
Write a balanced equation for the reaction of ammonia and oxygen in the presence of a catalyst:
(a)- \[N{{H}_{3}}+5{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow[Pt]{800K}NO+{{H}_{2}}O+\Delta \]
(b)- \[4N{{H}_{3}}+5{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow[Pt]{800K}4NO+6{{H}_{2}}O+\Delta \]
(c)- \[4N{{H}_{3}}+3{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow[Pt]{800K}4NO+{{H}_{2}}O+\Delta \]
(d)- \[N{{H}_{3}}+3{{O}_{2}}\xrightarrow[Pt]{800K}NO+{{H}_{2}}O+\Delta \]
Answer
582.6k+ views
Hint: First we have to find out the oxidation number of all atoms other than oxygen and hydrogen. Since only nitrogen is present other than hydrogen and oxygen, hence oxygen is used as another atom. Identify the oxidizing and reducing agents. Balancing of oxygen and hydrogen is done by hit and trial method.
Complete step by step answer:
When the ammonia reacts with oxygen it forms nitric oxide and water. Since this is an exothermic reaction, there is an evolution of heat.
The equation is balanced by the Oxidation number method.
Step by step we can balance the equation. In the first step write the skeletal equation and write the oxidation number of each atom.
$\begin{align}
& -3\text{ +1 0 +2 -2 +1 -2} \\
& \text{N }{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ + }{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{ }\to \text{ N O + }{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ O + }\Delta \\
\end{align}$
Next, find out the elements which change oxidation number.
Since only nitrogen is present other than O and H. O is used as another atom for finding the oxidizing and reducing agent.
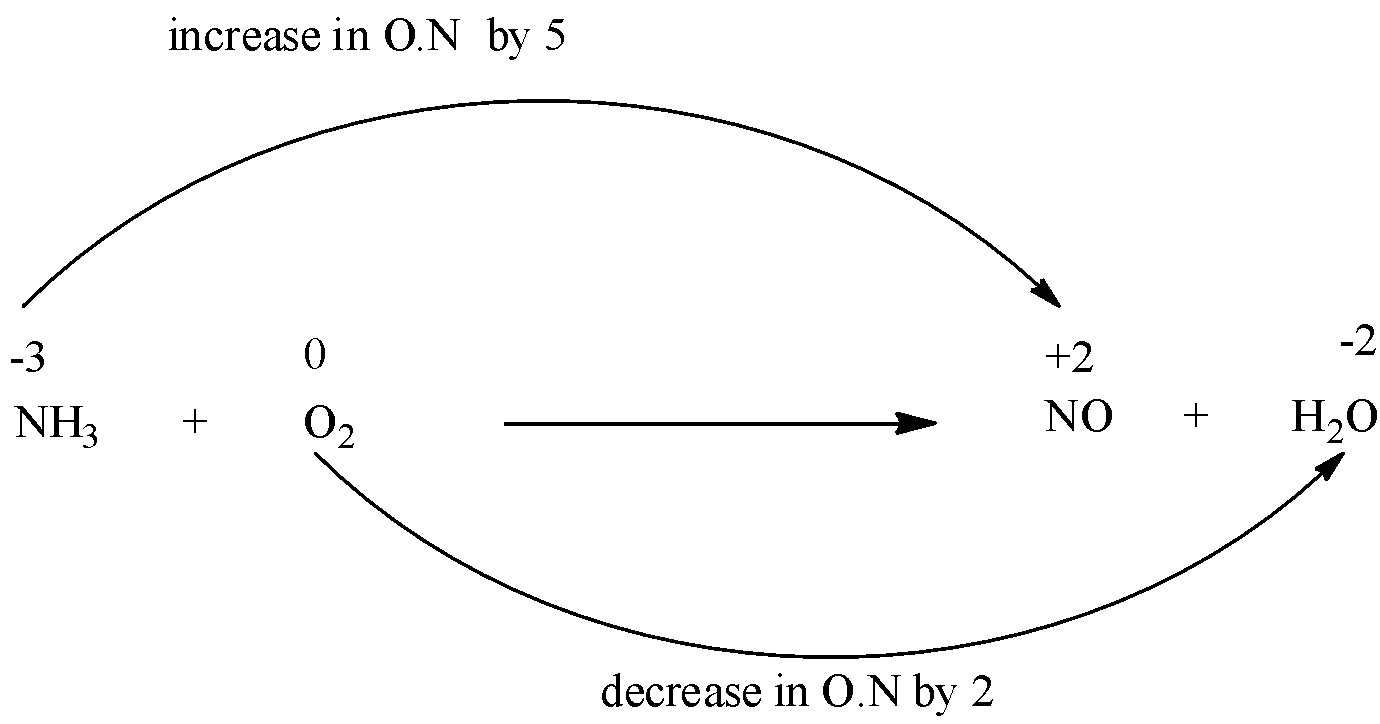
For the easy calculation we use the oxygen of water, not of nitric oxide.
The oxidation number of N increases from -3 to +2. And the oxidation number of O decreases from 0 to -2.
Next, find out the total change in oxidation number.
Since there is only one nitrogen in both L.H.S and R.H.S, the total increase in oxidation number is 5. The number of O atoms on L.H.S is 2 and on R.H.S is 1, so the total decrease of O.N will be 2 x 2 = 4.
Next, balance the oxidation number.
Since the total increase in the oxidation number is 5 and the total decrease is 4, therefore multiply $N{{H}_{3}}\text{ and NO}$ by 4 and multiply ${{O}_{2}}\text{ and }{{\text{H}}_{2}}O$ with 5.
$\text{4N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{+ 5}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{ }\to 4\text{NO + 5}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O }$
Next balance all atoms other than H and O.
No need to balance the equation because there are 4 N atoms on both sides.
Now balance the oxygen and hydrogen by hit and trial method.
There are 10 oxygen atoms on the L.H.S and 9 oxygen atoms on the R.H.S, therefore, add one${{H}_{2}}O$ molecule to the R.H.S.
$\text{4N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{+ 5}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{ }\to 4\text{NO + 6}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O }$
The hydrogen atoms get balanced automatically.
Hence, the balanced equation is: $\text{4N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{+ 5}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{ }\to 4\text{NO + 6}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O }$
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Note: The reaction takes place in platinum as a catalyst and at temperature 800 K. This reaction is used in the preparation of nitric acid which is called Ostwald's process.
Complete step by step answer:
When the ammonia reacts with oxygen it forms nitric oxide and water. Since this is an exothermic reaction, there is an evolution of heat.
The equation is balanced by the Oxidation number method.
Step by step we can balance the equation. In the first step write the skeletal equation and write the oxidation number of each atom.
$\begin{align}
& -3\text{ +1 0 +2 -2 +1 -2} \\
& \text{N }{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{ + }{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{ }\to \text{ N O + }{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{ O + }\Delta \\
\end{align}$
Next, find out the elements which change oxidation number.
Since only nitrogen is present other than O and H. O is used as another atom for finding the oxidizing and reducing agent.

For the easy calculation we use the oxygen of water, not of nitric oxide.
The oxidation number of N increases from -3 to +2. And the oxidation number of O decreases from 0 to -2.
Next, find out the total change in oxidation number.
Since there is only one nitrogen in both L.H.S and R.H.S, the total increase in oxidation number is 5. The number of O atoms on L.H.S is 2 and on R.H.S is 1, so the total decrease of O.N will be 2 x 2 = 4.
Next, balance the oxidation number.
Since the total increase in the oxidation number is 5 and the total decrease is 4, therefore multiply $N{{H}_{3}}\text{ and NO}$ by 4 and multiply ${{O}_{2}}\text{ and }{{\text{H}}_{2}}O$ with 5.
$\text{4N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{+ 5}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{ }\to 4\text{NO + 5}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O }$
Next balance all atoms other than H and O.
No need to balance the equation because there are 4 N atoms on both sides.
Now balance the oxygen and hydrogen by hit and trial method.
There are 10 oxygen atoms on the L.H.S and 9 oxygen atoms on the R.H.S, therefore, add one${{H}_{2}}O$ molecule to the R.H.S.
$\text{4N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{+ 5}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{ }\to 4\text{NO + 6}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O }$
The hydrogen atoms get balanced automatically.
Hence, the balanced equation is: $\text{4N}{{\text{H}}_{3}}\text{+ 5}{{\text{O}}_{2}}\text{ }\to 4\text{NO + 6}{{\text{H}}_{2}}\text{O }$
Hence, the correct option is (b).
Note: The reaction takes place in platinum as a catalyst and at temperature 800 K. This reaction is used in the preparation of nitric acid which is called Ostwald's process.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




