
Why do you use tangent?
Answer
540k+ views
Hint: Here we can see about the Tangent and its definition, a reference diagram and explanation for that diagram of how it touches the curve. We should know that a tangent is a straight line to a plane curve at a given point is the straight line that just touches the surface of the curve at that point.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We can first know the definition of a Tangent.
Definition: A tangent is a straight line or plane that just touches a curve or curved surface at a point, but if extends does not cross it at a point, i.e. touching the surface of the curved part but not intersecting.
We should know that tangents are used to find the missing side and angles of right triangles.
We can also define it trigonometrically as a tangent is a ratio of sine and the cosine of a triangle where cosine is not equal to zero and the tangent has an angle of measure \[\theta \] in radians.
\[\Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }\]
We can also know that the tangent is from the Latin word tangens or tangere which means a ‘touch gently’.
We can now take an example.
A tangent to a circle.
It is defined as a straight line which touches the circle at a single point. The point where the tangent touches a circle is known as point of tangency or the point of contact.
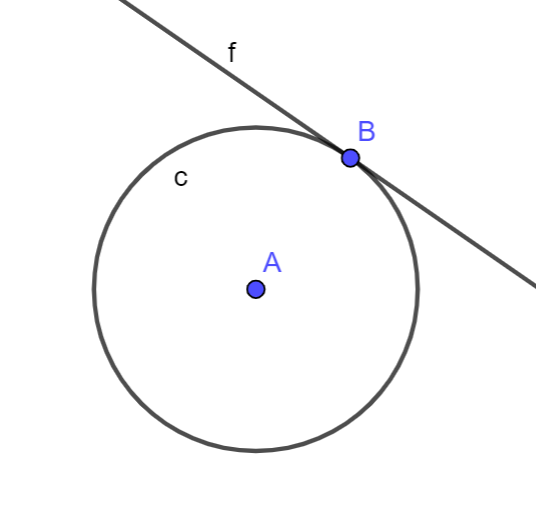
Where f is the tangent line, B is the point of contact of the circle.
Note: We should always remember that the tangent is a line which just touches a point on the surface of the curved part without intersecting. We can define tangent both in geometry and in trigonometry. The point where the tangent line meets the curve is called the point of tangency.
Complete step-by-step solution:
We can first know the definition of a Tangent.
Definition: A tangent is a straight line or plane that just touches a curve or curved surface at a point, but if extends does not cross it at a point, i.e. touching the surface of the curved part but not intersecting.
We should know that tangents are used to find the missing side and angles of right triangles.
We can also define it trigonometrically as a tangent is a ratio of sine and the cosine of a triangle where cosine is not equal to zero and the tangent has an angle of measure \[\theta \] in radians.
\[\Rightarrow \tan \theta =\dfrac{\sin \theta }{\cos \theta }\]
We can also know that the tangent is from the Latin word tangens or tangere which means a ‘touch gently’.
We can now take an example.
A tangent to a circle.
It is defined as a straight line which touches the circle at a single point. The point where the tangent touches a circle is known as point of tangency or the point of contact.

Where f is the tangent line, B is the point of contact of the circle.
Note: We should always remember that the tangent is a line which just touches a point on the surface of the curved part without intersecting. We can define tangent both in geometry and in trigonometry. The point where the tangent line meets the curve is called the point of tangency.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




