
Why does ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ dimerise?
Answer
595.5k+ views
Hint: Look at the valence electrons of the central atom of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ molecule along with the bonding that takes place in the molecule. By the type of bond we can calculate the number of electrons that are involved in the formation of that bond.
Complete step by step solution:
On dimerization of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$, ${ N }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }$ is produced. This dimerization takes place due to the formation of new covalent bonds between two molecules of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$.
Let us look at the structure of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$.
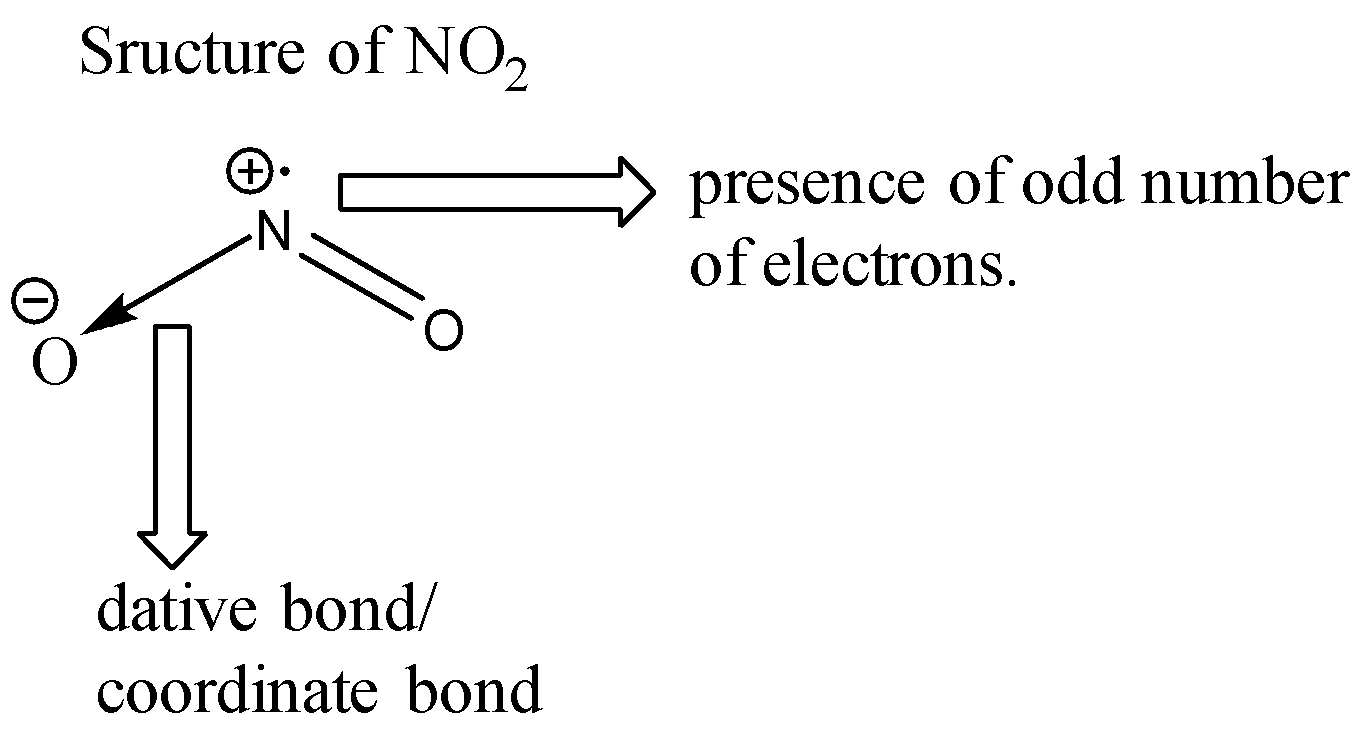
Nitrogen has a total of 5 valence electrons. 2 of these electrons are given away to an oxygen atom for the formation of a coordinate bond. Two electrons are used for forming double bonds with another oxygen atom. One electron is left behind unpaired (free radical) due to which the molecule of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ is highly unstable. Since each molecule of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ has an unpaired electron, when these two molecules combine together, a bond formation takes place and we get a new molecule of ${ N }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }$ which is more stable than ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ since ${ N }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }$ does not contain any odd electron. The reaction is shown below:
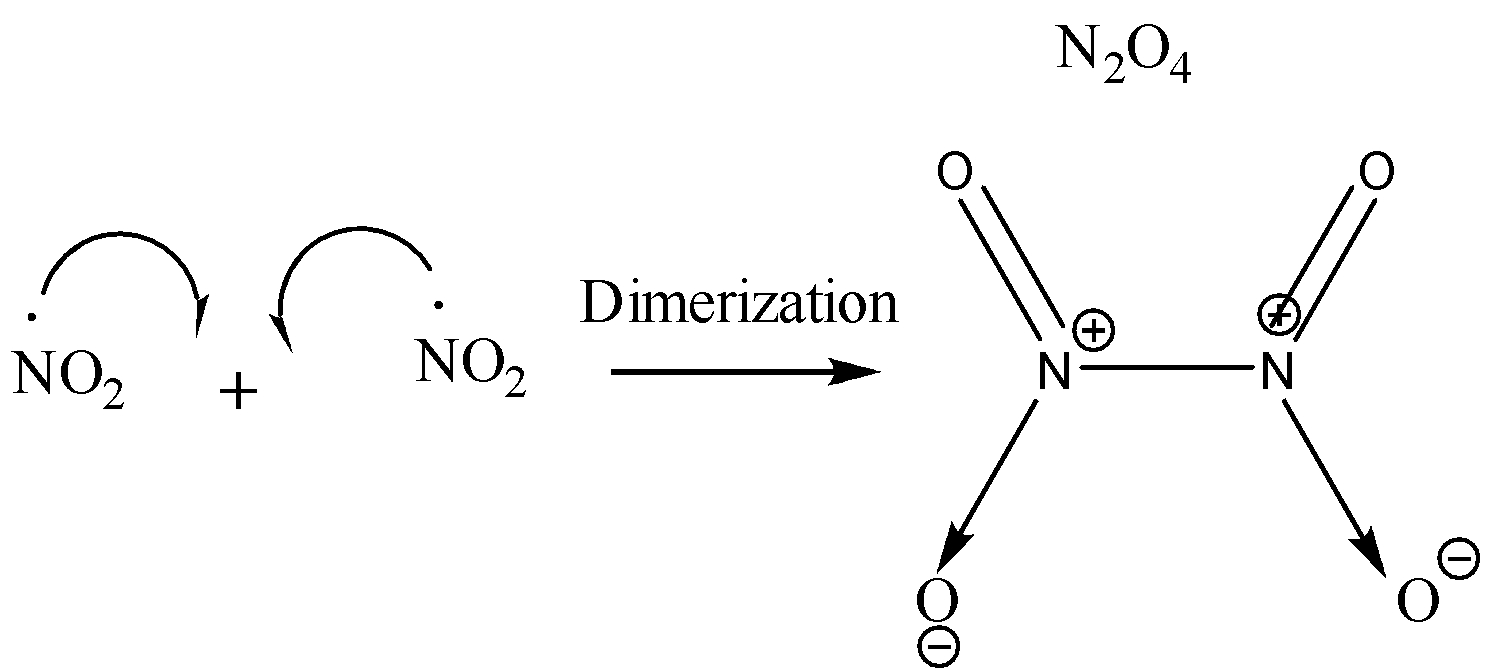
The presence of odd electrons in ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ has been confirmed by experimental analysis too. Since ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ has an odd electron, therefore it is weakly paramagnetic in nature but on dimerization, it loses its Para magnetism and becomes diamagnetic ${ N }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }$.
Therefore the dimerization of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ is due to the presence of an odd electron.
Note: For the formation of a dative bond, one atom needs to donate its electron pair to another atom. In this process, the donor atom acquires a positive charge since it donates its electrons and the accepting atom acquires a negative charge since it accepts the electron pair.
Complete step by step solution:
On dimerization of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$, ${ N }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }$ is produced. This dimerization takes place due to the formation of new covalent bonds between two molecules of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$.
Let us look at the structure of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$.

Nitrogen has a total of 5 valence electrons. 2 of these electrons are given away to an oxygen atom for the formation of a coordinate bond. Two electrons are used for forming double bonds with another oxygen atom. One electron is left behind unpaired (free radical) due to which the molecule of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ is highly unstable. Since each molecule of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ has an unpaired electron, when these two molecules combine together, a bond formation takes place and we get a new molecule of ${ N }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }$ which is more stable than ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ since ${ N }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }$ does not contain any odd electron. The reaction is shown below:

The presence of odd electrons in ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ has been confirmed by experimental analysis too. Since ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ has an odd electron, therefore it is weakly paramagnetic in nature but on dimerization, it loses its Para magnetism and becomes diamagnetic ${ N }_{ 2 }{ O }_{ 4 }$.
Therefore the dimerization of ${ NO }_{ 2 }$ is due to the presence of an odd electron.
Note: For the formation of a dative bond, one atom needs to donate its electron pair to another atom. In this process, the donor atom acquires a positive charge since it donates its electrons and the accepting atom acquires a negative charge since it accepts the electron pair.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




