
With the help of a neat labelled diagram describe the internal structure of the human heart.
Answer
531k+ views
Hint: One such organ that is inferred mesodermally is the human heart. The pericardium is a two-layered film that covers and protects this human heart. The heart is a double pumping organ in the human body.
Complete answer:
The heart is a hollow cone-shaped organ. It's about the size of the proprietor's closed clenched hand and weighs between 250 and 350 grammes in females and 300 to 350 grammes in males. The heart is located in the thoracic hole, which is located between the lungs (mediastinum) and the vertebral section, leading to the sternum. There are four chambers in the heart.
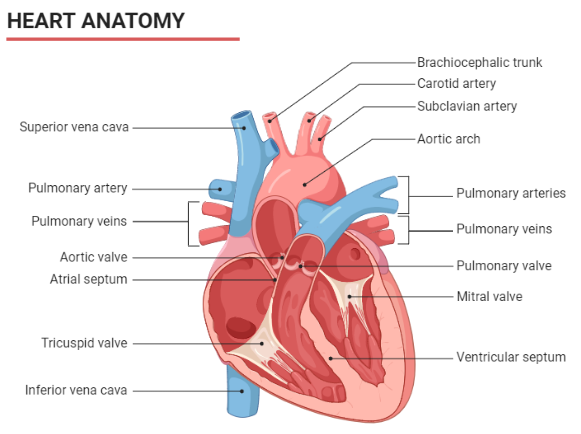
Septum divides the heart into four parts on the inside.
The atria are the two upper parts, and the ventricles are the lower parts. The atrial septum separates the two atria from one another, and the ventricular septum separates the right and left ventricles.
Deoxygenated blood in the right side of the heart is prevented from mixing with oxygenated blood in the left half of the heart by the atrial and ventricular septum’s walls of the ventricle are typically thicker than the walls of the atrium. The largest vein is the aorta, which emerges from the left ventricle and delivers blood to all of the body's organs. The respiratory conduit, which emerges from the right ventricle, transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
The right atrioventricular opening connects the correct chamber and the right ventricle.
The left atrioventricular gap connects the left chamber and the left ventricle.
The tricuspid valve keeps an eye on the auriculoventricular opening, while the mitral or bicuspid valve keeps an eye on the left atrioventricular gap.
Note:
The heart's base is located along the midline of the body, with the peak emphasising the left side. Because the heart focuses on one side, roughly two-thirds of the heart's mass is found on the left half of the body, with the remaining one-third on the right.
Complete answer:
The heart is a hollow cone-shaped organ. It's about the size of the proprietor's closed clenched hand and weighs between 250 and 350 grammes in females and 300 to 350 grammes in males. The heart is located in the thoracic hole, which is located between the lungs (mediastinum) and the vertebral section, leading to the sternum. There are four chambers in the heart.

Septum divides the heart into four parts on the inside.
The atria are the two upper parts, and the ventricles are the lower parts. The atrial septum separates the two atria from one another, and the ventricular septum separates the right and left ventricles.
Deoxygenated blood in the right side of the heart is prevented from mixing with oxygenated blood in the left half of the heart by the atrial and ventricular septum’s walls of the ventricle are typically thicker than the walls of the atrium. The largest vein is the aorta, which emerges from the left ventricle and delivers blood to all of the body's organs. The respiratory conduit, which emerges from the right ventricle, transports deoxygenated blood to the lungs.
The right atrioventricular opening connects the correct chamber and the right ventricle.
The left atrioventricular gap connects the left chamber and the left ventricle.
The tricuspid valve keeps an eye on the auriculoventricular opening, while the mitral or bicuspid valve keeps an eye on the left atrioventricular gap.
Note:
The heart's base is located along the midline of the body, with the peak emphasising the left side. Because the heart focuses on one side, roughly two-thirds of the heart's mass is found on the left half of the body, with the remaining one-third on the right.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

10 examples of friction in our daily life




