
Write a short note on hydrocarbons.
Answer
560.4k+ views
Hint: Hydrocarbons as the name suggests are compounds containing carbon atoms and hydrogen atoms in them. They are specifically known as organic compounds and are further classified as alkanes, arenes, cycloalkanes etc based on their structural arrangement.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to better understand the concept of hydrocarbons, let us first discuss the properties of carbon and hydrogen individually. We know that carbon belongs to the fourteenth group and hence it has four valence electrons. Therefore, each carbon atom can form four covalent bonds around it.
Similarly, we know that hydrogen atom belongs to the first group and hence its valency is one. Therefore, each hydrogen atom can form one covalent bond. This means that one carbon atom can react with four hydrogen atoms to form $C{H_4}$. This molecule is a basic hydrocarbon known as methane. Similarly there are several more compounds that can form carbon and hydrogen bonds in different ways to form different types of hydrocarbons.
Based on this, there are three types of hydrocarbons:
1) Saturated hydrocarbons: These compounds consist of carbon forming only single bonds with other atoms. The hybridization of carbon in this is $s{p^3}$.
Some examples are $C{H_3} - C{H_3}$, $C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$ etc.
2) Unsaturated hydrocarbons: In this, carbon forms more than one bond with other carbon atoms. Hybridization of carbon would be $s{p^2}$ or $sp$ depending on the number of bonds.
Some examples are \[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\], $CH \equiv CH$ etc.
3) Cyclic hydrocarbons: These compounds are closed chain compounds and if they contain at least one aromatic ring, they are known as aromatic compounds.
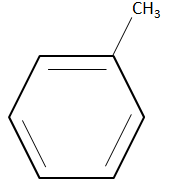
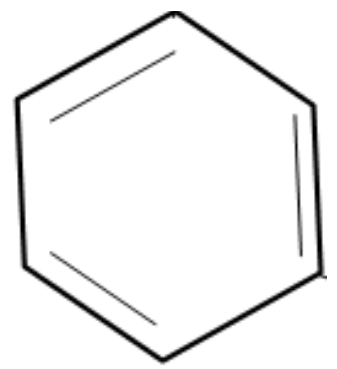
Note: It is to be noted that any compound that consists of a benzene ring is considered to be an aromatic compound. A benzene ring is basically a six carbon cyclic structure with alternating double bonds. The structure of benzene is given as follows.
Complete step by step solution:
In order to better understand the concept of hydrocarbons, let us first discuss the properties of carbon and hydrogen individually. We know that carbon belongs to the fourteenth group and hence it has four valence electrons. Therefore, each carbon atom can form four covalent bonds around it.
Similarly, we know that hydrogen atom belongs to the first group and hence its valency is one. Therefore, each hydrogen atom can form one covalent bond. This means that one carbon atom can react with four hydrogen atoms to form $C{H_4}$. This molecule is a basic hydrocarbon known as methane. Similarly there are several more compounds that can form carbon and hydrogen bonds in different ways to form different types of hydrocarbons.
Based on this, there are three types of hydrocarbons:
1) Saturated hydrocarbons: These compounds consist of carbon forming only single bonds with other atoms. The hybridization of carbon in this is $s{p^3}$.
Some examples are $C{H_3} - C{H_3}$, $C{H_3} - C{H_2} - C{H_3}$ etc.
2) Unsaturated hydrocarbons: In this, carbon forms more than one bond with other carbon atoms. Hybridization of carbon would be $s{p^2}$ or $sp$ depending on the number of bonds.
Some examples are \[C{H_2} = C{H_2}\], $CH \equiv CH$ etc.
3) Cyclic hydrocarbons: These compounds are closed chain compounds and if they contain at least one aromatic ring, they are known as aromatic compounds.

Note: It is to be noted that any compound that consists of a benzene ring is considered to be an aromatic compound. A benzene ring is basically a six carbon cyclic structure with alternating double bonds. The structure of benzene is given as follows.

Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Give 10 examples of unisexual and bisexual flowers




