
While assigning R, S configuration the correct order of priority of groups attached to chiral carbon atom is:
(A) $CON{H_2}$ > $COC{H_3}$ > $C{H_2}OH$ > $CHO$
(B) $CON{H_2}$ > $COC{H_3}$ > $CHO$ > $C{H_2}OH$
(C) $COC{H_3}$ > $CON{H_2}$ > $CHO$ > $C{H_2}OH$
(D) $CHO$ > $C{H_2}OH$ > $COC{H_3}$ > $CON{H_2}$
Answer
585.9k+ views
Hint: To answer the correct priority among the given groups, we should first check for chiral carbon. When we name the enantiomers of a chiral compound as left and right then we name it R and S configuration.
Complete step by step answer:
We use R and S configuration to name the enantiomers of a chiral compound. The stereocenters are labelled as R and S.
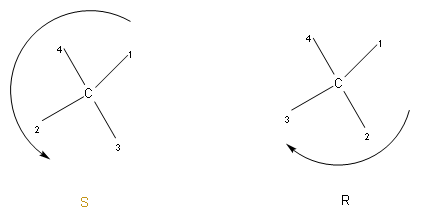
The above is the representation of R and S configuration. We should now know about chiral centres. We should know that an asymmetric carbon atom (chiral carbon) is a carbon atom that is attached to four different types of atoms or groups of atoms.
Now, we will discuss the priority of the group in R and S configuration. As we observe the option, we get to know that there are four compounds in each option which are the same. These compounds are: $CON{H_2}$, $COC{H_3}$, $C{H_2}OH$ and $CHO$. Let us place these on a carbon. This carbon will be chiral carbon.
We will give priority on the basis of atomic number. We should know that if the atom connected to the chiral centre has a high atomic number then it will have high priority.
So, based on this we will now give the priority.
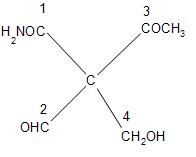
First, we will see the first atom. First atom is carbon, which is directly attached to the chiral centre. But all the carbon have the same atomic number which is 6. The next atom is oxygen in the first and third group. It is hydrogen in the second group and fourth group.
In the first group after oxygen there is nitrogen and in the third group there is carbon after oxygen atom. So, most priority will be given to the first group attached to the carbon centre. And after that comes the third group. Because in between first and third, the nitrogen at third position in first group has a higher atomic number than carbon attached at third position in group one at the chiral centre. So, it will have high priority.
Between the second and fourth group, there is a hydrogen atom at second position in both of them. And at third position, there is oxygen in the second group and there is again hydrogen in the fourth group, because there are two atoms of hydrogen. So, the second group will come before the fourth group.
Order of R, S priority will be as follows: $CON{H_2}$ > $COC{H_3}$ > $CHO$ > $C{H_2}OH$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We should know that optical isomers or enantiomers have the same sequence of atoms and bonds but are different in their 3D shape. We should note that two enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of one another. We can thus call them chiral.
Complete step by step answer:
We use R and S configuration to name the enantiomers of a chiral compound. The stereocenters are labelled as R and S.

The above is the representation of R and S configuration. We should now know about chiral centres. We should know that an asymmetric carbon atom (chiral carbon) is a carbon atom that is attached to four different types of atoms or groups of atoms.
Now, we will discuss the priority of the group in R and S configuration. As we observe the option, we get to know that there are four compounds in each option which are the same. These compounds are: $CON{H_2}$, $COC{H_3}$, $C{H_2}OH$ and $CHO$. Let us place these on a carbon. This carbon will be chiral carbon.
We will give priority on the basis of atomic number. We should know that if the atom connected to the chiral centre has a high atomic number then it will have high priority.
So, based on this we will now give the priority.

First, we will see the first atom. First atom is carbon, which is directly attached to the chiral centre. But all the carbon have the same atomic number which is 6. The next atom is oxygen in the first and third group. It is hydrogen in the second group and fourth group.
In the first group after oxygen there is nitrogen and in the third group there is carbon after oxygen atom. So, most priority will be given to the first group attached to the carbon centre. And after that comes the third group. Because in between first and third, the nitrogen at third position in first group has a higher atomic number than carbon attached at third position in group one at the chiral centre. So, it will have high priority.
Between the second and fourth group, there is a hydrogen atom at second position in both of them. And at third position, there is oxygen in the second group and there is again hydrogen in the fourth group, because there are two atoms of hydrogen. So, the second group will come before the fourth group.
Order of R, S priority will be as follows: $CON{H_2}$ > $COC{H_3}$ > $CHO$ > $C{H_2}OH$
So, the correct answer is “Option B”.
Note: We should know that optical isomers or enantiomers have the same sequence of atoms and bonds but are different in their 3D shape. We should note that two enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images of one another. We can thus call them chiral.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between homogeneous and heterogeneous class 12 chemistry CBSE




