
Write a short note on the nucleus.
Answer
597.9k+ views
Hint: Nucleus is the defining feature of eukaryotic animals. It is the most vital part of a cell. It controls the functioning of the cell.
Complete answer:
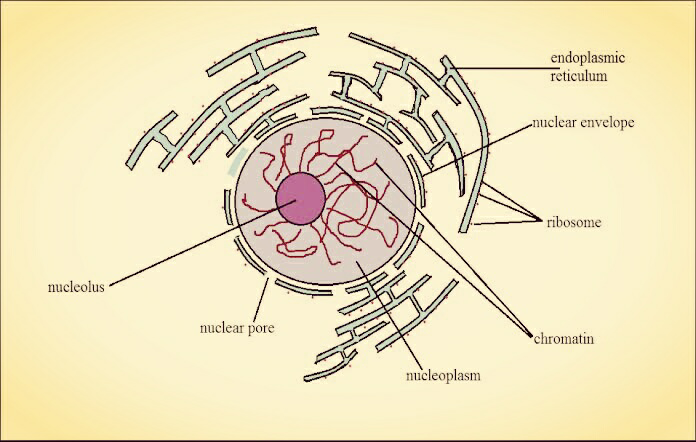
A nucleus is defined as a double-membraned eukaryotic cell organelle that contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes. It is the defining characteristic feature of eukaryotic cells. The credit for the discovery and naming of the nucleus goes to Robert Brown in 1833. Depending upon the number of the nucleus, a cell may be uninucleate, binucleate, or multinucleate. The shape of the nucleus may be discoid, ovoid, spherical, bilobed or multilobed. The outermost double-layered covering of the nucleus is called a nuclear membrane or karyotheca or nuclear envelope that is derived from phospholipids. The nuclear envelope is embedded by several small-sized pores known as nuclear pores. The nucleus is filled with nucleoplasm which contains chromatin i.e. thread-like structures of DNA. Within the nucleus, nucleolus is present which is a spherical body seen during interphase.
The functions of the nucleus are as follows:
1. It controls the heredity characteristics of an organism.
2. It maintains cellular metabolism by controlling the synthesis of particular enzymes.
3. It is responsible for the synthesis of RNA, protein synthesis, cell division, growth, and differentiation.
4. It stores hereditary material in the form of chromosomes which is made up of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) strands. It also stores proteins and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
5. It helps in the exchange of DNA and RNA (heredity materials) between the nucleus and the rest of the cell.
6. Nucleolus produces ribosomes and is known as protein factories.
Note:
1. Some cells such as sieve tubes of vascular plants and RBCs of mammals do not possess a nucleus though they originate from a eukaryotic organism.
2. The endoplasmic reticulum lies in close proximity to the nuclear envelope so that the internal compartment of the nuclear envelope is continuous with the lumen of the ER.
3. When a cell is “resting” i.e. not dividing, the chromosomes are organized into loose fibrous structures called chromatin and not into individual chromosomes.
Complete answer:
A nucleus is defined as a double-membraned eukaryotic cell organelle that contains the genetic material in the form of chromosomes. It is the defining characteristic feature of eukaryotic cells. The credit for the discovery and naming of the nucleus goes to Robert Brown in 1833. Depending upon the number of the nucleus, a cell may be uninucleate, binucleate, or multinucleate. The shape of the nucleus may be discoid, ovoid, spherical, bilobed or multilobed. The outermost double-layered covering of the nucleus is called a nuclear membrane or karyotheca or nuclear envelope that is derived from phospholipids. The nuclear envelope is embedded by several small-sized pores known as nuclear pores. The nucleus is filled with nucleoplasm which contains chromatin i.e. thread-like structures of DNA. Within the nucleus, nucleolus is present which is a spherical body seen during interphase.
The functions of the nucleus are as follows:
1. It controls the heredity characteristics of an organism.
2. It maintains cellular metabolism by controlling the synthesis of particular enzymes.
3. It is responsible for the synthesis of RNA, protein synthesis, cell division, growth, and differentiation.
4. It stores hereditary material in the form of chromosomes which is made up of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) strands. It also stores proteins and ribonucleic acid (RNA).
5. It helps in the exchange of DNA and RNA (heredity materials) between the nucleus and the rest of the cell.
6. Nucleolus produces ribosomes and is known as protein factories.
Note:
1. Some cells such as sieve tubes of vascular plants and RBCs of mammals do not possess a nucleus though they originate from a eukaryotic organism.
2. The endoplasmic reticulum lies in close proximity to the nuclear envelope so that the internal compartment of the nuclear envelope is continuous with the lumen of the ER.
3. When a cell is “resting” i.e. not dividing, the chromosomes are organized into loose fibrous structures called chromatin and not into individual chromosomes.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




