
With the help of a neat labelled diagram, explain the formation of spinal nerves.
Answer
561.6k+ views
Hint: Spinal nerves are a part of the peripheral nervous system. They transmit motor, sensory and autonomic signals between the central nervous system and the body. All spinal nerves are made up of both sensory and motor fibres, that is they are mixed nerves.
Complete answer:
There are about 31 pairs of spinal nerves present. They control the motor and sensory signalling, along with other functions. These nerves are present at the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and coccygeal levels. Out of 31 pairs of spinal nerves, 8 are cervical, 12 are thoracic, 5 are lumbar, 5 are sacral and 1 is coccygeal. Each pair of nerves connects the spinal cord with a specific region of the body. Spinal nerve present near the spinal cord branches into two roots. One branch is sensory fibres and the other is motor fibres. Each spinal cord segment has four roots- an anterior root and a posterior root that are present on the right and left side. Each of these roots further has the presence of 8 nerve rootlets. The anterior root contains efferent nerve fibres whose function is to carry the stimuli away from the central nervous system towards the target. The cell bodies of the ventral roots are present in the central grey matter of the spinal cord. Motor neurons that control skeletal muscles and preganglionic autonomic nerves are located in the ventral root.
The posterior root contains afferent nerve fibres whose function is to return the sensory information from the central nervous system’s trunk and limbs. The cell bodies are not present in the grey matter but are present in the dorsal root ganglion. The posterior and the anterior nerves join together and form nerve proper. The nerve proper is made up of a mixture of sensory, motor and autonomic fibres.
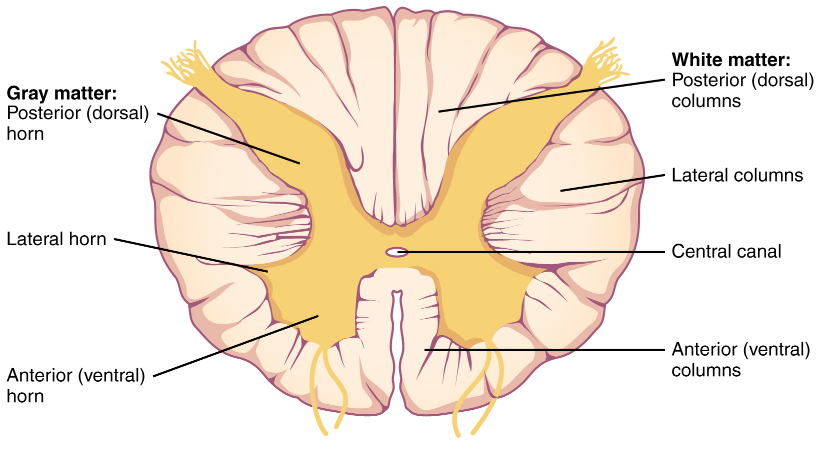
Note: The spinal cord is a long and fragile tubelike structure that extends from the brain to the bottom of the spine. The spinal cord is made up of nerve fibres that carry signals away from the brain to different parts of the body. If the spinal cord gets damaged, then the muscle will completely lose its function and there will be no sensation of the body.
Complete answer:
There are about 31 pairs of spinal nerves present. They control the motor and sensory signalling, along with other functions. These nerves are present at the cervical, thoracic, lumbar, and coccygeal levels. Out of 31 pairs of spinal nerves, 8 are cervical, 12 are thoracic, 5 are lumbar, 5 are sacral and 1 is coccygeal. Each pair of nerves connects the spinal cord with a specific region of the body. Spinal nerve present near the spinal cord branches into two roots. One branch is sensory fibres and the other is motor fibres. Each spinal cord segment has four roots- an anterior root and a posterior root that are present on the right and left side. Each of these roots further has the presence of 8 nerve rootlets. The anterior root contains efferent nerve fibres whose function is to carry the stimuli away from the central nervous system towards the target. The cell bodies of the ventral roots are present in the central grey matter of the spinal cord. Motor neurons that control skeletal muscles and preganglionic autonomic nerves are located in the ventral root.
The posterior root contains afferent nerve fibres whose function is to return the sensory information from the central nervous system’s trunk and limbs. The cell bodies are not present in the grey matter but are present in the dorsal root ganglion. The posterior and the anterior nerves join together and form nerve proper. The nerve proper is made up of a mixture of sensory, motor and autonomic fibres.

Note: The spinal cord is a long and fragile tubelike structure that extends from the brain to the bottom of the spine. The spinal cord is made up of nerve fibres that carry signals away from the brain to different parts of the body. If the spinal cord gets damaged, then the muscle will completely lose its function and there will be no sensation of the body.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




