
How much work would it take to push a $ 6kg $ weight up a plane that is at an incline of $ \dfrac{\pi }{4} $
Answer
527.1k+ views
Hint: The work required to push the object of some mass and against the gravity on an inclined plane is given by $ W = mg\sin \left( \phi \right).d $ where signs have the respective values. The work done is basically the product of force and displacement if it is in a straight line.
Complete step by step answer:
We want to find the work required to push the object up the inclined plane against any other forces that act against us.
Work done by a constant force is given by:
$ W = F \cdot dcos \cdot (\theta ) $
Where $ F $ is the applied force, $ d $ is the displacement, and $ \theta $ is the angle between the force and displacement vectors.
We are given,
Mass of body, $ m = 6kg $
Distance up to which the body is to be moved $ d = 2m $
Incline of ramp, $ \phi = \dfrac{\pi }{4} $
Note that the angle of incline of the ramp/plane is not the angle between the force and displacement vectors shown in the work equation. I have assigned $ \phi $ as the angle of the plane to avoid confusion with $ \theta $ .
In order to calculate the applied force required to find the work, which I will call $ {F_p} $ , we can take inventory of the forces acting on the weight.
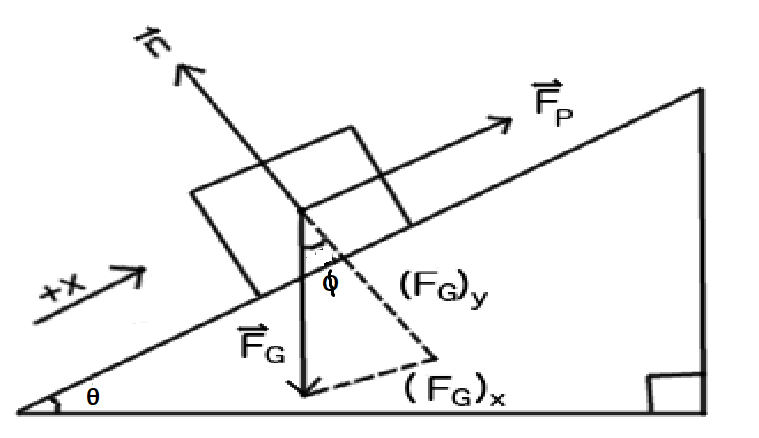
Where $ \overrightarrow n $ is the normal force, $ \overrightarrow {{F_p}} $ is the applied (pushing) force, and $ \overrightarrow {{F_G}} $ is the force of gravity, decomposed into its parallel (x) and perpendicular (y) components. The angle of incline is $ \phi $ .
We can sum the forces as:
$
\sum {{F_x} = {F_p} - {{\left( {{F_G}} \right)}_x} = m{a_x}} \\
\\
\sum {{F_y} = n - {{\left( {{F_G}} \right)}_y} = m{a_y}} \\
$
We will assume dynamic equilibrium in both the horizontal and vertical directions. Vertically, this is because the object does not move up or down relative to the surface of the incline. Horizontally, we assume that the object does not accelerate as we push it since it is implied that we are looking for the minimum force required to move the object.
$
\Rightarrow \sum {{F_x} = {F_p} - {{\left( {{F_G}} \right)}_x} = 0} \\
\\
\Rightarrow \sum {{F_y} = n - {{\left( {{F_G}} \right)}_y} = 0} \\
$
We can see then, with a bit of rearrangement, that the pushing force we apply must be equal to the parallel component of the force of gravity which acts against us. Therefore:
$ \Rightarrow {F_p} = {\left( {{F_G}} \right)_x} $
Using trigonometry, we can see from the diagram that $ {\left( {{F_G}} \right)_x} = mg\sin \left( \phi \right) $
$ \Rightarrow {F_p} = mg\sin \left( \phi \right) $
Going back to the work equation, we now have:
$ W = mg\sin \left( \phi \right).d.\cos \left( \theta \right) $
As said above, $ \theta $ is the angle between the force and displacement vectors. Since the relevant forces and displacement occur in the same direction (parallel to the incline), $ \theta = {0^ \circ } $ Therefore, we have:
$ W = mg\sin \left( \phi \right).d $
Substituting in our known values:
$
W = \left( {6kg} \right)\left( {9.8m{s^{ - 2}}} \right)\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right).\left( {2m} \right) \\
\\
\Rightarrow W = 6\, \times 9.8 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times 2\,J \\
\\
\Rightarrow W = 83.1557\,J \\
$
Note:
This problem could also be solved using the work-energy theorem, where the work done is equal to the change in energy. Change in energy will be the change in gravitational potential energy possessed by the object. We would need to use trigonometry to find the height of the ramp/incline.
Complete step by step answer:
We want to find the work required to push the object up the inclined plane against any other forces that act against us.
Work done by a constant force is given by:
$ W = F \cdot dcos \cdot (\theta ) $
Where $ F $ is the applied force, $ d $ is the displacement, and $ \theta $ is the angle between the force and displacement vectors.
We are given,
Mass of body, $ m = 6kg $
Distance up to which the body is to be moved $ d = 2m $
Incline of ramp, $ \phi = \dfrac{\pi }{4} $
Note that the angle of incline of the ramp/plane is not the angle between the force and displacement vectors shown in the work equation. I have assigned $ \phi $ as the angle of the plane to avoid confusion with $ \theta $ .
In order to calculate the applied force required to find the work, which I will call $ {F_p} $ , we can take inventory of the forces acting on the weight.

Where $ \overrightarrow n $ is the normal force, $ \overrightarrow {{F_p}} $ is the applied (pushing) force, and $ \overrightarrow {{F_G}} $ is the force of gravity, decomposed into its parallel (x) and perpendicular (y) components. The angle of incline is $ \phi $ .
We can sum the forces as:
$
\sum {{F_x} = {F_p} - {{\left( {{F_G}} \right)}_x} = m{a_x}} \\
\\
\sum {{F_y} = n - {{\left( {{F_G}} \right)}_y} = m{a_y}} \\
$
We will assume dynamic equilibrium in both the horizontal and vertical directions. Vertically, this is because the object does not move up or down relative to the surface of the incline. Horizontally, we assume that the object does not accelerate as we push it since it is implied that we are looking for the minimum force required to move the object.
$
\Rightarrow \sum {{F_x} = {F_p} - {{\left( {{F_G}} \right)}_x} = 0} \\
\\
\Rightarrow \sum {{F_y} = n - {{\left( {{F_G}} \right)}_y} = 0} \\
$
We can see then, with a bit of rearrangement, that the pushing force we apply must be equal to the parallel component of the force of gravity which acts against us. Therefore:
$ \Rightarrow {F_p} = {\left( {{F_G}} \right)_x} $
Using trigonometry, we can see from the diagram that $ {\left( {{F_G}} \right)_x} = mg\sin \left( \phi \right) $
$ \Rightarrow {F_p} = mg\sin \left( \phi \right) $
Going back to the work equation, we now have:
$ W = mg\sin \left( \phi \right).d.\cos \left( \theta \right) $
As said above, $ \theta $ is the angle between the force and displacement vectors. Since the relevant forces and displacement occur in the same direction (parallel to the incline), $ \theta = {0^ \circ } $ Therefore, we have:
$ W = mg\sin \left( \phi \right).d $
Substituting in our known values:
$
W = \left( {6kg} \right)\left( {9.8m{s^{ - 2}}} \right)\sin \left( {\dfrac{\pi }{4}} \right).\left( {2m} \right) \\
\\
\Rightarrow W = 6\, \times 9.8 \times \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 2 }} \times 2\,J \\
\\
\Rightarrow W = 83.1557\,J \\
$
Note:
This problem could also be solved using the work-energy theorem, where the work done is equal to the change in energy. Change in energy will be the change in gravitational potential energy possessed by the object. We would need to use trigonometry to find the height of the ramp/incline.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




