
Write a short note on the following process:-
Dow’s process
Answer
513.3k+ views
Hint: We know that Dow’s process is one of the famous organic synthesis and it is a commercial method of preparation of phenol. We have to explain about Dow’s process that involves hydrolysis of chlorobenzene at high pressure and temperature
conditions.
Complete answer:
Let us discuss about Dow’s process as follows:-
-Dow’s process is a synthesis in organic chemistry and was an early commercial method for the preparation of phenol (in the late early ${{20}^{th}}$ century). It is performed by the hydrolysis of chlorobenzene with a very strong base like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce a sodium phenoxide intermediate and this further yields phenol upon acidification . The process is shown below:-
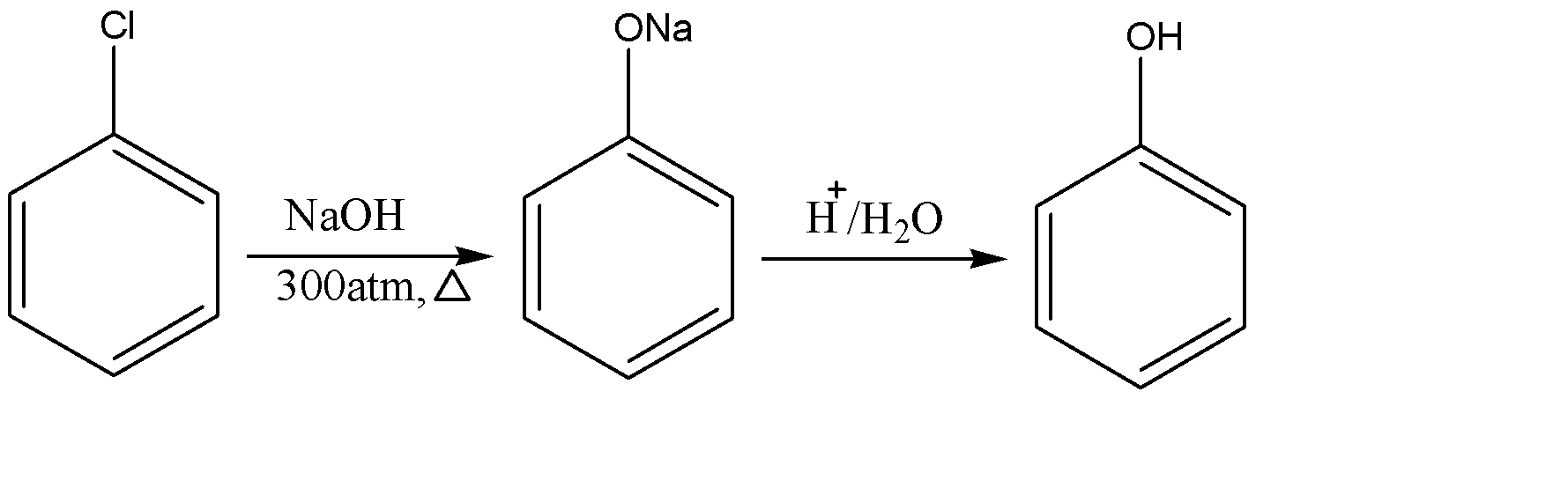
-Here the starting reactant is chlorobenzene which can be easily produced from benzene by electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. This compound is then treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide (NaOH) at 350 $^{\circ }C$ and 300 atm or we can also use molten sodium hydroxide at 350 $^{\circ }C$ to convert it to sodium phenoxide which acts as an intermediate.
- This yields phenol upon final work up which is acidification of phenoxide ion.
-When 1-[$^{14}C$]-1-chlorobenzene is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide (NaOH) at 395$^{\circ }C$, ipso substitution product that is 1-[$^{14}C$]-phenol is formed which has 54% yield whereas cine substitution product that is 2-[$^{14}C$]-phenol is formed which has 43% yield. This indicates that an elimination addition (benzyne) mechanism is always predominant in Dow’s process.
Note:
-Sometimes Dow’s process can also be explained as the electrolytic method of bromine extraction from brine as it is a process in inorganic chemistry. Here bromides containing brine minerals are treated with sulfuric acid and bleaching powder which oxidize bromide to bromine. This product bromine remains soluble in the water and proceeds for filtration and distillation.
conditions.
Complete answer:
Let us discuss about Dow’s process as follows:-
-Dow’s process is a synthesis in organic chemistry and was an early commercial method for the preparation of phenol (in the late early ${{20}^{th}}$ century). It is performed by the hydrolysis of chlorobenzene with a very strong base like sodium hydroxide (NaOH) to produce a sodium phenoxide intermediate and this further yields phenol upon acidification . The process is shown below:-

-Here the starting reactant is chlorobenzene which can be easily produced from benzene by electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction. This compound is then treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide (NaOH) at 350 $^{\circ }C$ and 300 atm or we can also use molten sodium hydroxide at 350 $^{\circ }C$ to convert it to sodium phenoxide which acts as an intermediate.
- This yields phenol upon final work up which is acidification of phenoxide ion.
-When 1-[$^{14}C$]-1-chlorobenzene is treated with aqueous sodium hydroxide (NaOH) at 395$^{\circ }C$, ipso substitution product that is 1-[$^{14}C$]-phenol is formed which has 54% yield whereas cine substitution product that is 2-[$^{14}C$]-phenol is formed which has 43% yield. This indicates that an elimination addition (benzyne) mechanism is always predominant in Dow’s process.
Note:
-Sometimes Dow’s process can also be explained as the electrolytic method of bromine extraction from brine as it is a process in inorganic chemistry. Here bromides containing brine minerals are treated with sulfuric acid and bleaching powder which oxidize bromide to bromine. This product bromine remains soluble in the water and proceeds for filtration and distillation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




