
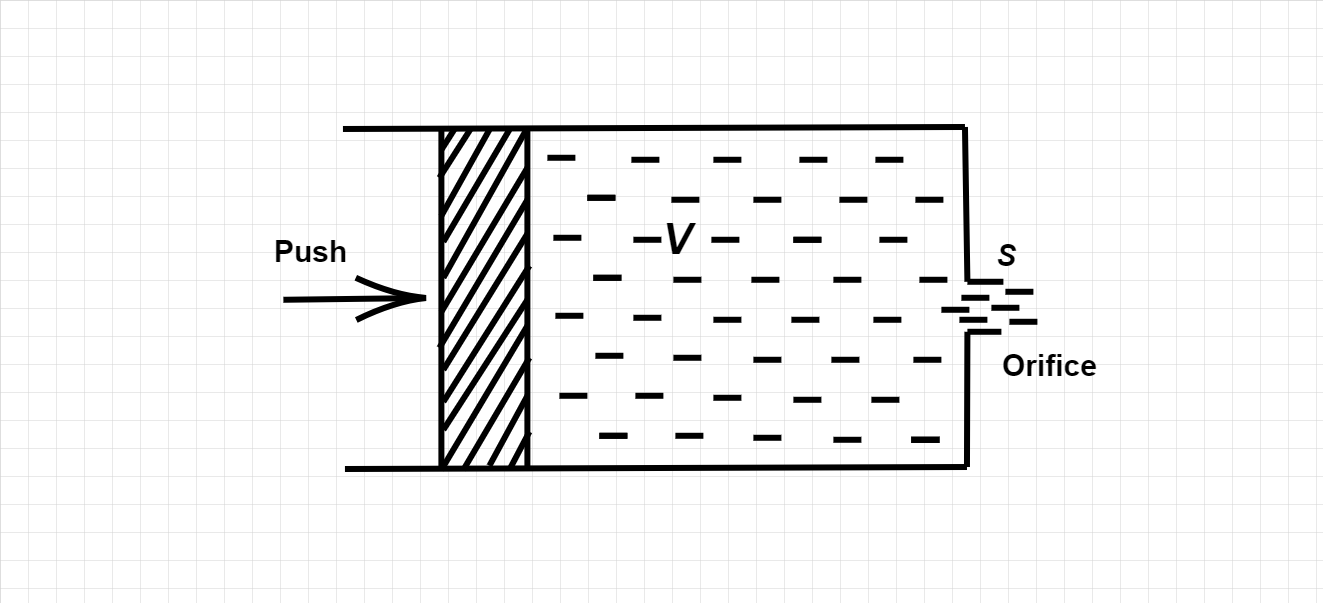
What work should be done in order to squeeze all the water from a horizontally located cylinder (figure shown above) during the time t by means of a constant force acting on the piston? The volume of a water in the cylinder is equal to V, the cross-sectional area of the orifice to s, with s being considerably less than the piston area. The friction and the viscosity are negligibly small.
A. $A = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho \dfrac{{{V^3}}}{{{{(St)}^2}}}$
B. $A = \dfrac{3}{2}\rho \dfrac{{{V^3}}}{{{{(St)}^2}}}$
C. $A = \dfrac{5}{2}\rho \dfrac{{{V^3}}}{{{{(St)}^2}}}$
D. None of these

Answer
598.2k+ views
Hint: Velocity at which water ejects out of the orifice is called discharge velocity or volume discharge rate. It is given by $v = \dfrac{{Volume}}{{Area \times time}}$
Formula Used:
1. Volume discharge rate velocity, $v = \dfrac{{Volume}}{{Area \times time}}$ …… (a)
2. Kinetic energy of mass moving with velocity $v$ given by, $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ ……. (b)
Complete step by step answer:
Given,
density of liquid in container $\rho $
Total volume of liquid to expel out $V$
Cross-sectional area of orifice $S$
Step 1 of 5:
From equation (a), Discharge rate $v$ of liquid out of orifice equals
$v = \dfrac{{Volume}}{{Area \times time}}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{V}{{St}}$ …… (1)
Step 2 of 5:
From work energy theorem, we know change in Kinetic energy is total work done by piston-
$ \Rightarrow \Delta K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} - \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}$
Step 3 of 5:
But, let’s say initial velocity is 0 (no water coming out before time t=0)
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ …… (2)
Step 4 of 5:
Total mass of water coming out through orifice $M = \rho V$…… (3)
Step 5 of 5:
Putting values from equation (1) and (3) in equation (2), we get,
Kinetic Energy, $A = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho \dfrac{{{V^3}}}{{{{(St)}^2}}}$
Correct Answer: A. $A = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho \dfrac{{{V^3}}}{{{{(St)}^2}}}$
Additional Information:
Another approach of solving the problem is by using Bernoulli principle of fluid flow. Here, Force is acting perpendicular to the cross section area. So, pressure can be calculated as $P = \dfrac{F}{A}$where F is a constant force on the piston. Using Bernoulli’s equation force given by,
$F = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}A$ where, $v$ is velocity of flow out of orifice. Then, by deducting the value of $v$ from equation (1) and putting in the equation of total work done. We will get the same answer.
Note: In order to use Bernoulli equation mark two points A and B. Bernoulli equation ensures continuity of flow.
Formula Used:
1. Volume discharge rate velocity, $v = \dfrac{{Volume}}{{Area \times time}}$ …… (a)
2. Kinetic energy of mass moving with velocity $v$ given by, $K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ ……. (b)
Complete step by step answer:
Given,
density of liquid in container $\rho $
Total volume of liquid to expel out $V$
Cross-sectional area of orifice $S$
Step 1 of 5:
From equation (a), Discharge rate $v$ of liquid out of orifice equals
$v = \dfrac{{Volume}}{{Area \times time}}$
$ \Rightarrow v = \dfrac{V}{{St}}$ …… (1)
Step 2 of 5:
From work energy theorem, we know change in Kinetic energy is total work done by piston-
$ \Rightarrow \Delta K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2} - \dfrac{1}{2}m{u^2}$
Step 3 of 5:
But, let’s say initial velocity is 0 (no water coming out before time t=0)
$ \Rightarrow K.E = \dfrac{1}{2}m{v^2}$ …… (2)
Step 4 of 5:
Total mass of water coming out through orifice $M = \rho V$…… (3)
Step 5 of 5:
Putting values from equation (1) and (3) in equation (2), we get,
Kinetic Energy, $A = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho \dfrac{{{V^3}}}{{{{(St)}^2}}}$
Correct Answer: A. $A = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho \dfrac{{{V^3}}}{{{{(St)}^2}}}$
Additional Information:
Another approach of solving the problem is by using Bernoulli principle of fluid flow. Here, Force is acting perpendicular to the cross section area. So, pressure can be calculated as $P = \dfrac{F}{A}$where F is a constant force on the piston. Using Bernoulli’s equation force given by,
$F = \dfrac{1}{2}\rho {v^2}A$ where, $v$ is velocity of flow out of orifice. Then, by deducting the value of $v$ from equation (1) and putting in the equation of total work done. We will get the same answer.
Note: In order to use Bernoulli equation mark two points A and B. Bernoulli equation ensures continuity of flow.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




