
With a neat labelled diagram, explain the formation of an image in a simple microscope.
Answer
591.9k+ views
Hint: A simple microscope is actually a convex lens of small focal length which is used to see the magnified image of a small object. Firstly, draw the ray diagram and then derive the expression for magnification using geometry.
Complete step by step answer:
The ray diagram to show the working of simple microscope is as below:
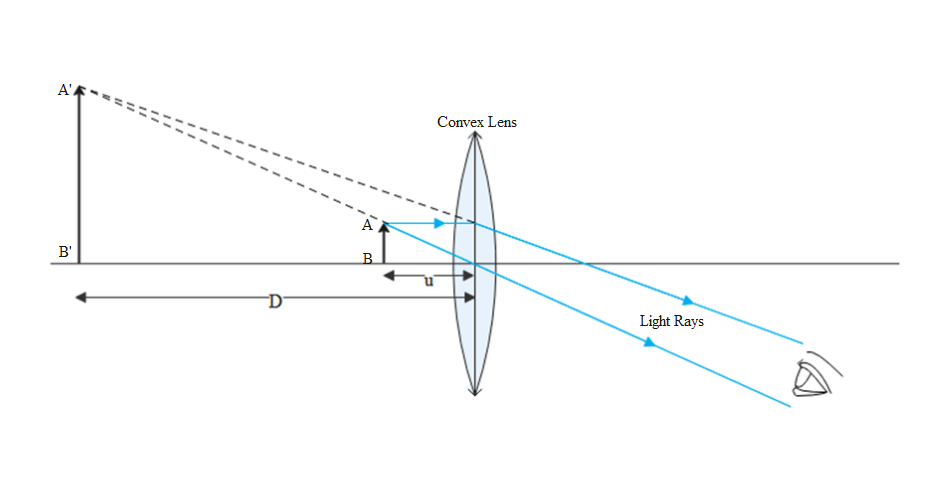
AB is the object which is to be magnified. AB is placed between principal focus and optical centre of the convex lens. Now, a ray of light parallel to the principal axis, which is coming from the point A of the object, passes through the focus after getting refracted by the convex lens. A second ray of light coming from the point A of the object passes through the optical centre of the convex lens along the straight line. As it's clear from the figure that the two rays(blue coloured) are diverging rays so these rays can intersect each other only at point A’ when produced backward. Now, on drawing A’B’ perpendicular from point A’ to the principal axis, we get the image A’B’ of the object which is virtual, erect and magnified.
We will now find the magnification. According to magnification formula for lens
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}$
Where
$m=$Magnification of the object
$v=$Distance of image from the optical centre of lens
$u=$Distance of the object from the optical centre of lens
In simple microscope, we adjust the convex lens such that the image is formed at distance $D=25cm$
According to lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{f}$
Therefore magnification,
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}=v\left( \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{f} \right)$
Where $f$ is the focal length of the convex lens.
Now, according to sign convention $v=-D$
Substituting this value and then solving for $m$, we get
$m=1+\dfrac{D}{f}$
Note:
From the expression obtained for magnification, it can be observed that for maximum magnification, the focal length should be small.
Simple microscope is used for basic purposes such as reading and magnifying glass.
Use of sign convention is essential in ray optics. Otherwise the result obtained, may not be appropriate.
Complete step by step answer:
The ray diagram to show the working of simple microscope is as below:

AB is the object which is to be magnified. AB is placed between principal focus and optical centre of the convex lens. Now, a ray of light parallel to the principal axis, which is coming from the point A of the object, passes through the focus after getting refracted by the convex lens. A second ray of light coming from the point A of the object passes through the optical centre of the convex lens along the straight line. As it's clear from the figure that the two rays(blue coloured) are diverging rays so these rays can intersect each other only at point A’ when produced backward. Now, on drawing A’B’ perpendicular from point A’ to the principal axis, we get the image A’B’ of the object which is virtual, erect and magnified.
We will now find the magnification. According to magnification formula for lens
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}$
Where
$m=$Magnification of the object
$v=$Distance of image from the optical centre of lens
$u=$Distance of the object from the optical centre of lens
In simple microscope, we adjust the convex lens such that the image is formed at distance $D=25cm$
According to lens formula,
$\dfrac{1}{f}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{u}\Rightarrow \dfrac{1}{u}=\dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{f}$
Therefore magnification,
$m=\dfrac{v}{u}=v\left( \dfrac{1}{v}-\dfrac{1}{f} \right)$
Where $f$ is the focal length of the convex lens.
Now, according to sign convention $v=-D$
Substituting this value and then solving for $m$, we get
$m=1+\dfrac{D}{f}$
Note:
From the expression obtained for magnification, it can be observed that for maximum magnification, the focal length should be small.
Simple microscope is used for basic purposes such as reading and magnifying glass.
Use of sign convention is essential in ray optics. Otherwise the result obtained, may not be appropriate.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

How is the angle of emergence e related to the angle class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between lanthanoids and actinoids class 12 chemistry CBSE

Derive Lens Makers formula for a convex lens class 12 physics CBSE

a Draw Labelled diagram of Standard Hydrogen Electrode class 12 chemistry CBSE




