spectrum.

Note:
The continuous spectrum from hot objects like stars, planets or moons is called a thermal spectrum because they emit electromagnetic radiation at all wavelengths. The shape of a continuous spectrum depends only on the temperature of the object and not on its chemical composition.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




