
With the help of a diagram, explain sexual reproduction in flowering plants.
Answer
566.7k+ views
Hint: The gynoecium is the female reproductive organ of the flower and the androecium is the male part respectively. In a complete flower, there exists four whorls namely the calyx, corolla, androecium and the gynoecium.
Complete answer:
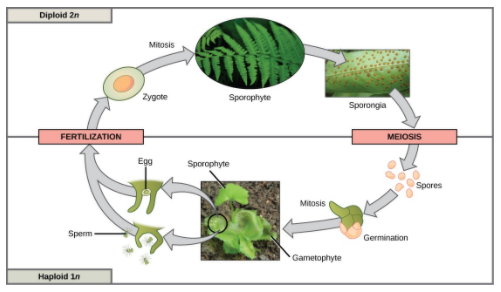
The androecium is the male reproductive organ of the flower that leads to the formation of the male gamete that is the pollen respectively. On the other hand the gynoecium is the female reproductive organ of the flower and is responsible for the formation of the female gamete that is the ovules or the eggs respectively. Pollination is a process by which the transfer of pollen occurs from a flower to the stigma of another or same flower. When the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of the same flower ,it is called self fertilization. On the other hand when the pollen of a particular flower lands on the stigma of another flower, it is called cross pollination. As the male and the female gamete fuses , fertilization occurs which is double fertilization. One of the male gametes fuses with the female gamete to form the zygote. Another male gamete fuses with the diploid nuclei to give rise to the endosperm tissue which provides nutrition to the growing embryo. After fertilization, the ovules develop into seeds which give rise to new plants.
Note: There are two types of pollination namely self and cross pollination. Cross pollination is highly preferred by nature as it gives rise to high genetic diversity with healthier progeny. In contrast to cross pollination, self pollination gives rise to weaker progeny and may be more susceptible to various plant diseases. To prevent self pollination, nature has devised various mechanical barriers related to the ovules that prevent self pollination.
Complete answer:

The androecium is the male reproductive organ of the flower that leads to the formation of the male gamete that is the pollen respectively. On the other hand the gynoecium is the female reproductive organ of the flower and is responsible for the formation of the female gamete that is the ovules or the eggs respectively. Pollination is a process by which the transfer of pollen occurs from a flower to the stigma of another or same flower. When the pollen of a flower lands on the stigma of the same flower ,it is called self fertilization. On the other hand when the pollen of a particular flower lands on the stigma of another flower, it is called cross pollination. As the male and the female gamete fuses , fertilization occurs which is double fertilization. One of the male gametes fuses with the female gamete to form the zygote. Another male gamete fuses with the diploid nuclei to give rise to the endosperm tissue which provides nutrition to the growing embryo. After fertilization, the ovules develop into seeds which give rise to new plants.
Note: There are two types of pollination namely self and cross pollination. Cross pollination is highly preferred by nature as it gives rise to high genetic diversity with healthier progeny. In contrast to cross pollination, self pollination gives rise to weaker progeny and may be more susceptible to various plant diseases. To prevent self pollination, nature has devised various mechanical barriers related to the ovules that prevent self pollination.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




