
Which type of transformation does not preserve orientation?
Answer
474.9k+ views
Hint: In geometry, the orientation, angular position, attitude, or direction of an object such as a line, plane or rigid body is part of the description of how it is placed in the space it occupies. In the above question, we have to determine the transformation in which the orientation of an object is not preserved. We will see an example to compare the orientation of a shape before and after its transformation to see if its orientation is preserved or not.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to determine the type of transformation in which the orientation of an object is preserved.In geometry, the orientation is sorted into two types. They are clockwise and counter clockwise or anti clockwise in terms of how the points align in a figure. Reverse orientation means that the points are opposite of the original shape. Whereas the same orientation means that the points are just a copy and are in perfectly the same order from the original figure.
Let us take an example of a right angled triangle \[\vartriangle ABC\]. We have to check and compare its orientation before and after the transformation to see if the orientation is preserved or not.
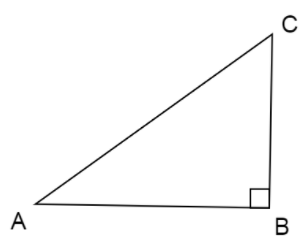
This is the figure of \[\vartriangle ABC\] before the transformation. We can notice that the direction of A to C and then C to B and then B back to A forms a clockwise orientation.Now we take the mirror image i.e. reflected image of the \[\vartriangle ABC\] then such figure will be formed:
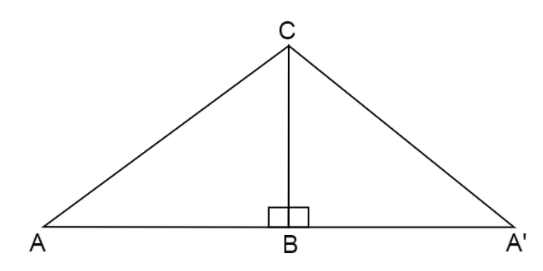
Here \[\vartriangle A'BC\] is the mirror image of \[\vartriangle ABC\] reflected through the side BC after the transformation.
Now, we can see that the vertices B and C are at the original place but the vertex A has shifted to the right of B at a new place A’. Here, the direction of A’ to C and then C to B and then B back to A’ forms an anticlockwise orientation.Hence, the orientation has changed from clockwise to anticlockwise.
Therefore, reflection does not preserve the orientation.
Note:Since reflection does not preserve the orientation of an object and alters it into the opposite image, but some of the other types of transformations are there which also preserve the orientation of the objects keeping the original image maintained after the transformation. Such as dilation or scaling, rotation and translation or shifting, which preserve the orientation of an object.
Complete step by step answer:
We have to determine the type of transformation in which the orientation of an object is preserved.In geometry, the orientation is sorted into two types. They are clockwise and counter clockwise or anti clockwise in terms of how the points align in a figure. Reverse orientation means that the points are opposite of the original shape. Whereas the same orientation means that the points are just a copy and are in perfectly the same order from the original figure.
Let us take an example of a right angled triangle \[\vartriangle ABC\]. We have to check and compare its orientation before and after the transformation to see if the orientation is preserved or not.

This is the figure of \[\vartriangle ABC\] before the transformation. We can notice that the direction of A to C and then C to B and then B back to A forms a clockwise orientation.Now we take the mirror image i.e. reflected image of the \[\vartriangle ABC\] then such figure will be formed:

Here \[\vartriangle A'BC\] is the mirror image of \[\vartriangle ABC\] reflected through the side BC after the transformation.
Now, we can see that the vertices B and C are at the original place but the vertex A has shifted to the right of B at a new place A’. Here, the direction of A’ to C and then C to B and then B back to A’ forms an anticlockwise orientation.Hence, the orientation has changed from clockwise to anticlockwise.
Therefore, reflection does not preserve the orientation.
Note:Since reflection does not preserve the orientation of an object and alters it into the opposite image, but some of the other types of transformations are there which also preserve the orientation of the objects keeping the original image maintained after the transformation. Such as dilation or scaling, rotation and translation or shifting, which preserve the orientation of an object.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




