
With the help of labelled diagrams, describe an activity to show that acids produce ions only in aqueous solutions.
Answer
539.4k+ views
Hint: Acids are ionic mixes that, when disintegrated in water, produce positive hydrogen particles $({H^ + })$ When broken down in water, acids taste acidic, direct power and respond with metals to make hydrogen gas. Certain pointer mixes might be utilized to recognize acids, for example, litmus. Acids change red paper into blue litmus.
Complete answer:
As per the Lewis definition, acids are particles or particles equipped for organizing with unshared electron matches, and bases are atoms or particles having unshared electron sets accessible for offering to acids. To be acidic in the Lewis sense, a particle should be electron inadequate.Take around $1g$ strong $NaCl$ in a perfect and dry test cylinder and add some concentrated sulphuric acid to it. Fit an elastic stopper with a little conveyance tube in the mouth of the test tube. Concentrated sulphuric acid responds with sodium chloride to frame hydrogen chloride gas. The hydrogen chloride gas begins emerging from the open finish of the glass tube. Presently, hold a 'dry' blue litmus paper in $HCl$ gas. There is no adjustment in shade of the 'dry' blue litmus paper. This shows that $HCl$ gas doesn't carry on as an acid without water. In any case, when we hold a 'damp' blue litmus paper turns red. This demonstrates that $HCl$ gas shows acidic conduct within the sight of water as hydrogen particles are shaped.
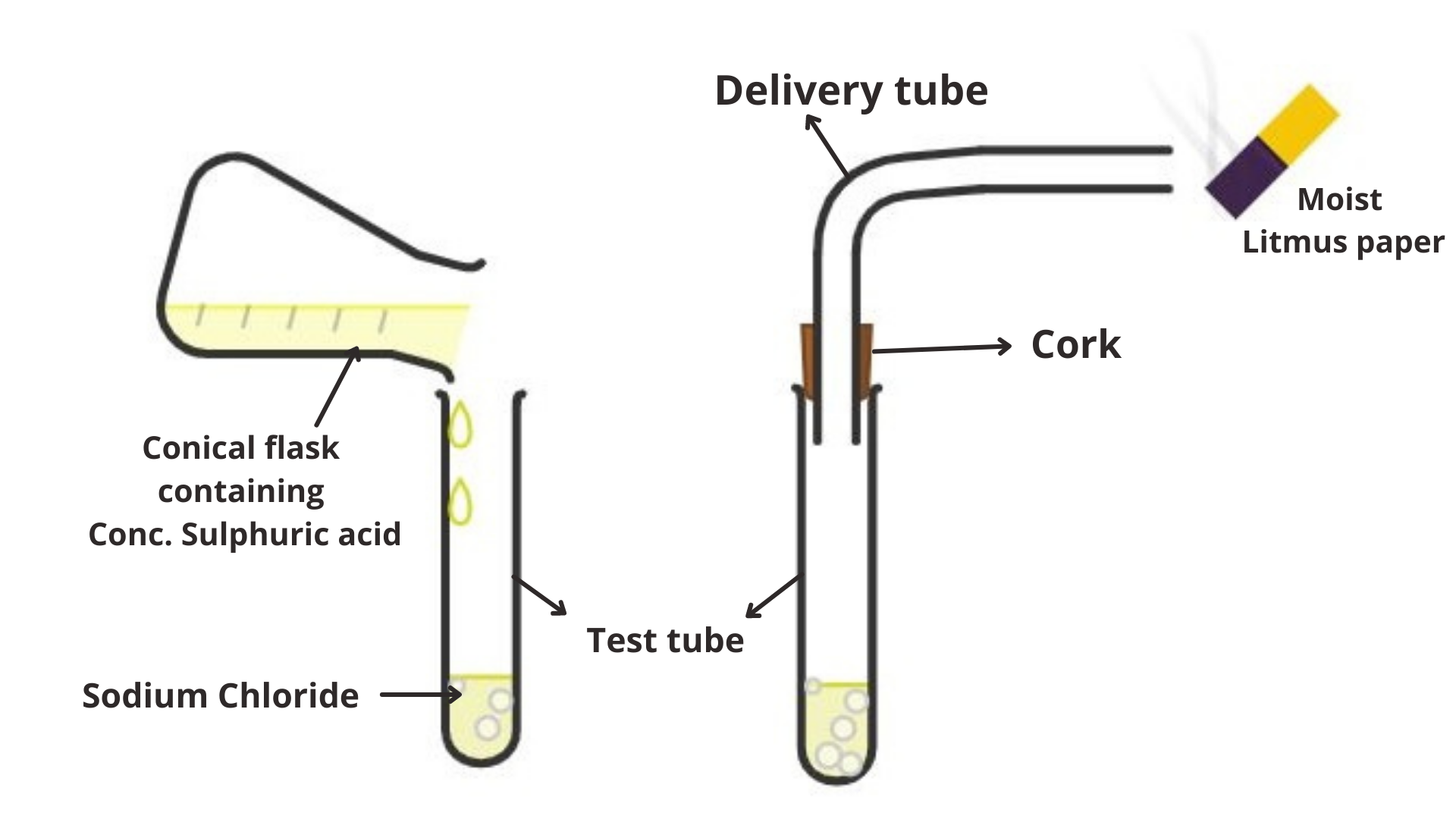
Additional information: Define acid and what are its properties?The term acid and base have been characterized in an unexpected way, contingent upon the specific perspective on properties of sharpness and basicity. Arrhenius previously characterized acids as mixes which ionize to create hydrogen particles, and bases as mixes which ionize to deliver hydroxide particles. As indicated by the Lowry-Bronsted definition, an acid is a proton giver and a base is a proton acceptor. This is the most broad acid base idea. All Lowery Bronstead acids are Lewis acids however, also, the Lewis definition incorporates numerous different reagents, for example, boron trifluoride, aluminum chloride, and so forth.
Properties of Acids :Acids are destructive in nature. They are acceptable conveyors of power. Their pH esteems are in every case under 7. When responded with metals, these substances produce hydrogen gas. Acids are acrid tasting substances. Models: Sulfuric acid [ ${H_2}S{O_4}$], Hydrochloric acid [ $HCl$ ], Acidic acid [ $C{H_3}COOH$].
Note: Acids assume critical functions inside the human body. The presence of hydrochloric corrosive in the stomach helps assimilation by separating enormous and complex food atoms. Amino acids are needed for protein blend expected to develop and fix body tissues.
Complete answer:
As per the Lewis definition, acids are particles or particles equipped for organizing with unshared electron matches, and bases are atoms or particles having unshared electron sets accessible for offering to acids. To be acidic in the Lewis sense, a particle should be electron inadequate.Take around $1g$ strong $NaCl$ in a perfect and dry test cylinder and add some concentrated sulphuric acid to it. Fit an elastic stopper with a little conveyance tube in the mouth of the test tube. Concentrated sulphuric acid responds with sodium chloride to frame hydrogen chloride gas. The hydrogen chloride gas begins emerging from the open finish of the glass tube. Presently, hold a 'dry' blue litmus paper in $HCl$ gas. There is no adjustment in shade of the 'dry' blue litmus paper. This shows that $HCl$ gas doesn't carry on as an acid without water. In any case, when we hold a 'damp' blue litmus paper turns red. This demonstrates that $HCl$ gas shows acidic conduct within the sight of water as hydrogen particles are shaped.

Additional information: Define acid and what are its properties?The term acid and base have been characterized in an unexpected way, contingent upon the specific perspective on properties of sharpness and basicity. Arrhenius previously characterized acids as mixes which ionize to create hydrogen particles, and bases as mixes which ionize to deliver hydroxide particles. As indicated by the Lowry-Bronsted definition, an acid is a proton giver and a base is a proton acceptor. This is the most broad acid base idea. All Lowery Bronstead acids are Lewis acids however, also, the Lewis definition incorporates numerous different reagents, for example, boron trifluoride, aluminum chloride, and so forth.
Properties of Acids :Acids are destructive in nature. They are acceptable conveyors of power. Their pH esteems are in every case under 7. When responded with metals, these substances produce hydrogen gas. Acids are acrid tasting substances. Models: Sulfuric acid [ ${H_2}S{O_4}$], Hydrochloric acid [ $HCl$ ], Acidic acid [ $C{H_3}COOH$].
Note: Acids assume critical functions inside the human body. The presence of hydrochloric corrosive in the stomach helps assimilation by separating enormous and complex food atoms. Amino acids are needed for protein blend expected to develop and fix body tissues.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




