
Which will form lactone on treatment with NaOH?
A. α-bromo acid
B. β-bromo acid
C. β-hydroxy acid
D. δ-bromo acid
Answer
569.7k+ views
Hint: \[NaOH\] is a base used in organic chemistry to abstract protons from an acid. The most acidic proton will be abstracted first than the less acidic one.
Complete step by step answer:
This is an example of lactonization reaction. This is a very useful reaction in organic chemistry for converting a straight chain compound into a cyclic ring compound.
In lactonization of an acid by removal of a halogen two key points are important. One is the ability of the leaving group to be a good leaving group. The other is the formation of ring size which depends on the strain of the ring formed. The six membered ring formations are the most favoured ones.
Let us take the lactonization of \[5\]-bromopentanoic acid as an example. In the first step the acidic proton is abstracted which then attacks the adjacent carbon containing bromo group. This results in an elimination reaction. The reaction sequence is shown as:
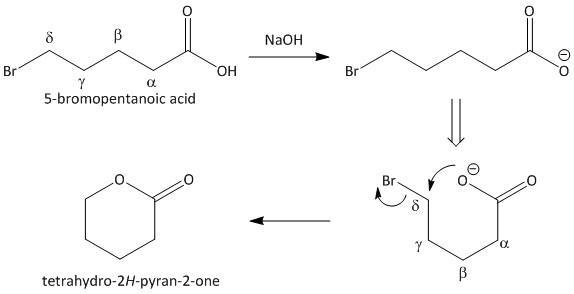
The formation of tetrahydro-\[2H\]-pyran-\[2\]-one clearly indicates that a bromo acid is the starting material required for the formation of a lactone.
Let us check the given starting materials for the formation of lactones.
α-bromo acid.
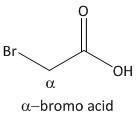
From the above mechanism the lactone formation is not possible for α-bromo acid.
β-bromo acid.
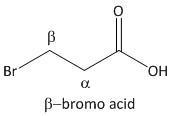
From the above mechanism the lactone formation is not possible for β-bromo acid as it leads to a highly strained four membered lactone which is not favorable.
β-hydroxy acid.
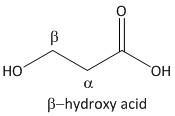
From the above mechanism the lactone formation is not possible for β-hydroxy acid due to unavailability of a good leaving group.
δ-bromo acid.
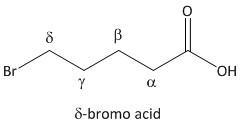
From the above mechanism the lactone formation is possible for δ-bromo acid. In fact the \[5\]-bromopentanoic acid is a δ-bromo acid.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The lactonization with \[NaOH\] is a reversible reaction if heated. The lactone is hydrolyzed into the parent compound and the reaction is said to be in equilibrium. It is a cyclic ester compound and the same methods of formation of ester are applied to the formation of lactone.
Complete step by step answer:
This is an example of lactonization reaction. This is a very useful reaction in organic chemistry for converting a straight chain compound into a cyclic ring compound.
In lactonization of an acid by removal of a halogen two key points are important. One is the ability of the leaving group to be a good leaving group. The other is the formation of ring size which depends on the strain of the ring formed. The six membered ring formations are the most favoured ones.
Let us take the lactonization of \[5\]-bromopentanoic acid as an example. In the first step the acidic proton is abstracted which then attacks the adjacent carbon containing bromo group. This results in an elimination reaction. The reaction sequence is shown as:

The formation of tetrahydro-\[2H\]-pyran-\[2\]-one clearly indicates that a bromo acid is the starting material required for the formation of a lactone.
Let us check the given starting materials for the formation of lactones.
α-bromo acid.

From the above mechanism the lactone formation is not possible for α-bromo acid.
β-bromo acid.

From the above mechanism the lactone formation is not possible for β-bromo acid as it leads to a highly strained four membered lactone which is not favorable.
β-hydroxy acid.

From the above mechanism the lactone formation is not possible for β-hydroxy acid due to unavailability of a good leaving group.
δ-bromo acid.

From the above mechanism the lactone formation is possible for δ-bromo acid. In fact the \[5\]-bromopentanoic acid is a δ-bromo acid.
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The lactonization with \[NaOH\] is a reversible reaction if heated. The lactone is hydrolyzed into the parent compound and the reaction is said to be in equilibrium. It is a cyclic ester compound and the same methods of formation of ester are applied to the formation of lactone.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




