
Write a short note on Mendeleev’s Periodic Law.
Answer
600k+ views
Hint: Think of what the major correction made was in the classification of the Modern Periodic Table to help rectify several issues that arose as a result of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table. This clue should help give you enough of an idea about what Mendeleev’s Periodic Law could be.
Complete answer:
Let us now try and perform a detailed analysis of Mendeleev’s periodic law and the resultant Periodic Table.
In March 1869, Mendeleev delivered a full paper to the Russian Chemical Society spelling out the most significant aspect of his system, that characteristics of the elements recur at a periodic interval as a function of their atomic weight. This was the first iteration of the periodic law.
Mendeleev’s system was not perfect but it had the hallmarks of a scientific law, one that would hold true through new discoveries and against all challenges.
One of the unique aspects of Mendeleev’s table was the gaps he left. In these places he not only predicted there were as-yet-undiscovered elements, but he predicted their atomic weights and their characteristics. The discovery of new elements in the 1870s that fulfilled several of his predictions brought increased interest to the periodic system and it became not only an object of study but a tool for research.
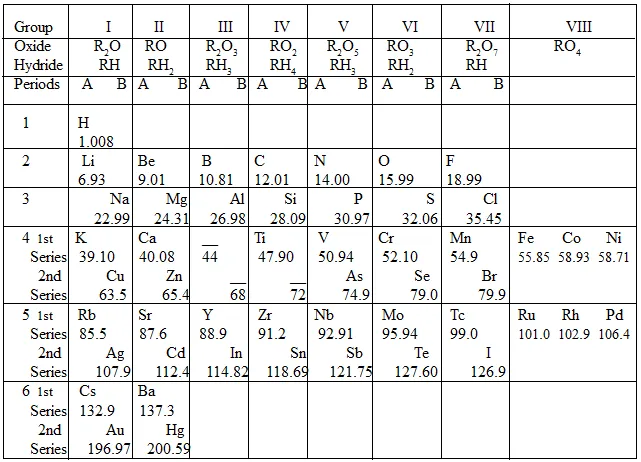
Now, let us perform an in-depth analysis of the properties of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.
Elements are arranged in the periodic table in the increasing order of their relative atomic masses.
Mendeleev divided his periodic table in eight groups and seven periods.
Groups from I to VII are meant for normal elements and group VIII is for transition elements.
Groups from I to VII have been divided in two sub groups, while group VIII is meant for three elements.
Periods from 4th to 7th have been divided in two series: 1st series and 2nd series.
Elements having similar properties have been kept in the same group. For example; lithium, potassium, rubidium, etc. are in the 1st group.
Two general formulae; one for oxides and second for hydrides; have been given for the elements of each group in the periodic table. For example: R2O for oxides and RH for hydrides, of the elements; of 1st group.
Note: If two elements are similar but not by much, then to distinguish between them one of them is placed below and slightly away from the other. Thus, each column will have two sub-columns A and B, thus elements will show more similarity in the same sub-columns.
Complete answer:
Let us now try and perform a detailed analysis of Mendeleev’s periodic law and the resultant Periodic Table.
In March 1869, Mendeleev delivered a full paper to the Russian Chemical Society spelling out the most significant aspect of his system, that characteristics of the elements recur at a periodic interval as a function of their atomic weight. This was the first iteration of the periodic law.
Mendeleev’s system was not perfect but it had the hallmarks of a scientific law, one that would hold true through new discoveries and against all challenges.
One of the unique aspects of Mendeleev’s table was the gaps he left. In these places he not only predicted there were as-yet-undiscovered elements, but he predicted their atomic weights and their characteristics. The discovery of new elements in the 1870s that fulfilled several of his predictions brought increased interest to the periodic system and it became not only an object of study but a tool for research.

Now, let us perform an in-depth analysis of the properties of Mendeleev’s Periodic Table.
Elements are arranged in the periodic table in the increasing order of their relative atomic masses.
Mendeleev divided his periodic table in eight groups and seven periods.
Groups from I to VII are meant for normal elements and group VIII is for transition elements.
Groups from I to VII have been divided in two sub groups, while group VIII is meant for three elements.
Periods from 4th to 7th have been divided in two series: 1st series and 2nd series.
Elements having similar properties have been kept in the same group. For example; lithium, potassium, rubidium, etc. are in the 1st group.
Two general formulae; one for oxides and second for hydrides; have been given for the elements of each group in the periodic table. For example: R2O for oxides and RH for hydrides, of the elements; of 1st group.
Note: If two elements are similar but not by much, then to distinguish between them one of them is placed below and slightly away from the other. Thus, each column will have two sub-columns A and B, thus elements will show more similarity in the same sub-columns.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




